Targeting Histone Deacetylases in Diseases: Where Are We?
- PMID: 24382114
- PMCID: PMC4492558
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5776
Targeting Histone Deacetylases in Diseases: Where Are We?
Abstract
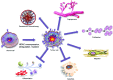
Significance: Epigenetic inactivation of pivotal genes involved in cell growth is a hallmark of human pathologies, in particular cancer. Histone acetylation balance obtained through opposing actions of histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone acetyltransferases is one epigenetic mechanism controlling gene expression and is, thus, associated with disease etiology and progression. Interfering pharmacologically with HDAC activity can correct abnormalities in cell proliferation, migration, vascularization, and death.
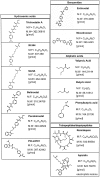
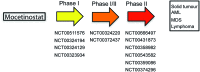
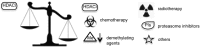
Recent advances: Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) represent a new class of cytostatic agents that interfere with the function of HDACs and are able to increase gene expression by indirectly inducing histone acetylation. Several HDACi, alone or in combination with DNA-demethylating agents, chemopreventive, or classical chemotherapeutic drugs, are currently being used in clinical trials for solid and hematological malignancies, and are, thus, promising candidates for cancer therapy.
Critical issues: (i) Non-specific (off-target) HDACi effects due to activities unassociated with HDAC inhibition. (ii) Advantages/disadvantages of non-selective or isoform-directed HDACi. (iii) Limited number of response-predictive biomarkers. (iv) Toxicity leading to dysfunction of critical biological processes.
Future directions: Selective HDACi could achieve enhanced clinical utility by reducing or eliminating the serious side effects associated with current first-generation non-selective HDACi. Isoform-selective and pan-HDACi candidates might benefit from the identification of biomarkers, enabling better patient stratification and prediction of response to treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Adams H, Fritzsche FR, Dirnhofer S, Kristiansen G, and Tzankov A. Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14: 577–584, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM, Venturelli S, Pathil A, Krusch M, Kaiser S, Jobst J, Smirnow I, Wagner A, Steinle A, and Salih HR. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of hepatoma cells via specific induction of NKG2D ligands by the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium valproate. Cancer Res 65: 6321–6329, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Atadja P. Development of the pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589): successes and challenges. Cancer Lett 280: 233–241, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

