Encephalitozoon intestinalis: A Rare Cause of Diarrhea in an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) Recipient Complicated by Albendazole-Related Hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 24385787
- PMCID: PMC3878461
- DOI: 10.4274/Tjh.90692
Encephalitozoon intestinalis: A Rare Cause of Diarrhea in an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) Recipient Complicated by Albendazole-Related Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
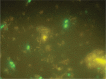
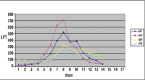
A 50-year-old male patient previously diagnosed with acute myelomonocytic (M4) leukemia in July 2009 underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). During the pre-transplant period complete blood count (CBC), liver and renal function tests, coagulation tests, and other parameters were normal. On the first day of transplantation teicoplanin (400 mg d-1 for the first 3 d, and then 400 mg d-1) and caspofungin (first dose was 1×70 mg d-1, followed by 1×50 mg d-1) were started intravenously due to white plaques and oropharyngeal candidiasis in the patient's mouth and perianal erythema. On the 14th d of transplantation watery diarrhea occurred, along with abdominal discomfort, nausea, and fatigue. Stool examination was negative for findings of bleeding. Investigation of Microsporidia confirmed a rare pathogen Encephalitozoon intestinalis in the patient's stool sample via species-specific immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) assay and albendazole treatment was started at a dose of 2×400 mg d-1. On the 5th d of albendazole treatment (d 18 of treatment) liver function test (LFT) results began to deteriorate. As LFT results continued to deteriorate, albendazole was withdrawn on the 7th d of treatment. Biopsy was performed on the 22nd d of transplantation and histopathological analysis confirmed the diagnosis of toxic hepatitis. LFT results began to decrease after withdrawal of albendazole treatment. On the 13th d of albendazole treatment all LFT values returned to normal. The presented allo-HSCT case had a rare pathogenic agent (E. intestinalis) that caused diarrhea, as well as hepatotoxicity due to albendazole treatment. This is the first reported case of E. intestinalis diagnosed via IFA in Turkey.
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Önceden akut myelomonositik lösemi(M4) tanısı almış 50 yaşındaki erkek hastaya, Temmuz 2009’da allojenik hematopoietik kök hücre nakli yapıldı (AHKHN). Nakil öncesi dönemde, tam kan sayımı, karaciğer ve böbrek fonksiyon testleri, koagulasyon parametreleri ve diğer ölçümler normal bulundu. Naklin birinci gününde,orofaringeal candidiasisle birlikte ağız içindeki beyaz plaklar ve ayrıca perianal eritem nedeniyle hastaya intravenöz teikoplanin (ilk 3 gün 400mg/gün ve sonrasında günde 400mg) ve kaspofungin (ilk doz 1x70 mg/gün ve sonrasında 1x50 mg/gün) başlandı. Naklin 14.gününde,karında huzursuzluk, bulantı ve yorgunluk gibi şikayetlerle birlikte sulu diare ortaya çıktı. gaita incelemesinde kanama bulgusu yoktu. Tür-özgün IFA metodu ile nadir bir patojen olan Encephalitozoon intestinalis tesbiti doğrulandı ve 2x400 mg/gün albendazol tedavisi hemen başlandı. Albendazol tedavisinin 5. gününde (naklin 18. günü), hastanın karaciğer fonksiyon testleri (KCFT) bozulmaya başladı. KCFT’nin bozulması devam ettiğinden, tedavinin 7. gününde albendazol kesildi. Naklin 22. gününde Kc biopsisi yapılarak, tanı patologlar tarafından ‘toxik hepatit’ olarak doğrulandı. KCFT albendazol tedavisinin kesilmesinden sonra hızla düzelmeye başladı. albendazol tedavi sürecinin 13.gününde tüm KCFT değerleri normale döndü. Bu vaka; AHKHN yapılmış bir hastada nadir diare etkeni - Encephalitozoon intestinalis- ile albendazol tedavisi sırasında gelişen hepatotoksisiteyi göstermektedir. Ayrıca, IFA metodu ile Türkiye’den bildirilen ilk E. intestinalis vakasıdır.
Keywords: Albendazole; Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT); Encephalitozoon intestinalis; Hepatotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Yolken RH, Bishop CA, Townsend TR, Bolyard EA, Bartlett J, Santos GW, Saral R. Infectious gastroenteritis in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. New Engl J Med. 1982;306:1010–1012. - PubMed
-
- Bilgrami S, Feingold JM, Dorsky D, Edwards RL, Bona RD, Khan AM, Rodriguez-Pinero F, Clive J, Tutschka PJ. Incidence and outcome of Clostridium difficile infection following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;23:1039–1042. - PubMed
-
- Lanternier F, Boutboul D, Menotti J, Chandesris MO, Sarfati C, Mamzer Bruneel MF, Calmus Y, Mechaï F, Viard JP, Lecuit M, Bougnoux ME, Lortholary O. Microsporidiosis in solid organ transplant recipients: two Enterocytozoon bieneusi cases and review. Transpl Infect Dis. 2009;11:83–88. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials