Age-dependent effect of Alzheimer's risk variant of CLU on EEG alpha rhythm in non-demented adults
- PMID: 24379779
- PMCID: PMC3861782
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2013.00086
Age-dependent effect of Alzheimer's risk variant of CLU on EEG alpha rhythm in non-demented adults
Abstract
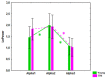
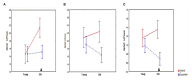
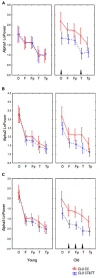
Polymorphism in the genomic region harboring the CLU gene (rs11136000) has been associated with the risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD). CLU C allele is assumed to confer risk for AD and the allele T may have a protective effect. We investigated the influence of the AD-associated CLU genotype on a common neurophysiological trait of brain activity (resting-state alpha-rhythm activity) in non-demented adults and elucidated whether this influence is modified over the course of aging. We examined quantitative electroencephalography (EEG) in a cohort of non-demented individuals (age range 20-80) divided into young (age range 20-50) and old (age range 51-80) cohorts and stratified by CLU polymorphism. To rule out the effect of the apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype on EEG characteristics, only subjects without the ApoE ε4 allele were included in the study. The homozygous presence of the AD risk variant CLU CC in non-demented subjects was associated with an increase of alpha3 absolute power. Moreover, the influence of CLU genotype on alpha3 was found to be higher in the subjects older than 50 years of age. The study also showed age-dependent alterations of alpha topographic distribution that occur independently of the CLU genotype. The increase of upper alpha power has been associated with hippocampal atrophy in patients with mild cognitive impairment (Moretti etal., 2012a). In our study, the CLU CC-dependent increase in upper alpha rhythm, particularly enhanced in elderly non-demented individuals, may imply that the genotype is related to preclinical dysregulation of hippocampal neurophysiology in aging and that this factor may contribute to the pathogenesis of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; EEG; aging; alpha rhythm; clusterin; genetic predisposition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuronal Hyperactivation in EEG Data during Cognitive Tasks Is Related to the Apolipoprotein J/Clusterin Genotype in Nondemented Adults.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5;24(7):6790. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076790. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047762 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association of apolipoprotein E genotype with EEG alpha rhythm slowing and functional brain network alterations during normal aging.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 1;16:931173. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.931173. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35979332 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity factor contributes to altered brain functional networks in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease: Neuroimaging-genetic evidence.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Aug;56:84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26899953
-
Alzheimer risk variant CLU and brain function during aging.Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Mar 1;73(5):399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.05.026. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22795969 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variant rs11136000 upregulates clusterin expression and reduces Alzheimer's disease risk.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 10;16:926830. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.926830. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36033622 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Heritability and molecular-genetic basis of resting EEG activity: a genome-wide association study.Psychophysiology. 2014 Dec;51(12):1225-45. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12344. Psychophysiology. 2014. PMID: 25387704 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of PICALM and CLU risk variants on beta EEG activity in Alzheimer's disease patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 14;11(1):20465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99589-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34650147 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs and Stem Cells as Promising Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(s1):S203-S225. doi: 10.3233/JAD-221298. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37212107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of AD-Related ABCA7 and CLU Variants on Default Mode Network Connectivity in Healthy Middle-Age Adults.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jul 31;13:145. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00145. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848603 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Clusterin and the CLU Gene rs11136000 Variant Are Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Jul 28;8:179. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00179. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27516739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babiloni C., Del Percio C., Lizio R., Marzano N., Infarinato F., Soricelli A., et al. (2014). Cortical sources of resting state electroencephalographic alpha rhythms deteriorate across time in subjects with amnesic mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 35 130–142 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C., Lizio R., Carducci F., Vecchio F., Redolfi A., Marino S., et al. (2011b). Resting state cortical electroencephalographic rhythms and white matter vascular lesions in subjects with Alzheimer’s disease: an Italian multicenter study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 26 331–346 10.3233/JAD-2011-101710 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

