Impact of anti-rheumatic treatment on immunogenicity of pandemic H1N1 influenza vaccine in patients with arthritis
- PMID: 24383620
- PMCID: PMC3978632
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4427
Impact of anti-rheumatic treatment on immunogenicity of pandemic H1N1 influenza vaccine in patients with arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: An adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 influenza (pH1N1) vaccine (Pandemrix) was reported as highly immunogenic resulting in seroconversion in 77 to 94% of adults after administration of a single dose. The aim of the study was to investigate the impact of different anti-rheumatic treatments on antibody response to pH1N1 vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and spondylarthropathy (SpA).
Methods: Patients with arthritis (n = 291; mean age 57 years, 64% women) participated. Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay was performed on blood samples drawn before and after a mean (SD) of 8.3 (4) months following vaccination. A positive immune response i.e. seroconversion was defined as negative prevaccination serum and postvaccination HI titer ≥40 or a ≥4-fold increase in HI titer. All patients were divided into predefined groups based on diagnosis (RA or SpA) and ongoing treatment: methotrexate (MTX), anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) as monotherapy, MTX combined with anti-TNF, other biologics (abatacept, rituximab, tocilizumab) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)/analgesics. Predictors of positive immune response were studied using logistic regression analysis.
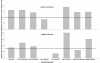
Results: The percentage of patients with positive immune response in the different treatment groups was: 1. RA on MTX 42%; 2. RA on anti-TNF monotherapy 53%; 3. RA on anti-TNF + MTX 43%; 4. RA on other biologics (abatacept 20%, rituximab 10% and tocilizumab 50%); 5. SpA on anti-TNF monotherapy 76%; 6. SpA on anti-TNF + MTX 47%; and 7. SpA on NSAIDs/analgesics 59%. RA patients on rituximab had significantly lower (P < 0.001) and SpA on anti-TNF monotherapy significantly better response rates compared to other treatment groups (P 0.001 to 0.033). Higher age (P < 0.001) predicted impaired immune response. Antibody titers 3 to 6 months after vaccination was generally lower compared to those within the first 3 months but no further decrease in titers were observed 6 to 22 months after vaccination.
Conclusions: Rituximab treatment severely reduced antibody response to pH1N1 influenza vaccine. The other treatment groups showed acceptable antibody responses. Protective antibody titers could be detected up to 22 months after vaccination in the current patient population, with the exception of rituximab treated patients.
Figures


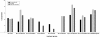
References
-
- The Influenza A(H1N1) 2009 Pandemic in Sweden, 2009–2010. A Report from the Swedish WHO National Influenza Centre. Available at: http://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/pagefiles/12852/the-influenza-a-h1n1-....
-
- Nicholson KG, Abrams KR, Batham S, Clark TW, Hoschler K, Lim WS, Medina MJ, Nguyen-Van-Tam JS, Read RC, Warren FC, Zambon M. Immunogenicity and safety of a two-dose schedule of whole-virion and AS03A-adjuvanted 2009 influenza A (H1N1) vaccines: a randomised, multicentre, age-stratified, head-to-head trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;16:91–101. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70296-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jackson LA, Chen WH, Stapleton JT, Dekker CL, Wald A, Brady RC, Edupuganti S, Winokur P, Mulligan MJ, Keyserling HL, Kotloff KL, Rouphael N, Noah DL, Hill H, Wolff MC. Immunogenicity and safety of varying dosages of a monovalent 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine given with and without AS03 adjuvant system in healthy adults and older persons. J Infect Dis. 2012;16:811–820. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

