miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation through myogenin regulation
- PMID: 24385428
- PMCID: PMC3924261
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.507343
miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation through myogenin regulation
Abstract
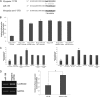
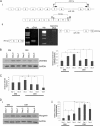
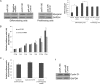
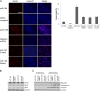
The complex process of skeletal muscle differentiation is organized by the myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), Myf5, MyoD, Myf6, and myogenin, where myogenin plays a critical role in the regulation of the final stage of muscle differentiation. In an effort to investigate the role microRNAs (miRNAs) play in regulating myogenin, a bioinformatics approach was used and six miRNAs (miR-182, miR-186, miR-135, miR-491, miR-329, and miR-96) were predicted to bind the myogenin 3'-untranslated region (UTR). However, luciferase assays showed only miR-186 inhibited translation and 3'-UTR mutagenesis analysis confirmed this interaction was specific. Interestingly, the expression of miR-186 mirrored that of its host gene, ZRANB2, during development. Functional studies demonstrated that miR-186 overexpression inhibited the differentiation of C2C12 and primary muscle cells. Our findings therefore identify miR-186 as a novel regulator of myogenic differentiation.
Keywords: Differentiation; Gene Regulation; MicroRNA; Muscle; Myogenesis; Myogenin.
Figures

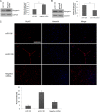
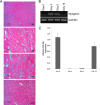
References
-
- Lassar A. B., Skapek S. X., Novitch B. (1994) Regulatory mechanisms that coordinate skeletal muscle differentiation and cell cycle withdrawal. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 6, 788–794 - PubMed
-
- Sabourin L. A., Rudnicki M. A. (2000) The molecular regulation of myogenesis. Clin. Genet. 57, 16–25 - PubMed
-
- Weintraub H. (1993) The MyoD family and myogenesis: redundancy, networks, and thresholds. Cell 75, 1241–1244 - PubMed
-
- Chargé S. B., Rudnicki M. A. (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 84, 209–238 - PubMed
-
- Pownall M. E., Gustafsson M. K., Emerson C. P., Jr. (2002) Myogenic regulatory factors and the specification of muscle progenitors in vertebrate embryos. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 747–783 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

