New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment
- PMID: 24382387
- PMCID: PMC3871231
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI69738
New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment
Abstract
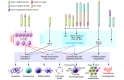
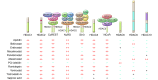
Epigenetic enzymes are often dysregulated in human tumors through mutation, altered expression, or inappropriate recruitment to certain loci. The identification of these enzymes and their partner proteins has driven the rapid development of small-molecule inhibitors that target the cancer epigenome. Herein, we discuss the influence of aberrantly regulated histone deacetylases (HDACs) in tumorigenesis. We examine HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) targeting class I, II, and IV HDACs that are currently under development for use as anticancer agents following the FDA approval of two HDACis, vorinostat and romidepsin.
Figures
References
-
- Olsen CA. Expansion of the lysine acylation landscape. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012;51(16):3755–3756. - PubMed
-
- Spange S, Wagner T, Heinzel T, Krämer OH. Acetylation of non-histone proteins modulates cellular signalling at multiple levels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41(1):185–198. - PubMed
-
- Fraga MF, et al. Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat Genet. 2005;37(4):391–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

