Clinical and angiographic features and stroke types in adult moyamoya disease
- PMID: 24384121
- PMCID: PMC7965144
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A3819
Clinical and angiographic features and stroke types in adult moyamoya disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study was conducted to elucidate the association between clinical and angiographic characteristics and stroke types in adult Moyamoya disease that has been rarely evaluated.
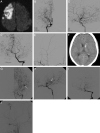
Materials and methods: We analyzed the clinical and radiologic data obtained from a retrospective adult Moyamoya disease cohort with acute strokes, which were classified into 7 categories: large-artery infarct, hemodynamic infarct, perforator infarct, deep intracerebral hemorrhage, lobar intracerebral hemorrhage, intraventricular hemorrhage, and SAH. With conventional angiography, which was performed in the hemispheres with acute strokes, the Suzuki angiographic stage, intracranial aneurysm, major artery occlusion, and collateral vessel development were confirmed within 1 month of stroke onset.
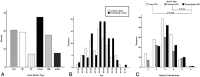
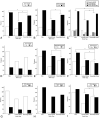
Results: This study included 79 patients with acute ischemic stroke and 96 patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke. The angiographic stage had a strong tendency to be more advanced in the hemorrhagic than the ischemic patients (P = .061). Intracranial aneurysms were more frequently found in the hemorrhagic than ischemic or control hemispheres (P = .002). Occlusions of the anterior cerebral artery and development of fetal-type posterior cerebral artery were more frequently observed in the hemorrhagic than the ischemic (P = .001 and .01, respectively) or control hemispheres (P = .011 and .013, respectively). MCA occlusion (P = .039) and collateral flow development, including the ethmoidal Moyamoya vessels (P = .036) and transdural anastomosis of the external carotid artery (P = .022), occurred more often in the hemorrhagic than the ischemic hemispheres. Anterior cerebral artery occlusion occurred more frequently in patients with deep intracerebral hemorrhage or intraventricular hemorrhage than with lobar intracerebral hemorrhage (P = .009).
Conclusions: In adult Moyamoya disease, major artery occlusion and collateral compensation occurred more often in the hemorrhagic than in the ischemic hemispheres. Thus, anterior cerebral artery occlusion with or without MCA occlusion and intracranial aneurysms may be the main contributing factors to hemorrhagic stroke in adult patients with Moyamoya disease.
© 2014 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
References
-
- Fukui M. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis (‘Moyamoya’ disease): Research Committee on Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis (Moyamoya Disease) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1997;99(Suppl 2):S238–40 - PubMed
-
- Han DH, Kwon OK, Byun BJ, et al. . A co-operative study: clinical characteristics of 334 Korean patients with Moyamoya disease treated at neurosurgical institutes (1976–1994): The Korean Society for Cerebrovascular Disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2000;142:1263–73 - PubMed
-
- Fukui M, Kono S, Sueishi K, et al. . Moyamoya disease. Neuropathology 2000;20(Suppl):S61–64 - PubMed
-
- Research Committee on the Pathology and Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis; Health Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for Intractable Diseases. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of Moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis). Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2012;52:245–66 - PubMed
-
- Morioka M, Hamada J, Kawano T, et al. . Angiographic dilatation and branch extension of the anterior choroidal and posterior communicating arteries are predictors of hemorrhage in adult Moyamoya patients. Stroke 2003;34:90–95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
