A genome wide association study identifies common variants associated with lipid levels in the Chinese population
- PMID: 24386095
- PMCID: PMC3875415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082420
A genome wide association study identifies common variants associated with lipid levels in the Chinese population
Abstract
Plasma lipid levels are important risk factors for cardiovascular disease and are influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Recent genome wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several lipid-associated loci, but these loci have been identified primarily in European populations. In order to identify genetic markers for lipid levels in a Chinese population and analyze the heterogeneity between Europeans and Asians, especially Chinese, we performed a meta-analysis of two genome wide association studies on four common lipid traits including total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) in a Han Chinese population totaling 3,451 healthy subjects. Replication was performed in an additional 8,830 subjects of Han Chinese ethnicity. We replicated eight loci associated with lipid levels previously reported in a European population. The loci genome wide significantly associated with TC were near DOCK7, HMGCR and ABO; those genome wide significantly associated with TG were near APOA1/C3/A4/A5 and LPL; those genome wide significantly associated with LDL were near HMGCR, ABO and TOMM40; and those genome wide significantly associated with HDL were near LPL, LIPC and CETP. In addition, an additive genotype score of eight SNPs representing the eight loci that were found to be associated with lipid levels was associated with higher TC, TG and LDL levels (P = 5.52 × 10(-16), 1.38 × 10(-6) and 5.59 × 10(-9), respectively). These findings suggest the cumulative effects of multiple genetic loci on plasma lipid levels. Comparisons with previous GWAS of lipids highlight heterogeneity in allele frequency and in effect size for some loci between Chinese and European populations. The results from our GWAS provided comprehensive and convincing evidence of the genetic determinants of plasma lipid levels in a Chinese population.
Conflict of interest statement
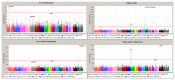
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association studies in Samoans give insight into the genetic architecture of fasting serum lipid levels.J Hum Genet. 2021 Feb;66(2):111-121. doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-0816-9. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 32759990 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study for blood lipid phenotypes in the Framingham Heart Study.BMC Med Genet. 2007 Sep 19;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S17. BMC Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17903299 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic loci associated with plasma concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein A1, and Apolipoprotein B among 6382 white women in genome-wide analysis with replication.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2008 Oct;1(1):21-30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.773168. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2008. PMID: 19802338 Free PMC article.
-
From lipid locus to drug target through human genomics.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Jul 15;114(9):1258-1270. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy120. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29800275 Review.
-
Sortilin as a regulator of lipoprotein metabolism.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012 Jun;14(3):211-8. doi: 10.1007/s11883-012-0248-x. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012. PMID: 22538429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association study of genetic variants at newly identified lipid gene TRIB1 with coronary heart disease in Chinese Han population.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 May 19;14:46. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0043-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 25986010 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-based association study for lipid traits in diverse cohorts implicates BACE1 and SIDT2 regulation in triglyceride levels.PeerJ. 2018 Jan 29;6:e4314. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4314. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29404214 Free PMC article.
-
Association of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms with blood lipids and their interaction with dietary factors.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Apr 30;17(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0744-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29712557 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic association of LIPC variants with lipid and urinary 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine levels in a Taiwanese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 May 10;18(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1057-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31077211 Free PMC article.
-
Genome- and epigenome-wide association study of hypertriglyceridemic waist in Mexican American families.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Jan 20;8:6. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0173-x. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 26798409 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

