Genetically determined mitochondrial preservation and cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in a consomic rat model
- PMID: 24380873
- PMCID: PMC3949105
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00118.2013
Genetically determined mitochondrial preservation and cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in a consomic rat model
Abstract
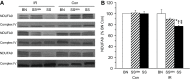
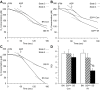
Cardioprotection may be genome dependent. One example is the increased tolerance to cardiac ischemia-reperfusion (IR) in Brown Norway (BN) compared with Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats. By narrowing the genetic difference to chromosome 6 only, we found the consomic SS(6BN) to be similarly IR tolerant as BN. We hypothesized that better preserved mitochondrial structure and function are genetically determined and therefore critically linked to myocardial IR tolerance associated with BN chromosome 6. Langendorff-prepared BN, SS, and SS(6BN) rat hearts were subjected to IR, while corresponding controls were continuously perfused. Though largely equal in nonischemic controls, assessment of functional data and ventricular infarct size in IR experiments confirmed that BN and SS(6BN) have an equally higher tolerance to IR than SS hearts. This was complemented by equally better preserved mitochondrial structure, oxidative phosphorylation, and calcium retention capacity in BN and SS(6BN) vs. SS hearts. For the first time, our data indicate that SS(6BN) are as resistant to IR injury as BN hearts in mitochondrial and myocardial function and viability compared with SS hearts. These findings not only link myocardial and mitochondrial protection in a genetic model but also suggest that genetic information on rat chromosome 6 is critical for mitochondrial preservation and IR tolerance.
Keywords: Brown Norway; Dahl salt sensitive; SS6BN; myocardium.
Figures



References
-
- An JZ, Varadarajan SG, Novalija E, Stowe DF. Ischemic and anesthetic preconditioning reduces cytosolic [Ca2+] and improves Ca2+ responses in intact hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281: H1508–H1523, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Baker JE, Konorev EA, Gross GJ, Chilian WM, Jacob HJ. Resistance to myocardial ischemia in five rat strains: is there a genetic component of cardioprotection? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278: H1395–H1400, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976 - PubMed
-
- Brar S, Ma Q, Dobra A, Zhang Z, Mackensen B, Podgoreanu MV. Susceptibility to global myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat is genetically determined. Anesthesia Analgesia 112: SCA46, 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

