Duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy, chronic pain or fibromyalgia
- PMID: 24385423
- PMCID: PMC10711341
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007115.pub3
Duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy, chronic pain or fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: Duloxetine is a balanced serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor licensed for the treatment of major depressive disorders, urinary stress incontinence and the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A number of trials have been conducted to investigate the use of duloxetine in neuropathic and nociceptive painful conditions. This is the first update of a review first published in 2010.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy and different types of chronic pain.
Search methods: On 19th November 2013, we searched The Cochrane Neuromuscular Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, DARE, HTA, NHSEED, MEDLINE, and EMBASE. We searched ClinicalTrials.gov for ongoing trials in April 2013. We also searched the reference lists of identified publications for trials of duloxetine for the treatment of painful peripheral neuropathy or chronic pain.
Selection criteria: We selected all randomised or quasi-randomised trials of any formulation of duloxetine, used for the treatment of painful peripheral neuropathy or chronic pain in adults.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by The Cochrane Collaboration.
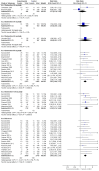
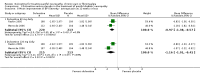
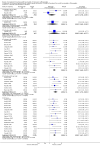
Main results: We identified 18 trials, which included 6407 participants. We found 12 of these studies in the literature search for this update. Eight studies included a total of 2728 participants with painful diabetic neuropathy and six studies involved 2249 participants with fibromyalgia. Three studies included participants with depression and painful physical symptoms and one included participants with central neuropathic pain. Studies were mostly at low risk of bias, although significant drop outs, imputation methods and almost every study being performed or sponsored by the drug manufacturer add to the risk of bias in some domains. Duloxetine at 60 mg daily is effective in treating painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the short term, with a risk ratio (RR) for ≥ 50% pain reduction at 12 weeks of 1.73 (95% CI 1.44 to 2.08). The related NNTB is 5 (95% CI 4 to 7). Duloxetine at 60 mg daily is also effective for fibromyalgia over 12 weeks (RR for ≥ 50% reduction in pain 1.57, 95% CI 1.20 to 2.06; NNTB 8, 95% CI 4 to 21) and over 28 weeks (RR 1.58, 95% CI 1.10 to 2.27) as well as for painful physical symptoms in depression (RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.19 to 1.59; NNTB 8, 95% CI 5 to 14). There was no effect on central neuropathic pain in a single, small, high quality trial. In all conditions, adverse events were common in both treatment and placebo arms but more common in the treatment arm, with a dose-dependent effect. Most adverse effects were minor, but 16% of participants stopped the drug due to adverse effects. Serious adverse events were rare.
Authors' conclusions: There is adequate amounts of moderate quality evidence from eight studies performed by the manufacturers of duloxetine that doses of 60 mg and 120 mg daily are efficacious for treating pain in diabetic peripheral neuropathy but lower daily doses are not. Further trials are not required. In fibromyalgia, there is lower quality evidence that duloxetine is effective at similar doses to those used in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and with a similar magnitude of effect. The effect in fibromyalgia may be achieved through a greater improvement in mental symptoms than in somatic physical pain. There is low to moderate quality evidence that pain relief is also achieved in pain associated with depressive symptoms, but the NNTB of 8 in fibromyalgia and depression is not an indication of substantial efficacy. More trials (preferably independent investigator led studies) in these indications are required to reach an optimal information size to make convincing determinations of efficacy.Minor side effects are common and more common with duloxetine 60 mg and particularly with 120 mg daily, than 20 mg daily, but serious side effects are rare.Improved direct comparisons of duloxetine with other antidepressants and with other drugs, such as pregabalin, that have already been shown to be efficacious in neuropathic pain would be appropriate. Unbiased economic comparisons would further help decision making, but no high quality study includes economic data.
Conflict of interest statement
RACH has no competing interests which affect his impartiality in preparing this review.
PJW: none known.
MPL has received honoraria for consultation from Baxter Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring and LfB and a travel support grant from Grifols, all manufacturers of IVIg. He was a blinded investigator in the study of Comi et al. 2002.
MPL is one of two Joint Co‐ordinating Editors of the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group and RACH is a member of the group's editorial board. Editorial decisions regarding the review were handled by other members of the editorial board without the influence of the review authors.
Figures












































Update of
-
Duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy or chronic pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 7;(4):CD007115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007115.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 03;(1):CD007115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007115.pub3. PMID: 19821395 Updated.
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: In neuropathy, fibromyalgia, or chronic pain, duloxetine reduces pain but increases adverse events.Ann Intern Med. 2014 Apr 15;160(8):JC12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-160-8-201404150-02012. Ann Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24733217 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arnold 2004 {published data only}
-
- Arnold LM, Lu Y, Crofford LJ, Wohlreich M, Detke MJ, Iyengar S, et al for the Duloxetine Fibromyalgia Trial Group. A double‐blind multicenter trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the treatment of fibromyalgia patients with or without major depressive disorder. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;50(9):2974‐84. [PUBMED: 15457467] - PubMed
Arnold 2005 {published data only}
-
- Arnold LM, Rosen A, Pritchett YL, D'Souza DN, Goldstein DJ, Iyengar S, et al. A randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of duloxetine in the treatment of women with fibromyalgia with or without major depressive disorder. Pain 2005;119(1‐3):5‐15. [PUBMED: 16298061] - PubMed
Arnold 2010 {published data only}
-
- Arnold LM, Clauw D, Wang F, Ahl J, Gaynor PJ, Wohlreich MM. Flexible dosed duloxetine in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial [A study comparing duloxetine and placebo in the treatment of fibromyalgia]. Journal of Rheumatology 2010;37(12):2578‐86. [PUBMED: 20843911] - PubMed
Arnold 2012 {published data only}
-
- Arnold LM, Zhang S, Pangallo BA. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine 30 mg/d in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Clinical Journal of Pain 2012;28(9):775‐81. [PUBMED: 22971669] - PubMed
Brecht 2007 {published data only}
-
- Brecht S, Courtecuisse C, Debieuvre C, Croenlein J, Desaiah D, Raskin J, et al. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine 60 mg once daily in the treatment of pain in patients with major depressive disorder and at least moderate pain of unknown etiology: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2007;68(11):1707‐16. [PUBMED: 18052564] - PubMed
Chappell 2008 {published data only}
Gao 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gao Y, Ning G, Jia WP, Zhou ZG, Xu ZR, Liu ZM, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain in China. Chinese Medical Journal 2010;123(22):3184‐92. [CTG: NCT00408993; PUBMED: 21163113] - PubMed
Gaynor 2011a {published data only}
-
- Gaynor PJ, Gopal M, Zheng W, Martinez JM, Robinson MJ, Hann D, Marangell LB. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of major depressive disorder and associated painful physical symptoms: a replication study. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2011;27(10):1859‐67. [PUBMED: 21838410] - PubMed
Gaynor 2011b {published data only}
-
- Gaynor PJ, Gopal M, Zheng W, Martinez JM, Robinson MJ, Marangell LB. A randomized placebo‐controlled trial of duloxetine in patients with major depressive disorder and associated painful physical symptoms. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2011;27(10):1849‐58. [PUBMED: 21838411] - PubMed
Goldstein 2005 {published data only}
-
- Goldstein DJ, Lu Y, Detke MJ, Lee TC, Iyengar S. Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 2005;116(1‐2):109‐18. [PUBMED: 15927394] - PubMed
Kaur 2011 {published data only}
Raskin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Raskin J, Pritchett YL, Wang F, D'Souza DN, Waninger AL, Iyengar S, et al. A double‐blind, randomized multicentre trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Medicine 2005;6(5):346‐56. [PUBMED: 16266355] - PubMed
Rowbotham 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rowbotham MC, Arslanian A, Nothaft W, Duan WR, Best AE, Pritchett Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of the α4β2 neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist ABT‐894 in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain [Safety and efficacy study in subjects with diabetic neuropathic pain]. Pain 2012;153(4):862‐8. [CTG: NCT00507936; PUBMED: 22386472] - PubMed
Russell 2008 {published data only}
-
- Russell IJ, Mease PJ, Smith TR, Kajdasz DK, Wohlreich MM, Detke MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine for the treatment of fibromyalgia in patients with or without major depressive disorder: results from a 6‐month randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, fixed‐dose trial. Pain 2008;136(3):432‐44. [PUBMED: 18395345] - PubMed
Tesfaye 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tesfaye S, Wilhelm S, Lledo A, Schacht A, Tölle T, Bouhassira D, et al. Duloxetine and pregabalin: high‐dose monotherapy or their combination? The “COMBO‐DN study” – a multinational, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group study in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain [Use of duloxetine or pregabalin in monotherapy versus combination therapy of both drugs in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy "The COMBO ‐ DN (COmbination vs Monotherapy of pregaBalin and dulOxetine in Diabetic Neuropathy) Study"]. Pain 2013 May 31 [Epub ahead of print]. [CTG: NCT01089556; PUBMED: 23732189] - PubMed
Vranken 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vranken JH, Hollmann MW, Vegt MH, Kruis MR, Heesen M, Vos K, et al. Duloxetine in patients with central neuropathic pain caused by spinal cord injury or stroke: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Pain 2011;152(2):267‐73. - PubMed
Wernicke 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wernicke JF, Pritchett YL, D'Souza DN, Waninger A, Tran P, Iyengar S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of duloxetine in diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Neurology 2006;67(8):1411‐20. [PUBMED: 17060567] - PubMed
Yasuda 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Yasuda H, Hotta N, Nakao K, Kasuga M, Kashiwagi A, Kawamori R. Superiority of duloxetine to placebo in improving painful diabetic neuropathic pain: results of a randomized controlled trial in Japan [A superiority study of LY248686 versus placebo in the treatment of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain]. Journal of Diabetes Investigation 2011;2(2):132‐9. - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Boyle 2012 {published data only}
-
- Boyle J, Eriksson ME, Gribble L, Gouni R, Johnsen S, Coppini DV, Kerr D. Randomized, placebo‐controlled comparison of amitriptyline, duloxetine, and pregabalin in patients with chronic diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: impact on pain, polysomnographic sleep, daytime functioning, and quality of life. [Effects of pregabalin, duloxetine & amitriptyline on pain & sleep (NCT00370656)]. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12):2451‐8. [DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0656] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Brannan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Brannan SK, Mallinckrodt CH, Brown EB, Wohlreich MM, Watkin JG, Schatzberg AF. Duloxetine 60mg once daily in the treatment of painful physical symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2005;39(1):43‐53. [PUBMED: 15504423] - PubMed
Canovas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cánovas L, Illodo G, Castro M, Mouriz L, Vázquez‐Martínez A, Centeno J, et al. Effects of duloxetin and amitriptilin in neuropathic pain: study in 180 patients [Efectos de duloxetina y amitriptilina en el dolor neuropatico: estudio en 180 casos]. Revista de la Sociedad Espanola del Dolor 2007;14(8):568‐73.
Chappell 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chappell AS, Ossanna MJ, Liu‐Seifert H, Iyengar S, Skljarevski V, Li LC, et al. Duloxetine, a centrally acting analgesic, in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis knee pain: a 13‐week, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Pain 2009;146(3):253‐60. [PUBMED: 19625125] - PubMed
Chappell 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chappell AS, Desaiah D, Liu‐Seifert H, Zhang S, Skljarevski V, Belenkov Y, et al. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of duloxetine for the treatment of chronic pain due to osteoarthritis of the knee. Pain Practice 2011;11(1):33‐41. [PUBMED: 20602715] - PubMed
Goldstein 2004 {published data only}
-
- Goldstein DJ, Lu Y, Detke MJ, Wiltse C, Mallinckrodt C, Demitrack MA. Duloxetine in the treatment of depression: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled comparison with paroxetine. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2004;24(4):389‐99. [PUBMED: 15232330] - PubMed
Harrison 2013 {published data only}
-
- Harrison T, Miyahara S, Lee A, Evans S, Bastow B, Simpson D, et al. ACTG A5252 Team. Experience and challenges presented by a multicenter crossover study of combination analgesic therapy for the treatment of painful HIV‐associated polyneuropathies [Combination Pain Therapy in HIV Neuropathy]. Pain Medicine 2013;14(7):1039‐47. - PMC - PubMed
Lavoie Smith 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lavoie Smith EM, Pang H, Cirrincione C, Fleishman SB, Paskett ED, Fadul CE, et al. CALGB 170601: A phase III double blind trial of duloxetine to treat painful chemotherapy‐induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Journal of clinical oncology 2012;Conference:32676.
NCT00125892 {published data only}
-
- NCT00125892. A study of duloxetine in the treatment of fibromyalgia ‐ [A 1‐year safety study of duloxetine in patients with fibromyalgia; www.lillytrials.com/results/Cymbalta.pdf]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00125892; (Accessed 7 November 2013). [Lilly Clinical Trials Register Reference Summary #: 9075]
NCT00266643 {published data only}
-
- NCT00266643. Tolerability of switching to duloxetine for the management of diabetic nerve pain (NCT00266643) [A comparison of strategies for switching patients from amitriptyline to duloxetine for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (Lilly trial reference Summary ID# 8952).]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00266643; www.lillytrials.com/results/Cymbalta.pdf (accessed 7 November 2013). [Lilly trial reference Summary ID#: 8952]
NCT00385671 {published data only}
-
- NCT00385671. An open‐label comparison of duloxetine to other alternatives for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00385671 (Accessed 7 November 2013).
NCT00425230 {published data only}
-
- NCT00425230. Open label study of duloxetine for the treatment of phantom limb pain [Pilot study of use of duloxetine for the treatment of phantom limb pain]. www.clinicaltrials.org/show/NCT00425230 (accessed 7 November 2013).
NCT00552682 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00552682. Pilot, opened, randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy of duloxetine in the treatment of fibromyalgia in patients with infection by HIV 1+. www.clinicaltrials.gov\show\NCT00552682 (Accessed 7 November).
NCT00641719 {published data only}
-
- NCT00641719. A long‐term study for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00641719 (Accessed 7 November 2013).
NCT01451606 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01451606. Duloxetine for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01451606 (Accessed 7 November 2013). [CTG: NCT01451606]
Raskin 2005a {published data only}
-
- Raskin J, Pritchett YL, Chappell AS, D‐Souza DN, Wong CK, Ferdinand SJ, et al. Duloxetine in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain ‐ results from three clinical trials. European Journal of Neurology 2005;12(s2):221.
Raskin 2006a {published data only}
-
- Raskin J, Smith TR, Wong K, Pritchett YL, D'Souza DN, Iyengar S, et al. Duloxetine versus routine care in the long‐term management of diabetic neuropathic pain. Journal of Palliative Medicine 2006;9(1):29‐40. [PUBMED: 16430342] - PubMed
Raskin 2006b {published data only}
-
- Raskin J, Wang F, Pritchett YL, Goldstein DJ. Duloxetine for patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a 6‐month open‐label safety study. Pain Medicine 2006;7(5):373‐85. [PUBMED: 17014595] - PubMed
Russell 2006 {published data only}
-
- Russell JW. Does duloxetine safely and effectively reduce the severity of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain?. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology 2006;2(1):18‐9. [PUBMED: 16932514] - PubMed
Skljarevski 2008 {published data only}
-
- Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Liu‐Siefert H, Zhang Q, Chappell AS, Detke MJ, et al. Efficacy of duloxetine in low back pain. European Journal of Neurology 2008;15(Suppl 3):320.
Skljarevski 2009 {published data only}
-
- Skljarevski V, Ossanna M, Liu‐Seifert H, Zhang Q, Chappell A, Iyengar S, et al. A double‐blind, randomized trial of duloxetine versus placebo in the management of chronic low back pain. European Journal of Neurology 2009;16(9):1041‐8. [PUBMED: 19469829] - PubMed
Skljarevski 2009a {published data only}
-
- Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Zhang Q, Chappell AS, Detke MJ, Gross JL, et al. Evaluating the maintenance of effect of duloxetine in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain [Maintenance of effect of duloxetine in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain]. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2009;25(7):623‐31. [CTG: NCT00322621; PUBMED: 19637208] - PubMed
Skljarevski 2010 {published data only}
-
- Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Liu‐Seifert H, Zhang Q, Chappell AS, Detke MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine 2010;35(13):E578‐85. [PUBMED: 20461028] - PubMed
Skljarevski 2010b {published data only}
-
- Skljarevski V, Zhang S, Desaiah D, Alaka KJ, Palacios S, Miazgowski T, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in patients with chronic low back pain: a 12‐week, fixed‐dose, randomized, double‐blind trial. Journal of Pain 2010;11(12):1282‐90. - PubMed
Smith 2013 {published data only}
Tanenberg 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tanenberg RJ, Irving GA, Risser RC, Ahl J, Robinson MJ, Skljarevski V, et al. Duloxetine, pregabalin, and duloxetine plus gabapentin for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain management in patients with inadequate pain response to gabapentin: an open‐label, randomized, noninferiority comparison. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2011;86(7):615‐26. - PMC - PubMed
Vollmer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vollmer T, Robinson M, Risser R, Malcolm SK, Carlson J. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of duloxetine for the treatment of central neuropathic pain associated with multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal 2011;17 (10 suppl):P1044. - PubMed
Wernicke 2006b {published data only}
Wu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wu EQ, Birnbaum HJ, Mareva MN, Le TK, Robinson RL, Rosen A, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of duloxetine versus routine treatment for U.S. patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. The Journal of Pain 2006;7(6):399‐407. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT00603265 {published data only}
-
- NCT00603265. A phase 2a, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study to assess the safety and efficacy of ADL5859 100 mg BID in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy [Safety and efficacy study of ADL5859 in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00603265 (Accessed 7 November 2013). [CTG: NCT00603265]
References to ongoing studies
NCT00457730 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00457730. A randomized placebo controlled trial of duloxetine for central pain in multiple sclerosis [A study to test the use of duloxetine for pain in MS]. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00457730 Accessed 19 December 2013.
NCT00619983 {published data only}
-
- NCT00619983. Three way interaction between gabapentin, duloxetine, and donepezil in patients with diabetic neuropathy. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00619983 Accessed 19 December 2013.
NCT01179672 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01179672. A study in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain in China. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01179672 (Accessed 19 December 2013).
NCT01237587 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01237587. Effect of duloxetine 30/60 mg once daily versus placebo in adolescents with juvenile primary fibromyalgia syndrome [A study of duloxetine in adolescents with juvenile primary fibromyalgia syndrome]. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01237587 Accessed 19 December 2013.
NCT01552057 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01552057. A phase III clinical trial of duloxetine in participants with fibromyalgia [A study of duloxetine in fibromyalgia]. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01552057 Accessed 19 December 2013.
Additional references
Aronson 2007
-
- Aronson JK. Chapter 2 Antidepressant Drugs. In: Aronson JK editor(s). Side Effects of Drugs. Vol. 29, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007:23.
Aronson 2008
-
- Aronson JK. Chapter 2 Antidepressant Drugs. In: Aronson JK editor(s). Side Effects of Drugs. Vol. 30, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008:19.
Attal 2006
-
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T, et al. EFNS Task Force. EFNS guidelines on pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. European Journal of Neurology 2006;13(11):1153‐69. - PubMed
Beard 2008
-
- Beard SM, McCrink L, Le TK, Garcia‐Cebrian A, Monz B, Malik RA. Cost effectiveness of duloxetine in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain in the UK. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2008;24(2):385‐99. - PubMed
Bellows 2012
-
- Bellows BK, Dahal A, Jiao T, Biskupiak J. A cost‐utility analysis of pregabalin versus duloxetine for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Journal of Pain & Palliative Care Pharmacotherapy 2012;26(2):153–64. - PubMed
Breivik 2006
-
- Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V, Cohen R, Gallacher D. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. European Journal of Pain 2006;10(4):287‐333. - PubMed
Burckhardt 1991
-
- Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM. The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validation. Journal of Rheumatology 1991;18(5):728‐33. - PubMed
Bymaster 2001
-
- Bymaster FP, Dreshfield‐Ahmad LJ, Threlkeld PG, Shaw JL, Thompson L, Nelson DL, et al. Comparative affinity of duloxetine and venlafaxine for serotonin and norepinephrine transporters in vitro and in vivo, human serotonin receptor subtypes, and other neuronal receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001;25(6):871‐80. - PubMed
Bymaster 2005
-
- Bymaster FP, Lee TC, Knadler MP, Detke MJ, Iyengar S. The dual transporter inhibitor duloxetine: a review of its preclinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetic profile, and clinical results in depression. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2005;11(12):1475‐93. - PubMed
Dadabhoy 2006
-
- Dadabhoy D, Clauw DJ. Therapy Insight: fibromyalgia ‐ a different type of pain needing a different type of treatment. Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology 2006;2(7):364‐72. - PubMed
Daousi 2004
-
- Daousi C, MacFarlane IA, Woodward A, Nurmikko TJ, Bundred PE, Benbow SJ. Chronic painful peripheral neuropathy in an urban community: a controlled comparison of people with and without diabetes. Diabetic Medicine 2004;21(9):976‐82. - PubMed
Dworkin 2008
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, Beaton D, Cleeland CS, Farrar JT, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Journal of Pain 2008;9(2):105‐21. - PubMed
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Fava 2004
-
- Fava M, Mallinckrodt CH, Detke MJ, Watkin JG, Wohlreich MM. The effect of duloxetine on painful physical symptoms in depressed patients: do improvements in these symptoms result in higher remission rates?. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2004;65(4):521‐30. - PubMed
Gahimer 2007
-
- Gahimer J, Wernicke J, Yalcin I, Ossanna MJ, Wulster‐Radcliffe M, Viktrup L. A retrospective polled analysis of duloxetine safety in 23,983 subjects. Current Medical Research Opinion 2007;23(1):175‐84. - PubMed
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann. GRADEpro. Version Version 3.2 for Windows. Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann, 2008.
Hall 2006
-
- Hall GC, Carroll D, Parry D, McQuay HJ. Epidemiology and treatment of neuropathic pain: the UK primary care perspective. Pain 2006;122(1‐2):156‐62. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2008:187‐244. [MEDLINE: ]
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kajdasz 2007
-
- Kajdasz DK, Iyengar S, Desaiah D, Backonja MM, Farrar JT, Fishbain DA, et al. Duloxetine for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: evidence‐based findings from post hoc analysis of three multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group studies. Clinical Therapeutics 2007;29(Supplement):2536‐46. - PubMed
Mariappan 2009
Mease 2011
-
- Mease PJ, Spaeth M, Clauw DJ, Arnold LM, Bradley LA, Russell IJ, et al. Estimation of minimum clinically important difference for pain in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care & Research (Hoboken). 2011;63(8):821‐6. - PubMed
Moore 2009
Moore 2012
Nagda 2004
-
- Nagda J, Bajwa ZH. Definitions and Classification of Pain. Principles and practice of pain management. New York: McGraw Hill, 2004:51‐4.
Nose 2007
-
- Nose M, Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Omori I, Churchill R, McGuire H et al for the Meta‐Analysis of New Generation Antidepressants (MANGA) Study Group. Duloxetine versus other anti‐depressive agents for depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005454.pub2] - DOI
O'Connor 2008
-
- O'Connor AB, Noyes K, Holloway RG. A cost‐utility comparison of four first‐line medications in painful diabetic neuropathy. Pharmacoeconomics 2008;26(12):1045‐64. - PubMed
Perahia 2006
-
- Perahia DG, Pritchett YL, Desaiah D, Raskin J. Efficacy of duloxetine in painful symptoms: analgesic or antidepressant effect?. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2006;21(6):311‐7. - PubMed
Saarto 2007
Salaffi 2004
-
- Salaffi F, Stancati A, Silvestri CA, Ciapetti A, Grassi W. Minimal clinically important changes in chronic musculoskeletal pain intensity measured on a numerical rating scale. European Journal of Pain 2004;8(4):283‐91. - PubMed
Schuessler 2006
-
- Scheussler B. What do we know about duloxetine's mode of action? Evidence from animals to humans. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2006;113 Suppl 1:5‐9. - PubMed
Thorlund 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. Trial Sequential Analysis. Version Version 0.9 beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trials Unit, 2011.
Treede 2008
-
- Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, et al. Neuropathic pain: Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008;70(18):1630‐35. - PubMed
Wernicke 2007
-
- Wernicke J, Lledo A, Raskin J, Kajdasz DK, Wang F. An evaluation of the cardiovascular safety profile of duloxetine. Drug Safety 2007;30(5):437‐55. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lunn 2008
-
- Lunn MPT, Hughes RAC, Wiffen PJ. Duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy or chronic pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007115] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

