Natural products as promising drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: molecular mechanism aspect
- PMID: 24381531
- PMCID: PMC3744904
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X11311040005
Natural products as promising drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: molecular mechanism aspect
Abstract
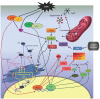
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder to date, with no curative or preventive therapy. Histopathological hallmarks of AD include deposition of β-amyloid plaques and formation of neurofibrillary tangles. Extent studies on pathology of the disease have made important discoveries regarding mechanism of disease and potential therapeutic targets. Many cellular changes including oxidative stress, disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis, inflammation, metabolic disturbances, and accumulation of unfolded/misfolded proteins can lead to programmed cell death in AD. Despite intensive research, only five approved drugs are available for the management of AD. Hence, there is a need to look at alternative therapies. Use of natural products and culinary herbs in medicine has gained popularity in recent years. Several natural substances with neuroprotective effects have been widely studied. Most of these compounds have remarkable antioxidant properties and act mainly by scavenging free radical species. Some of them increase cell survival and improve cognition by directly affecting amyloidogenesis and programmed cell death pathways. Further studies on these natural products and their mechanism of action, parallel with the use of novel pharmaceutical drug design and delivery techniques, enable us to offer an addition to conventional medicine. This review discussed some natural products with potential neuroprotective properties against Aβ with respect to their mechanism of action.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid β; Apoptosis; Natural products; Neuroprotection; Tau protein..
Figures
References
-
- Casey G. Alzheimer's and other dementias. Nurs. N. Z. 2012;18(6): 20–4. - PubMed
-
- Marchbanks RM. Biochemistry of Alzheimer's dementia. J. Neurochem. 1982;39(1):9–15. - PubMed
-
- Blass JP, Ko L, Wisniewski HM. Pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Psychiatr. Clin. North. Am. 1991;14(2):397–420. - PubMed
-
- Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Hanse E. Amyloid beta and APP as biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2010;45(1): 23–9. - PubMed
-
- Obulesu M, Venu R, Somashekhar R. Tau mediated neurodegeneration an insight into Alzheimer's disease pathology. Neurochem. Res. 2011;36(8):1329–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous