How does symmetry impact the flexibility of proteins?
- PMID: 24379431
- PMCID: PMC3871301
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2012.0041
How does symmetry impact the flexibility of proteins?
Abstract
It is well known that (i) the flexibility and rigidity of proteins are central to their function, (ii) a number of oligomers with several copies of individual protein chains assemble with symmetry in the native state and (iii) added symmetry sometimes leads to added flexibility in structures. We observe that the most common symmetry classes of protein oligomers are also the symmetry classes that lead to increased flexibility in certain three-dimensional structures-and investigate the possible significance of this coincidence. This builds on the well-developed theory of generic rigidity of body-bar frameworks, which permits an analysis of the rigidity and flexibility of molecular structures such as proteins via fast combinatorial algorithms. In particular, we outline some very simple counting rules and possible algorithmic extensions that allow us to predict continuous symmetry-preserving motions in body-bar frameworks that possess non-trivial point-group symmetry. For simplicity, we focus on dimers, which typically assemble with twofold rotational axes, and often have allosteric function that requires motions to link distant sites on the two protein chains.
Keywords: allostery; flexibility; pebble game algorithms; proteins; rigidity of frameworks; symmetry.
Figures
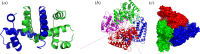
 ,
,  and
and  symmetry. (a) The dimer tryptophan repressor—shown in cartoon representation—has
symmetry. (a) The dimer tryptophan repressor—shown in cartoon representation—has  symmetry, where the two colours represent the two chains. (b) Bacterial
symmetry, where the two colours represent the two chains. (b) Bacterial  symmetry. (c) N-phosphonacetyl-
symmetry. (c) N-phosphonacetyl- symmetry, where colours distinguish separate chains. This complex is formed with two types of chains, six copies of each, which corresponds to the 6 + 6 notation for this family of proteins in table 1. Each colour contains two dimers with two different chains in each dimer (i.e. in each colour, one dimer is built of chains A and C, and the other dimer is built of chains B and D). These structures were generated with Pymol (
symmetry, where colours distinguish separate chains. This complex is formed with two types of chains, six copies of each, which corresponds to the 6 + 6 notation for this family of proteins in table 1. Each colour contains two dimers with two different chains in each dimer (i.e. in each colour, one dimer is built of chains A and C, and the other dimer is built of chains B and D). These structures were generated with Pymol (
 symmetry, and it is speculated that
symmetry, and it is speculated that  symmetry is preserved in (b), as has been observed for symmetric allosteric proteins such as arginine repressor [24]. (Online version in colour.)
symmetry is preserved in (b), as has been observed for symmetric allosteric proteins such as arginine repressor [24]. (Online version in colour.)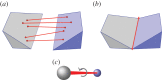
 , shown looking down the axis. (a) The infinitesimal flex shown is
, shown looking down the axis. (a) The infinitesimal flex shown is  -symmetric, since all the velocity vectors remain unchanged by the half-turn C2. (b) The infinitesimal motion shown is a
-symmetric, since all the velocity vectors remain unchanged by the half-turn C2. (b) The infinitesimal motion shown is a  -symmetric trivial infinitesimal motion (corresponding to a rotation about the C2 axis). (c) The trivial infinitesimal motion shown is not
-symmetric trivial infinitesimal motion (corresponding to a rotation about the C2 axis). (c) The trivial infinitesimal motion shown is not  -symmetric, since the initial velocity vectors of the motion are reversed by C2. (Online version in colour.)
-symmetric, since the initial velocity vectors of the motion are reversed by C2. (Online version in colour.)

 symmetry. Larger and smaller spheres indicate atoms that lie respectively in front of and behind the median plane of the structure.
symmetry. Larger and smaller spheres indicate atoms that lie respectively in front of and behind the median plane of the structure.

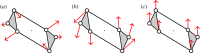
 . It accepts all other edges not crossing ℓ in
. It accepts all other edges not crossing ℓ in  and all bridging edges (crossing ℓ) in E2. So, in step (1), the algorithm predicts no non-trivial motion since |E1∪E*1∪E2|= 6+6+6=18=6|B|−6. In step (2), the algorithm predicts a non-trivial symmetric motion since |E1∪E3|=6+3=9<10=6|B0|−2. (b) The algorithm (applied to the same graph as in (a), but with a different choice of representatives for the vertex orbits) accepts all edges not crossing the new line ℓ in
and all bridging edges (crossing ℓ) in E2. So, in step (1), the algorithm predicts no non-trivial motion since |E1∪E*1∪E2|= 6+6+6=18=6|B|−6. In step (2), the algorithm predicts a non-trivial symmetric motion since |E1∪E3|=6+3=9<10=6|B0|−2. (b) The algorithm (applied to the same graph as in (a), but with a different choice of representatives for the vertex orbits) accepts all edges not crossing the new line ℓ in  . All bridging edges except r and r′ are placed in E2, while r and r′ (tested last among bridging pairs) are placed in R1. So the counts are |E1∪E*1∪E2|=3+3+12=18=6|B|−6 (again predicting no non-trivial motion in step (1)) and |E1∪E3|=3+6=9<10=6|B0|−2 (again predicting symmetric flexibility in step (2)). (c) All edges not crossing ℓ are placed in
. All bridging edges except r and r′ are placed in E2, while r and r′ (tested last among bridging pairs) are placed in R1. So the counts are |E1∪E*1∪E2|=3+3+12=18=6|B|−6 (again predicting no non-trivial motion in step (1)) and |E1∪E3|=3+6=9<10=6|B0|−2 (again predicting symmetric flexibility in step (2)). (c) All edges not crossing ℓ are placed in  , all bridging edges except q and q′ are placed in E2, and q and q′ are placed in Q. Therefore, in step (1) of the algorithm we obtain |E1∪E*1∪E2|= 3+3+12=18=6|B|−6, and in step (2) we obtain |E1∪E3|=3+7=10=6|B0|−2, and hence no non-trivial motion is detected. (Online version in colour.)
, all bridging edges except q and q′ are placed in E2, and q and q′ are placed in Q. Therefore, in step (1) of the algorithm we obtain |E1∪E*1∪E2|= 3+3+12=18=6|B|−6, and in step (2) we obtain |E1∪E3|=3+7=10=6|B0|−2, and hence no non-trivial motion is detected. (Online version in colour.)
 -symmetric ‘orbit graph’ G0 of cyclohexane. (c,d) The graph
-symmetric ‘orbit graph’ G0 of cyclohexane. (c,d) The graph  and its symmetric copy
and its symmetric copy  . (Online version in colour.)
. (Online version in colour.)
References
-
- Schulz GE, Schirmer RH. 1979. Principles of protein structures. New York, NY: Springer.
-
- Tay T-S. 1984. Rigidity of multi-graphs, linking rigid bodies in $n$-space. J. Comb. Theory B 36, 95–112. ( 10.1016/0095-8956(84)90016-9) - DOI
-
- Whiteley W. 1996. Some matroids from discrete applied geometry. Contemporary Mathematics, vol. 197, pp. 171–311. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
