Identification and characterization of novel ER-based hsp90 gene in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum
- PMID: 24379085
- PMCID: PMC4147069
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-013-0487-y
Identification and characterization of novel ER-based hsp90 gene in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum
Abstract
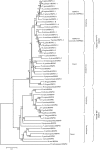
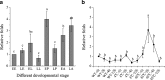
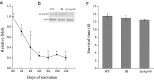
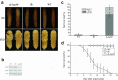
Heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90) is a highly conserved molecular chaperone found in all species except for Archaea, which is required not only for stress tolerance but also for normal development. Recently, it was reported that HSP83, one member of the cytosolic HSP90 family, contributes to oogenesis and responds to heat resistance in Tribolium castaneum. Here, a novel ER-based HSP90 gene, Tchsp90, has been identified in T. castaneum. Phylogenetic analysis showed that hsp90s and hsp83s evolved separately from a common ancestor but that hsp90s originated earlier. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction illustrated that Tchsp90 is expressed in all developmental stages and is highly expressed at early pupa and late adult stages. Tchsp90 was upregulated in response to heat stress but not to cold stress. Laval RNAi revealed that Tchsp90 is important for larval/pupal development. Meanwhile, parental RNAi indicated that it completely inhibited female fecundity and partially inhibited male fertility once Tchsp90 was knocked down and that it will further shorten the lifespan of T. castaneum. These results suggest that Tchsp90 is essential for development, lifespan, and reproduction in T. castaneum in addition to its response to heat stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization and functional analysis of hsp18.3 gene in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Insect Sci. 2019 Apr;26(2):263-273. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12543. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Insect Sci. 2019. PMID: 28980406 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative RNA-sequencing analysis of ER-based HSP90 functions and signal pathways in Tribolium castaneum.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 Jan;23(1):29-43. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0821-x. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 28681272 Free PMC article.
-
Post-embryonic functions of HSP90 in Tribolium castaneum include the regulation of compound eye development.Dev Genes Evol. 2011 Dec;221(5-6):357-62. doi: 10.1007/s00427-011-0379-z. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Dev Genes Evol. 2011. PMID: 22081039
-
A Major Facilitator Superfamily protein encoded by TcMucK gene is not required for cuticle pigmentation, growth and development in Tribolium castaneum.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Jun;49:43-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24681434
-
Expression of the Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) hsp83 gene and its relation to oogenesis during ovarian maturation.J Genet Genomics. 2010 Aug;37(8):513-22. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60071-0. J Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20816384
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of Three Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) Homologs in the Brown Planthopper.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 12;11(9):1074. doi: 10.3390/genes11091074. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32932648 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of the evolutionary capacitor Hsp90 is mediated by social cues.Proc Biol Sci. 2015 Nov 22;282(1819):20152041. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.2041. Proc Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26582024 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling analysis reveals the role of latrophilin in controlling development, reproduction and insecticide susceptibility in Tribolium castaneum.Genetica. 2018 Jun;146(3):287-302. doi: 10.1007/s10709-018-0020-4. Epub 2018 May 24. Genetica. 2018. PMID: 29797154
-
Characterization and functional analysis of hsp18.3 gene in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Insect Sci. 2019 Apr;26(2):263-273. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12543. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Insect Sci. 2019. PMID: 28980406 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative RNA-sequencing analysis of ER-based HSP90 functions and signal pathways in Tribolium castaneum.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 Jan;23(1):29-43. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0821-x. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 28681272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arakane Y, Li B, Muthukrishnan S, Beeman RW, Kramer KJ, Park Y. Functional analysis of four neuropeptides, EH, ETH, CCAP and bursicon, and their receptors in adult ecdysis behavior of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Mech Dev. 2008;125:984–995. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boher F, Trefault N, Piulachs MD, Belles X, Godoy-Herrera R, Bozinovic F. Biogeographic origin and thermal acclimation interact to determine survival and hsp90 expression in Drosophila species submitted to thermal stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2012;162:391–396. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.04.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

