Natural history-driven, plant-mediated RNAi-based study reveals CYP6B46's role in a nicotine-mediated antipredator herbivore defense
- PMID: 24379363
- PMCID: PMC3910579
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1314848111
Natural history-driven, plant-mediated RNAi-based study reveals CYP6B46's role in a nicotine-mediated antipredator herbivore defense
Erratum in
-
Correction for Kumar et al., Natural history-driven, plant-mediated RNAi-based study reveals CYP6B46's role in a nicotine-mediated antipredator herbivore defense.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 1;113(9):E1328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600609113. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26884204 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
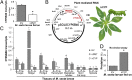
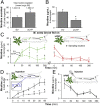
Manduca sexta (Ms) larvae are known to efficiently excrete ingested nicotine when feeding on their nicotine-producing native hostplant, Nicotiana attenuata. Here we describe how ingested nicotine is co-opted for larval defense by a unique mechanism. Plant-mediated RNAi was used to silence a midgut-expressed, nicotine-induced cytochrome P450 6B46 (CYP6B46) in larvae consuming transgenic N. attenuata plants producing MsCYP6B46 dsRNA. These and transgenic nicotine-deficient plants were planted into native habitats to study the phenotypes of larvae feeding on these plants and the behavior of their predators. The attack-behavior of a native wolf spider (Camptocosa parallela), a major nocturnal predator, provided the key to understanding MsCYP6B46's function: spiders clearly preferred CYP6B46-silenced larvae, just as they had preferred larvae fed nicotine-deficient plants. MsCYP6B46 redirects a small amount (0.65%) of ingested nicotine from the midgut into hemolymph, from which nicotine is exhaled through the spiracles as an antispider signal. CYP6B46-silenced larvae were more susceptible to spider-attack because they exhaled less nicotine because of lower hemolymph nicotine concentrations. CYP6B46-silenced larvae were impaired in distributing ingested nicotine from midgut to hemolymph, but not in the clearing of hemolymph nicotine or in the exhalation of nicotine from hemolymph. MsCYP6B46 could be a component of a previously hypothesized pump that converts nicotine to a short-lived, transportable, metabolite. Other predators, big-eyed bugs, and antlion larvae were insensitive to this defense. Thus, chemical defenses, too toxic to sequester, can be repurposed for defensive functions through respiration as a form of defensive halitosis, and predators can assist the functional elucidation of herbivore genes.
Keywords: Coyote tobacco; Lepidoptera; alkaloid; reverse genetics; tobacco hornworm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Peterson SC, Johnson ND, Leguyader JL. Defensive regurgitation of allelochemicals derived from host cyanogenesis by eastern tent caterpillars. Ecology. 1987;68(5):1268–1272.
-
- Bowers MD, Larin Z. Acquired chemical defense in the lycaenid butterfly, Eumaeus atala. J Chem Ecol. 1989;15(4):1133–1146. - PubMed
-
- Eisner T, Eisner M. Unpalatability of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid containing moth, Utetheisa ornatrix, and its larva, to wolf spiders. Psyche (Stuttg) 1991;98(1):111–118.
-
- Bowers MD. Aposematic Caterpillars: Life-Styles of the Warningly Colored and Unpalatable. New York: Chapman and Hall; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

