Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective
- PMID: 24379683
- PMCID: PMC3872270
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S53876
Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective
Abstract
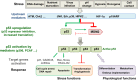
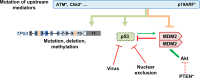
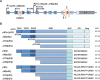
Thirty-five years of research on p53 gave rise to more than 68,000 articles and reviews, but did not allow the uncovering of all the mysteries that this major tumor suppressor holds. How p53 handles the different signals to decide the appropriate cell fate in response to a stress and its implication in tumorigenesis and cancer progression remains unclear. Nevertheless, the uncovering of p53 isoforms has opened new perspectives in the cancer research field. Indeed, the human TP53 gene encodes not only one but at least twelve p53 protein isoforms, which are produced in normal tissues through alternative initiation of translation, usage of alternative promoters, and alternative splicing. In recent years, it became obvious that the different p53 isoforms play an important role in regulating cell fate in response to different stresses in normal cells by differentially regulating gene expression. In cancer cells, abnormal expression of p53 isoforms contributes actively to cancer formation and progression, regardless of TP53 mutation status. They can also be associated with response to treatment, depending on the cell context. The determination of p53 isoform expression and p53 mutation status helps to define different subtypes within a particular cancer type, which would have different responses to treatment. Thus, the understanding of the regulation of p53 isoform expression and their biological activities in relation to the cellular context would constitute an important step toward the improvement of the diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive values of p53 in cancer treatment. This review aims to summarize the involvement of p53 isoforms in cancer and to highlight novel potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: alternative splicing; cancer; isoforms; p53; p63; p73.
Figures

References
-
- Bénard J, Douc-Rasy S, Ahomadegbe JC. TP53 family members and human cancers. Hum Mutat. 2003;21(3):182–191. - PubMed
-
- Melino G, Lu X, Gasco M, Crook T, Knight RA. Functional regulation of p73 and p63: development and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28(12):663–670. - PubMed
-
- Flores ER, Sengupta S, Miller JB, et al. Tumor predisposition in mice mutant for p63 and p73: evidence for broader tumor suppressor functions for the p53 family. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):363–373. - PubMed
-
- Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90(4):809–819. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

