Marine oil dietary supplementation reduces delayed onset muscle soreness after a 30 km run
- PMID: 24379715
- PMCID: PMC3873794
- DOI: 10.2147/OAJSM.S41706
Marine oil dietary supplementation reduces delayed onset muscle soreness after a 30 km run
Abstract
Objective: Runners are prone to delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) during long distance training. This especially holds for unaccustomed training volumes at moderate to high intensities. We investigated the effects of a marine oil complex, PCSO-524®, derived from the New Zealand green-lipped mussel (formulated as Lyprinol® and Omega XL®) on DOMS after a 30 km training run.
Methods: Initially, peak oxygen uptake of 32 distance runners (4 female, 28 male; median age 45 years, range 28-53) was measured on a treadmill with a 1.5 km hour(-1) increase every 4 minutes starting from 8.5 km hour(-1). At least 1-week after this initial test, they participated in a 30 km road run at a speed corresponding to about 70% of their individual peak oxygen uptake on a flat terrain. Before and after (0, 24, and 48 hours) the run, blood concentration of creatine kinase (CK) were measured and pain sensation was determined (pain scale from 0 = no pain to 10 = extremely painful). Runners were then matched in pairs based on maximal CK and peak oxygen uptake, and allocated randomly into two different groups. One group was supplemented with 400 mg per day of PCSO-524® for 11 weeks, the other group with an olive oil placebo. After that period, CK and pain sensations were remeasured following a second 30 km run at the same speed and on the same terrain.
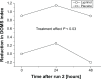
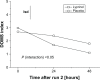
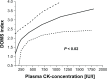
Results: The general pattern of soreness in the PCSO-524® supplemented group was reduced by 1.1 units (standard error 0.41) compared to the placebo (P < 0.05), the effects being greater in lesser trained runners (P < 0.05). CK levels were positively associated with pain sensation (P < 0.05), but trends toward lower CK in the PCSO-524® group, which were also more pronounced in the lesser trained runners, were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Pain sensations experienced by distance runners following a 30 km run were reduced by supplementation with the marine oil complex PCSO-524®, an effect which was greater in lesser trained runners.
Keywords: DOMS; creatine kinase; marine oil; running.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects PCSO-524®, a patented marine oil lipid and omega-3 PUFA blend derived from the New Zealand green lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus), on indirect markers of muscle damage and inflammation after muscle damaging exercise in untrained men: a randomized, placebo controlled trial.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Feb 19;12:10. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0073-z. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25722660 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of PCSO-524®, a Patented Marine Oil Lipid derived from the New Zealand Green Lipped Mussel (Perna canaliculus), on Pulmonary and Respiratory Muscle Function in Non-asthmatic Elite Runners.Int J Exerc Sci. 2018 Jun 1;11(3):669-680. doi: 10.70252/HDSA3416. eCollection 2018. Int J Exerc Sci. 2018. PMID: 29997731 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a combined New Zealand green-lipped mussel and Antarctic krill oil supplement on markers of exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation in untrained men.J Diet Suppl. 2022;19(2):184-211. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2020.1853649. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Diet Suppl. 2022. PMID: 33292022
-
Muscle tenderness and peak torque changes after downhill running following a prior bout of isokinetic eccentric exercise.J Sports Sci. 1996 Aug;14(4):291-9. doi: 10.1080/02640419608727714. J Sports Sci. 1996. PMID: 8887208 Clinical Trial.
-
Is there an optimal training intensity for enhancing the maximal oxygen uptake of distance runners?: empirical research findings, current opinions, physiological rationale and practical recommendations.Sports Med. 2006;36(2):117-32. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200636020-00003. Sports Med. 2006. PMID: 16464121 Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary Study on Treatment Outcomes and Prednisolone Tapering after Marine Lipid Extract EAB-277 Supplementation in Dogs with Immune-Mediated Hemolytic Anemia.Vet Sci. 2023 Jun 30;10(7):425. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10070425. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37505830 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance exercise: a mighty tool that adapts, destroys, rebuilds and modulates the molecular and structural environment of skeletal muscle.Phys Act Nutr. 2023 Jun;27(2):78-95. doi: 10.20463/pan.2023.0021. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Phys Act Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37583075 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of New Zealand Greenshell™ Mussel Powder Supplementation in Supporting Muscle Recovery Following Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Healthy, Untrained Adult Males.Nutrients. 2023 May 15;15(10):2316. doi: 10.3390/nu15102316. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242198 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects PCSO-524®, a patented marine oil lipid and omega-3 PUFA blend derived from the New Zealand green lipped mussel (Perna canaliculus), on indirect markers of muscle damage and inflammation after muscle damaging exercise in untrained men: a randomized, placebo controlled trial.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Feb 19;12:10. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0073-z. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25722660 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Cardiac Stress During a Marathon Could be Associated with Dietary Intake During the Week Before the Race.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 25;12(2):316. doi: 10.3390/nu12020316. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31991778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis PB, Ruby D, Bush-Joseph CA. Muscle soreness and delayed-onset muscle soreness. Clin Sports Med. 2012;31(2):255–262. - PubMed
-
- Howatson G, van Someren KA. The prevention and treatment of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 2008;38(6):483–503. - PubMed
-
- Newham DJ, McPhail G, Mills KR, Edwards RH. Ultrastructural changes after concentric and eccentric contractions of human muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1983;61(1):109–122. - PubMed
-
- Connolly DA, Sayers SP, McHugh MP. Treatment and prevention of delayed onset muscle soreness. J Strength Cond Res. 2003;17(1):197–208. - PubMed
-
- Whitehouse MW. Prostanoids as friends, not foes: further evidence from the interference by cycloxygenase-inhibitory drugs when inducing tolerance to experimental arthritigens in rats. Inflammopharmacology. 2005;12(5–6):481–492. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

