Children with invasive Staphylococcus aureus disease exhibit a potently neutralizing antibody response to the cytotoxin LukAB
- PMID: 24379282
- PMCID: PMC3957992
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01558-13
Children with invasive Staphylococcus aureus disease exhibit a potently neutralizing antibody response to the cytotoxin LukAB
Abstract
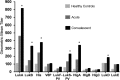
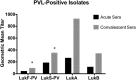
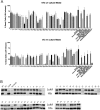
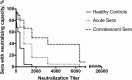
Despite the importance of Staphylococcus aureus as a common invasive bacterial pathogen, the humoral response to infection remains inadequately defined, particularly in children. The purpose of this study was to assess the humoral response to extracellular staphylococcal virulence factors, including the bicomponent leukotoxins, which are critical for the cytotoxicity of S. aureus toward human neutrophils. Children with culture-proven S. aureus infection were prospectively enrolled and stratified by disease type. Fifty-three children were enrolled in the study, of which 90% had invasive disease. Serum samples were obtained during the acute (within 48 h) and convalescent (4 to 6 weeks postinfection) phases, at which point both IgG titers against S. aureus exotoxins were determined, and the functionality of the generated antibodies was evaluated. Molecular characterization of clinical isolates was also performed. We observed a marked rise in antibody titer from acute-phase to convalescent-phase sera for LukAB, the most recently described S. aureus bicomponent leukotoxin. LukAB production by the isolates was strongly correlated with cytotoxicity in vitro, and sera containing anti-LukAB antibodies potently neutralized cytotoxicity. Antibodies to S. aureus antigens were detectable in healthy pediatric controls but at much lower titers than in sera from infected subjects. The discovery of a high-titer, neutralizing antibody response to LukAB during invasive infections suggests that this toxin is produced in vivo and that it elicits a functional humoral response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Commercial Intravenous Immunoglobulin Preparations Contain Functional Neutralizing Antibodies against the Staphylococcus aureus Leukocidin LukAB (LukGH).Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Oct 24;61(11):e00968-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00968-17. Print 2017 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28874371 Free PMC article.
-
Host response to Staphylococcus aureus cytotoxins in children with cystic fibrosis.J Cyst Fibros. 2016 Sep;15(5):597-604. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.12.023. Epub 2016 Jan 25. J Cyst Fibros. 2016. PMID: 26821814 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic Detection of Antibodies Targeting the Leukocidin LukAB Strongly Predicts Staphylococcus aureus in Children With Invasive Infection.J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2019 May 11;8(2):128-135. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piy017. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2019. PMID: 29538707 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of bacterial virulence by antibody neutralization of immune-activating toxins.Virulence. 2010 Sep-Oct;1(5):409-13. doi: 10.4161/viru.1.5.12705. Virulence. 2010. PMID: 21178480 Review.
-
Structure and Function of the Two-Component Cytotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus - Learnings for Designing Novel Therapeutics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;966:15-35. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_200. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28455832 Review.
Cited by
-
Context matters: The importance of dimerization-induced conformation of the LukGH leukocidin of Staphylococcus aureus for the generation of neutralizing antibodies.MAbs. 2016 Oct;8(7):1347-1360. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1215791. Epub 2016 Jul 28. MAbs. 2016. PMID: 27467113 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Impairs the Function of and Kills Human Dendritic Cells via the LukAB Toxin.mBio. 2019 Jan 2;10(1):e01918-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01918-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30602580 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of B Lymphocytes and the IgG-Binding Protein Sbi in Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infection.Pathogens. 2016 Jan 27;5(1):12. doi: 10.3390/pathogens5010012. Pathogens. 2016. PMID: 26828524 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological and Clinical Evidence for the Role of Toxins in S. aureus Human Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun 19;12(6):408. doi: 10.3390/toxins12060408. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal mastitis in dairy cows.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 28;11:1356259. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1356259. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38863450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dantes R, Mu Y, Belflower R, Aragon D, Dumyati G, Harrison LH, Lessa FC, Lynfield R, Nadle J, Petit S, Ray SM, Schaffner W, Townes J, Fridkin S. 2013. National burden of invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, United States, 2011. JAMA Intern. Med. 173:1970–1978. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10423 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weems JJ., Jr 2001. The many faces of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Recognizing and managing its life-threatening manifestations. Postgrad. Med. 110:24–26, 29–31, 35–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

