Id3 and Id2 act as a dual safety mechanism in regulating the development and population size of innate-like γδ T cells
- PMID: 24379125
- PMCID: PMC3899720
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302694
Id3 and Id2 act as a dual safety mechanism in regulating the development and population size of innate-like γδ T cells
Abstract
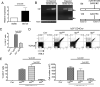
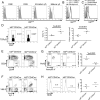
The innate-like T cells expressing Vγ1.1 and Vδ6.3 represent a unique T cell lineage sharing features with both the γδ T and the invariant NKT cells. The population size of Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cells is tightly controlled and usually contributes to a very small proportion of thymic output, but the underlying mechanism remains enigmatic. Deletion of Id3, an inhibitor of E protein transcription factors, can induce an expansion of the Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cell population. This phenotype is much stronger on the C57BL/6 background than on the 129/sv background. Using quantitative trait linkage analysis, we identified Id2, a homolog of Id3, to be the major modifier of Id3 in limiting Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cell expansion. The Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) phenotype is attributed to an intrinsic weakness of Id2 transcription from Id2 C57BL/6 allele, leading to an overall reduced dosage of Id proteins. However, complete removal of both Id2 and Id3 genes in developing T cells suppressed the expansion of Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cells because of decreased proliferation and increased cell death. We showed that conditional knockout of Id2 alone is sufficient to promote a moderate expansion of γδ T cells. These regulatory effects of Id2 and Id3 on Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cells are mediated by titration of E protein activity, because removing one or more copies of E protein genes can restore Vγ1.1(+)Vδ6.3(+) T cell expansion in Id2 and Id3 double conditional knockout mice. Our data indicated that Id2 and Id3 collaboratively control survival and expansion of the γδ lineage through modulating a proper threshold of E proteins.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of DNA binding 3 limits development of murine slam-associated adaptor protein-dependent "innate" gammadelta T cells.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 19;5(2):e9303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009303. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174563 Free PMC article.
-
Id3 restricts the developmental potential of gamma delta lineage during thymopoiesis.J Immunol. 2009 May 1;182(9):5306-16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804249. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19380777 Free PMC article.
-
Combined deletion of Id2 and Id3 genes reveals multiple roles for E proteins in invariant NKT cell development and expansion.J Immunol. 2013 Nov 15;191(10):5052-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301252. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24123680 Free PMC article.
-
Shifting gears: Id3 enables recruitment of E proteins to new targets during T cell development and differentiation.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 2;13:956156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.956156. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35983064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The divergence between T cell and innate lymphoid cell fates controlled by E and Id proteins.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 10;13:960444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960444. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Concerted Action of E2-2 and HEB Is Critical for Early Lymphoid Specification.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 18;10:455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00455. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30936870 Free PMC article.
-
E proteins control the development of NKγδT cells through their invariant T cell receptor.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 13;15(1):5078. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49496-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38871720 Free PMC article.
-
Id Proteins Suppress E2A-Driven Invariant Natural Killer T Cell Development prior to TCR Selection.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 24;9:42. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00042. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29416542 Free PMC article.
-
The E protein-TCF1 axis controls γδ T cell development and effector fate.Cell Rep. 2021 Feb 2;34(5):108716. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108716. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33535043 Free PMC article.
-
Reference Transcriptomes of Porcine Peripheral Immune Cells Created Through Bulk and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 23;12:689406. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.689406. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34249103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonneville M, O'Brien RL, Born WK. Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2010;10:467–478. - PubMed
-
- Carding SR, Egan PJ. Gammadelta T cells: functional plasticity and heterogeneity. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2002;2:336–345. - PubMed
-
- Xiong N, Raulet DH. Development and selection of gammadelta T cells. Immunological reviews. 2007;215:15–31. - PubMed
-
- Grigoriadou K, Boucontet L, Pereira P. Most IL-4-producing gamma delta thymocytes of adult mice originate from fetal precursors. J Immunol. 2003;171:2413–2420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

