Neutrophil-mediated IFN activation in the bone marrow alters B cell development in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 24379124
- PMCID: PMC3907774
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302112
Neutrophil-mediated IFN activation in the bone marrow alters B cell development in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
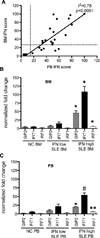
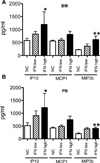
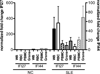
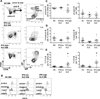
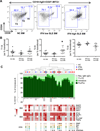
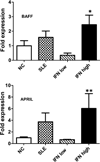
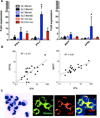
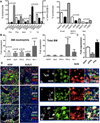
Inappropriate activation of type I IFN plays a key role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we report the presence of IFN activation in SLE bone marrow (BM), as measured by an IFN gene signature, increased IFN regulated chemokines, and direct production of IFN by BM-resident cells, associated with profound changes in B cell development. The majority of SLE patients had an IFN signature in the BM that was more pronounced than the paired peripheral blood and correlated with both higher autoantibodies and disease activity. Pronounced alterations in B cell development were noted in SLE in the presence of an IFN signature with a reduction in the fraction of pro/pre-B cells, suggesting an inhibition in early B cell development and an expansion of B cells at the transitional stage. These B cell changes strongly correlated with an increase in BAFF and APRIL expression in the IFN-high BM. Furthermore, we found that BM neutrophils in SLE were prime producers of IFN-α and B cell factors. In NZM lupus-prone mice, similar changes in B cell development were observed and mediated by IFN, given abrogation in NZM mice lacking type-I IFNR. BM neutrophils were abundant, responsive to, and producers of IFN, in close proximity to B cells. These results indicate that the BM is an important but previously unrecognized target organ in SLE with neutrophil-mediated IFN activation and alterations in B cell ontogeny and selection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England journal of medicine. 2008;358:929–939. - PubMed
-
- Baechler EC, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. The emerging role of interferon in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Current opinion in immunology. 2004;16:801–807. - PubMed
-
- Jego G, Palucka AK, Blanck JP, Chalouni C, Pascual V, Banchereau J. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce plasma cell differentiation through type I interferon and interleukin 6. Immunity. 2003;19:225–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

