A novel assay for high-throughput screening of anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs to determine their efficacy by real-time monitoring of changes in PC12 cell proliferation
- PMID: 24378397
- PMCID: PMC3926499
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1608
A novel assay for high-throughput screening of anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs to determine their efficacy by real-time monitoring of changes in PC12 cell proliferation
Abstract
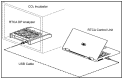
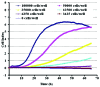
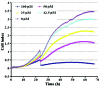
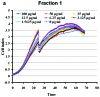
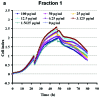
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by the accumulation of senile plaque and neurofibrilary tangle formation in the brain, including the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Nowadays, the first-line treatment for AD is the application of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. However, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are basically anti-symptomatic for a limited aspect of AD pathology and are associated with serious side-effects. With the advantage of multiple targets, pathways and systems, Chinese herbal compounds hold promising potential for the development of drugs for the treatment of AD. Over the past few years, with the development of Chinese herbal compounds and in vitro pharmacological studies, cell-based disease models are one of the main methods used to screen Chinese herbal compounds for potential efficacy. Testing the efficacy of possible anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs and the development of new drugs are hindered by the lack of objective high-throughput screening methods. Currently, the assessment of the effects of drugs is usually made by MTT assays, involving laborious, subjective, low-throughput methods. Herein, we suggest a novel application for a real-time cell monitoring device (xCELLigence) that can simply and objectively assess the effective composition of Chinese herbal compounds by assessing amyloid-β peptide Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. We detected the proliferation and motility of the cells using a fully automated high-throughput and real-time system. We quantitatively assessed cell motility and determined the real-time IC50 values of various anti-AD drugs that intervene in several developmental stages of Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells, Then, we identified the optimal time phase by curative efficacy. Our data indicate that this technique may aid in the discovery and development of novel anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs. It is possible to utilize a similar technique to measure changes in electrical impedance as cells attach and spread in a culture dish covered with a gold microelectrode array that covers approximately 80% of the area on the bottom of a well. As cells attach and spread on the electrode surface, it leads to an increase in electrical impedance of 9-12. The impedance is displayed as a dimensionless para-meter termed the cell index, which is directly proportional to the total area of tissue culture well that is covered by the cells. Hence, the cell index can be used to monitor cell adhesion, spreading, morphological variation and cell density.
Figures














Similar articles
-
A real-time electrical impedance based technique to measure invasion of endothelial cell monolayer by cancer cells.J Vis Exp. 2011 Apr 1;(50):2792. doi: 10.3791/2792. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21490581 Free PMC article.
-
Oxymatrine-mediated prevention of amyloid β-peptide-induced apoptosis on Alzheimer's model PC12 cells: in vitro cell culture studies and in vivo cognitive assessment in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2685-2699. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01291-0. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37515653
-
Neuroprotective effects of a Rhodiola crenulata extract on amyloid-β peptides (Aβ1-42) -induced cognitive deficits in rat models of Alzheimer's disease.Phytomedicine. 2019 Apr;57:331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.042. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30807987
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Therapeutic potentials of herbal drugs for Alzheimer’s disease—An overview.Indian J Exp Biol. 2017 Feb;55(2):63-73. Indian J Exp Biol. 2017. PMID: 30183230 Review.
Cited by
-
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide encapsulated Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid Nanofibers: cost effective herbal medicine for potential application in peripheral nerve tissue engineering.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 6;8(1):8669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26837-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29875468 Free PMC article.
-
Application of xCELLigence real-time cell analysis to the microplate assay for pertussis toxin induced clustering in CHO cells.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 15;16(3):e0248491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248491. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33720984 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cell seeding density on real-time monitoring of anti-proliferative effects of transient gene silencing.J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2016 Dec 1;23:20. doi: 10.1186/s40709-016-0057-4. eCollection 2016 Dec. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2016. PMID: 27981039 Free PMC article.
-
Novel screening techniques for ion channel targeting drugs.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(6):367-75. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1079675. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26556400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultra rapid in vivo screening for anti-Alzheimer anti-amyloid drugs.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 22;6:23349. doi: 10.1038/srep23349. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27000658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li XL, Wang de S, Zhao BQ, Li Q, et al. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine fuzhisan on aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 2008;43:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Holliday R. The urgency of research on ageing. Bioessays. 1996;18:89–90. - PubMed
-
- Ifeoma O, Samuel O, Itohan AM, Adeola SO. Isolation, fractionation and evaluation of the antiplasmodial properties of Phyllanthus niruri resident in its chloroform fraction. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6:169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

