Total IgA and IgA reactivity to antigen I/II epitopes in HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects
- PMID: 24386612
- PMCID: PMC3875298
- DOI: 10.4236/oji.2013.33012
Total IgA and IgA reactivity to antigen I/II epitopes in HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects
Abstract
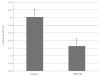
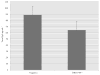
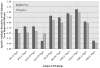
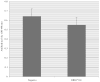
Bacterial adherence to the acquired dental pellicle, important in dental caries (caries), is mediated by receptor-adhesins such as salivary agglutinin binding to Streptococcus mutans antigen I/II (I/II). Ten selected I/II epitopes were chosen to determine their reactivity to human salivary IgA. Previous studies suggested that a specific HLA biomarker group (HLA-DRB1*04) may have differential influence of immune responses to I/II. However, it was not known whether secretory IgA (SIgA) responses to the selected epitopes from HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects were different compared to controls, or across other caries-related factors such as total IgA (TIgA). Thirty-two total subjects were matched according to HLA type, gender, ethnicity and age. HLA genotyping, oral bacterial, immunoglobulin and antibody analyses were performed. A large observed difference emerged with regard to the natural immune reservoir of TIgA in HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects, specifically, a 27.6% reduction compared to controls. In contrast to all other epitopes studied, HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects also exhibited reduced reactivity to I/II epitope 834-853. HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects exhibited lower specific SIgA activity/TIgA to 834-853 and also a lower specific reactivity to 834-853/whole cell S. mutans UA159. Furthermore, HLA-DRB1*04 positive subjects exhibited lower responses to I/II in its entirety. The large observed difference in TIgA and the 834-853 reactivity pattern across multiple measures suggest potentially important connections pertaining to the link between HLA-DRB1*04 and caries.
Keywords: DRB1; DRB1*04; Dental Caries; HLA-II; I/II; IgA; Immunogenetics; Immunomodulation; Streptococcus mutans.
Figures
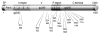

References
-
- Boyton RJ, Smith J, Jones M, Reynolds C, Ozerovitch L, Chaudhry A, et al. Human leucocyte antigen class II association in idiopathic bronchiectasis, a disease of chronic lung infection, implicates a role for adaptive immunity. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 2008;152:95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03596.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
