Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial iron accumulation
- PMID: 24382354
- PMCID: PMC3904631
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI72931
Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial iron accumulation
Abstract
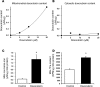
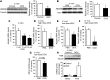
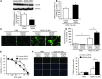
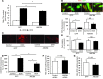
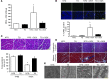
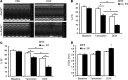
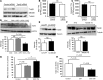
Doxorubicin is an effective anticancer drug with known cardiotoxic side effects. It has been hypothesized that doxorubicin-dependent cardiotoxicity occurs through ROS production and possibly cellular iron accumulation. Here, we found that cardiotoxicity develops through the preferential accumulation of iron inside the mitochondria following doxorubicin treatment. In isolated cardiomyocytes, doxorubicin became concentrated in the mitochondria and increased both mitochondrial iron and cellular ROS levels. Overexpression of ABCB8, a mitochondrial protein that facilitates iron export, in vitro and in the hearts of transgenic mice decreased mitochondrial iron and cellular ROS and protected against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Dexrazoxane, a drug that attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, decreased mitochondrial iron levels and reversed doxorubicin-induced cardiac damage. Finally, hearts from patients with doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy had markedly higher mitochondrial iron levels than hearts from patients with other types of cardiomyopathies or normal cardiac function. These results suggest that the cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin develop from mitochondrial iron accumulation and that reducing mitochondrial iron levels protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Binaschi M, et al. Anthracyclines: selected new developments. Current medicinal chemistry. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2001;1(2):113–130. - PubMed
-
- Ferrans VJ, Clark JR, Zhang J, Yu ZX, Herman EH. Pathogenesis and prevention of doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Tsitologiia. 1997;39(10):928–937. - PubMed
-
- Jones RL, Swanton C, Ewer MS. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2006;5(6):791–809. - PubMed
-
- Simunek T, Sterba M, Popelova O, Adamcova M, Hrdina R, Gersl V. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: overview of studies examining the roles of oxidative stress and free cellular iron. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61(1):154–171. - PubMed
-
- Berthiaume JM, Wallace KB. Adriamycin-induced oxidative mitochondrial cardiotoxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2007;23(1):15–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

