Immunotherapy for idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy
- PMID: 24379134
- PMCID: PMC11534091
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009722.pub2
Immunotherapy for idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy (ILSP), also called lumbosacral plexitis or non-diabetic lumbosacral (radiculo)plexus neuropathy is a rare clinical entity. The core features are (sub)acute, severe, asymmetrical leg pain, followed by asymmetrical multifocal weakness and atrophy in the subsequent weeks or months. Sensory symptoms include paresthesias, hypesthesia, allodynia, and autonomic dysfunction. ILSP generally runs a monophasic and self limiting course. Recovery starts slowly over months to several years and is nearly always incomplete. Some studies suggest that the condition has an immune-mediated etiology. Biopsies of distal cutaneous nerve segments have shown features suggestive of an inflammatory microvasculitis causing ischemic damage of the nerves. The clinical and pathological findings are similar to those found in diabetic lumbosacral plexus neuropathy and suggest that inflammation may form part of the final common pathway in both conditions.
Objectives: To assess the effects of any form of immunotherapy in the treatment of ILSP.
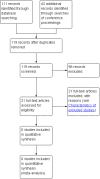
Search methods: On 15 October 2013, we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, LILACS, and Index to Theses. We scanned conference abstracts, and searched trials databases for ongoing trials. We checked all references in the identified trials and contacted authors to identify any additional published or unpublished data.
Selection criteria: We intended to include all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs of any immunotherapy given within six weeks of disease onset, in participants with conditions fulfilling all the following: acute or subacute onset of pain and lower motor neuron weakness involving predominantly the proximal muscles of the lower limbs, weakness that is not confined to one nerve or nerve root distribution, electrophysiological tests showing predominantly axonal neuropathies, exclusion of other causes of lumbosacral radiculopathy and plexopathy as well as patients with plasma sugar in the diabetic range (fasting greater than 7.0 mmol/L, random greater than 11.1 mmol/L).
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently examined all references retrieved by the search to select those meeting the inclusion criteria, according to standard Cochrane methodology.
Main results: We identified no RCTs of any immunotherapy for ILSP.
Authors' conclusions: There is at present no evidence from randomized trials to support any recommendation on the use of any immunotherapy treatment in ILSP.
Conflict of interest statement
JvE, YCC, JR: no known conflicts of interest.
Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009722
References
References to studies excluded from this review
Bhanushali 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bhanushali MJ, Muley SA. Diabetic and non‐diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Neurology India 2008;56(4):420‐5. - PubMed
Bradley 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bradley WG, Chad D, Verghese JP, Liu HC, Good P, Gabbai AA, et al. Painful lumbosacral plexopathy with elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate: a treatable inflammatory syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1984;15(5):457‐64. - PubMed
Cape 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cape CA. Lumbosacral plexus neuropathy. Neurology 1990;40(4 Suppl 1):118‐9.
Dalla Torre 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Dalla Torre C, Manfrin P, Luchetta M, Cacciavillani M, Manara R, Briani C. Relapsing lumbosacral plexopathy: MRI follow‐up. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 2011;16(Suppl 2):S11‐12.
Dyck 2001a {published data only}
-
- Dyck PJ, Norell JE, Dyck PJ. Methylprednisolone may improve lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 2001;28(3):224‐7. - PubMed
Dyck 2001b {published data only}
-
- Dyck PJ, Norell JE, Dyck PJ. Non‐diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: natural history, outcome and comparison with the diabetic variety. Brain 2001;124(6):1197‐207. - PubMed
Dyck 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dyck PJ, Windebank AJ. Diabetic and nondiabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathies: new insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Muscle & Nerve 2002;25(4):477‐91. - PubMed
Herdmann 1988 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Herdmann J, Benecke R, Meyer BU, Freund HJ. Succesful corticoid treatment of lumbosacral plexus neuropathy in heroin abuse. Clinical aspects, electrophysiology, therapy and follow‐up. Nervenarzt 1988;59(11):683‐6. - PubMed
Inoue 1999 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Inoue C, Hayashi A, Yoshizawa T, Sato A, Shoji S. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a case of idiopathic recurrent brachial and lumbosacral plexopathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1999;39(6):661‐4. - PubMed
Ishii 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ishii K, Tamaoka A, Shoji S. MRI of idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy. Neurology 2004 July;63(2):E6. - PubMed
Kramberger 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kramberger MG, Trost M, Zidar J. Acute brachial and lumbosacral plexopathy after intravenous self‐administration of heroin. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14(Suppl s1):262‐3, P2397.
Marra 1987 {published data only}
-
- Marra TR. The clinical and electrodiagnostic features of idiopathic lumbo‐sacral and brachial plexus neuropathy: a review of 20 cases. Electromyography and Clinical Neurophysiology 1987;27(5):305‐15. - PubMed
Martin‐Estefania 2001 {published data only}
-
- Martín‐Estefanía C, Benito‐León J. Idiopathic lumbosacral plexitis: a potentially treatable condition. Revista de Neurologia 2001;32(12):1199‐200. - PubMed
Park 2005 {published data only}
-
- Park DH, Park YK, Kim JH. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for idiopathic postoperative lumbosacral plexopathy. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2005;12(3):313‐5. - PubMed
Seror 2005 {published data only}
-
- Seror P, Maisonobe T, Viala K, Bouche P. Idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy. Presse Medicale 2005;34(12):856‐8. - PubMed
Takata 2007 {published data only}
-
- Takata Y, Noda K, Fujishima K, Hattori N, Mizuno Y, Okuma Y. A case of neuralgic amyotrophy in the lower extremity (lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy). Brain and Nerve 2007;59(4):435‐8. - PubMed
Tarulli 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tarulli A, Rutkove SB. Lumbosacral plexitis. Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease 2005;7(2):72‐8. - PubMed
Thaisetthawatkul 2010 {published data only}
-
- Thaisetthawatkul P, Dyck PJ. Treatment of diabetic and nondiabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Current Treatment Options in Neurology 2010;12(2):95‐9. - PubMed
Triggs 1997 {published data only}
-
- Triggs WJ, Young MS, Eskin T, Valenstein E. Treatment of idiopathic lumbosacral plexopathy with intravenous immunoglobulin. Muscle & Nerve 1997;20(2):244‐6. - PubMed
Tumani 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tumani H. Rare indications of IVIG therapy in neurological diseases based on case reports and small studies. Journal of Neurology 2006;253(Suppl 5):V66‐9; Erratum in: Journal of Neurology 2008;255(2):308. - PubMed
Verma 1994 {published data only}
-
- Verma A, Bradley WG. High‐dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in chronic progressive lumbosacral plexopathy. Neurology 1994;44(2):248‐50. - PubMed
Additional references
Awerbuch 1989
-
- Awerbuch GI, Nigro MA, Dabrowski E, Levin JR. Childhood lumbosacral plexus neuropathy. Pediatric Neurology 1989;5(5):314‐6. - PubMed
Chan 2009
Dyck 1980
-
- Dyck PJ, Sherman WR, Hallcher LM, Service FJ, O'Brien PC, Grina LA, et al. Human diabetic endoneurial sorbitol, fructose, and myo‐inositol related to sural nerve morphometry. Annals of Neurology 1980;8(6):590‐6. - PubMed
Dyck 1994
-
- Dyck PJ, Litchy WJ, Kratz KM, Suarez GA, Low PA, Pineda AA, et al. A plasma exchange versus immune globulin infusion trial in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Annals of Neurology 1994;36(6):838‐45. - PubMed
Dyck 2000a
-
- Dyck PJB, Engelstad J, Norell J, Dyck PJ. Microvasculitis in non‐diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy (LSRPN): similarity to the diabetic variety (DLSRPN). Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 2000;59(6):525‐38. - PubMed
Dyck 2000b
-
- Dyck PJB, Dyck PJ. Intravenous methylprednisolone may ameliorate non‐diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Neurology 2000;54(7 Suppl 3):A212.
Dyck 2006
-
- Dyck PJB, O'Brien P, Bosch EP, Grant I, Burns T, Windebank A, et al. The multi‐centre double‐blind controlled trial of IV methylprednisolone in diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Neurology 2006;66(5 Suppl 2):A191.
Evans 1981
-
- Evans BA, Stevens JC, Dyck PJ. Lumbosacral plexus neuropathy. Neurology 1981;31(10):1327‐30. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman, DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kleyweg 1991
-
- Kleyweg RP, Meché FG, Schmitz PI. Interobserver agreement in the assessment of muscle strength and functional abilities in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Muscle & Nerve 1991;14(11):1103‐9. - PubMed
Melzack 1975
-
- Melzack R. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: major properties and scoring methods. Pain 1975;1(3):277‐99. - PubMed
Merkies 2002
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Sander 1981
-
- Sander JE, Sharp FR. Lumbosacral plexus neuritis. Neurology 1981;31(4):470‐3. - PubMed
van Swieten 1988
-
- Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, Gijn J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 1988;19(5):604‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical