Association of STAT4 polymorphism with severe renal insufficiency in lupus nephritis
- PMID: 24386384
- PMCID: PMC3873995
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084450
Association of STAT4 polymorphism with severe renal insufficiency in lupus nephritis
Abstract
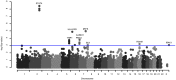
Lupus nephritis is a cause of significant morbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and its genetic background has not been completely clarified. The aim of this investigation was to analyze single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for association with lupus nephritis, its severe form proliferative nephritis and renal outcome, in two Swedish cohorts. Cohort I (n = 567 SLE cases, n = 512 controls) was previously genotyped for 5676 SNPs and cohort II (n = 145 SLE cases, n = 619 controls) was genotyped for SNPs in STAT4, IRF5, TNIP1 and BLK. Case-control and case-only association analyses for patients with lupus nephritis, proliferative nephritis and severe renal insufficiency were performed. In the case-control analysis of cohort I, four highly linked SNPs in STAT4 were associated with lupus nephritis with genome wide significance with p = 3.7 × 10(-9), OR 2.20 for the best SNP rs11889341. Strong signals of association between IRF5 and an HLA-DR3 SNP marker were also detected in the lupus nephritis case versus healthy control analysis (p <0.0001). An additional six genes showed an association with lupus nephritis with p <0.001 (PMS2, TNIP1, CARD11, ITGAM, BLK and IRAK1). In the case-only meta-analysis of the two cohorts, the STAT4 SNP rs7582694 was associated with severe renal insufficiency with p = 1.6 × 10(-3) and OR 2.22. We conclude that genetic variations in STAT4 predispose to lupus nephritis and a worse outcome with severe renal insufficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ortega LM, Schultz DR, Lenz O, Pardo V, Contreras GN (2010) Review: Lupus nephritis: pathologic features, epidemiology and a guide to therapeutic decisions. Lupus 19: 557–574. - PubMed
-
- Churg J, Bernstein J, Glassock RJ (1995) Lupus nephritis. Renal disease: classification and atlas of glomerular diseases. 2 ed. New York: Igaku-Shoin. pp. 151–155.
-
- Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, Taylor KE, Ortmann W, et al. (2008) Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N? Engl? J? Med 358: 900–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

