Change in brain and lesion volumes after CEE therapies: the WHIMS-MRI studies
- PMID: 24384646
- PMCID: PMC3917682
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000079
Change in brain and lesion volumes after CEE therapies: the WHIMS-MRI studies
Abstract
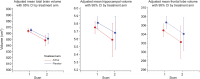
Objectives: To determine whether smaller brain volumes in older women who had completed Women's Health Initiative (WHI)-assigned conjugated equine estrogen-based hormone therapy (HT), reported by WHI Memory Study (WHIMS)-MRI, correspond to a continuing increased rate of atrophy an average of 6.1 to 7.7 years later in WHIMS-MRI2.
Methods: A total of 1,230 WHI participants were contacted: 797 (64.8%) consented, and 729 (59%) were rescanned an average of 4.7 years after the initial MRI scan. Mean annual rates of change in total brain volume, the primary outcome, and rates of change in ischemic lesion volumes, the secondary outcome, were compared between treatment groups using mixed-effect models with adjustment for trial, clinical site, age, intracranial volumes, and time between MRI measures.
Results: Total brain volume decreased an average of 3.22 cm(3)/y in the active arm and 3.07 cm(3)/y in the placebo arm (p = 0.53). Total ischemic lesion volumes increased in both arms at a rate of 0.12 cm(3)/y (p = 0.88).
Conclusions: Conjugated equine estrogen-based postmenopausal HT, previously assigned at WHI baseline, did not affect rates of decline in brain volumes or increases in brain lesion volumes during the 4.7 years between the initial and follow-up WHIMS-MRI studies. Smaller frontal lobe volumes were observed as persistent group differences among women assigned to active HT compared with placebo. Women with a history of cardiovascular disease treated with active HT, compared with placebo, had higher rates of accumulation in white matter lesion volume and total brain lesion volume. Further study may elucidate mechanisms that explain these findings.
Figures

Comment in
-
Past hormone therapy in older women: does the brain recover from adverse effects?Neurology. 2014 Feb 4;82(5):380-1. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000093. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24384642 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson GL, Manson J, Wallace R, et al. Implementation of the Women's Health Initiative study design. Ann Epidemiol 2003;13:S5–S17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
