Immunochip analysis identifies multiple susceptibility loci for systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 24387989
- PMCID: PMC3882906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.12.002
Immunochip analysis identifies multiple susceptibility loci for systemic sclerosis
Abstract
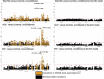
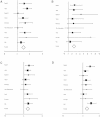
In this study, 1,833 systemic sclerosis (SSc) cases and 3,466 controls were genotyped with the Immunochip array. Classical alleles, amino acid residues, and SNPs across the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region were imputed and tested. These analyses resulted in a model composed of six polymorphic amino acid positions and seven SNPs that explained the observed significant associations in the region. In addition, a replication step comprising 4,017 SSc cases and 5,935 controls was carried out for several selected non-HLA variants, reaching a total of 5,850 cases and 9,401 controls of European ancestry. Following this strategy, we identified and validated three SSc risk loci, including DNASE1L3 at 3p14, the SCHIP1-IL12A locus at 3q25, and ATG5 at 6q21, as well as a suggested association of the TREH-DDX6 locus at 11q23. The associations of several previously reported SSc risk loci were validated and further refined, and the observed peak of association in PXK was related to DNASE1L3. Our study has increased the number of known genetic associations with SSc, provided further insight into the pleiotropic effects of shared autoimmune risk factors, and highlighted the power of dense mapping for detecting previously overlooked susceptibility loci.
Copyright © 2014 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bolster M.B., Silver R.S. Clinical features of systemic sclerosis. In: Hochberg M.C., Silman A.J., Smolen J.S., Weinblatt M.E., Weisman M.H., editors. Fifth Edition. Mosby, Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2011. pp. 1373–1386. (Rheumatology).
-
- LeRoy E.C., Black C., Fleischmajer R., Jablonska S., Krieg T., Medsger T.A., Jr., Rowell N., Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988;15:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Steen V.D. Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;35:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Martín J.E., Bossini-Castillo L., Martín J. Unraveling the genetic component of systemic sclerosis. Hum. Genet. 2012;131:1023–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 3UL1RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50AR054144/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055258/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR054144/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR02251/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051089/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR002251/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI090909/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR060241/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024149/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2RR024149-04/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR060780/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR059763/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 20385/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000371/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

