DNA damage in inflammation-related carcinogenesis and cancer stem cells
- PMID: 24382987
- PMCID: PMC3870134
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/387014
DNA damage in inflammation-related carcinogenesis and cancer stem cells
Abstract
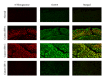
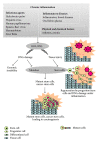
Infection and chronic inflammation have been recognized as important factors for carcinogenesis. Under inflammatory conditions, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are generated from inflammatory and epithelial cells and result in oxidative and nitrative DNA damage, such as 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG) and 8-nitroguanine. The DNA damage can cause mutations and has been implicated in the initiation and/or promotion of inflammation-mediated carcinogenesis. It has been estimated that various infectious agents are carcinogenic to humans (IARC group 1), including parasites (Schistosoma haematobium (SH) and Opisthorchis viverrini (OV)), viruses (hepatitis C virus (HCV), human papillomavirus (HPV), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)), and bacterium Helicobacter pylori (HP). SH, OV, HCV, HPV, EBV, and HP are important risk factors for bladder cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, cervical cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and gastric cancer, respectively. We demonstrated that 8-nitroguanine was strongly formed via inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression at these cancer sites of patients. Moreover, 8-nitroguanine was formed in Oct3/4-positive stem cells in SH-associated bladder cancer tissues and in Oct3/4- and CD133-positive stem cells in OV-associated cholangiocarcinoma tissues. Therefore, it is considered that oxidative and nitrative DNA damage in stem cells may play a key role in inflammation-related carcinogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y. Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage as biomarker for carcinogenesis with special reference to inflammation. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2006;8(5-6):1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- IARC. Chronic infectionsin. In: Stewart BW, Kleihues P, editors. World Cancer Report. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008. pp. 128–135.
-
- Hussain SP, Harris CC. Inflammation and cancer: an ancient link with novel potentials. International Journal of Cancer. 2007;121(11):2373–2380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

