Indefinite antiviral therapy may be required after surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma complicating chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 24379852
- PMCID: PMC3872615
Indefinite antiviral therapy may be required after surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma complicating chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
This report describes a 66-year-old male who had a long history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. He was found hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) 5 months after lamivudine resistance mutation and then received a successful hepatectomy. Three years later, hepatitis B envelope antigen seroconversion was achieved and nucleoside analogs were discontinued. After the withdrawn of antiviral treatment, HBV reactivated and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) occurred. Anti-HBV treatment improved the patient clinical condition. Three months after the remission of ACLF, the patient was diagnosed as HCC recurrence and received another hepatectomy. This case illustrates indefinite duration antiviral therapy and tight viral control should be performed in patients with HBV-related HCC.
Keywords: Carcinoma; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular; recurrence; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
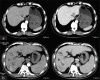
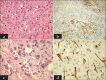

References
-
- Liu J, Fan D. Hepatitis B in China. Lancet. 2007;369:1582–3. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Chuma M, Hige S, Kamiyama T, Meguro T, Nagasaka A, Nakanishi K, et al. The influence of hepatitis B DNA level and antiviral therapy on recurrence after initial curative treatment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:991–9. - PubMed
-
- Asia-Pacific Working Party on Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia-Pacific region: Consensus statements. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:657–63. - PubMed
-
- Elefsiniotis I, Buti M, Jardi R, Vezali E, Esteban R. Clinical outcome of lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients with compensated cirrhosis under adefovir salvage treatment. Importance of HCC surveillance. Eur J Intern Med. 2009;20:478–81. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
