Genetics of follicular lymphoma transformation
- PMID: 24388756
- PMCID: PMC4100800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.027
Genetics of follicular lymphoma transformation
Abstract
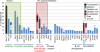
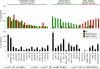
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is an indolent disease, but 30%-40% of cases undergo histologic transformation to an aggressive malignancy, typically represented by diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The pathogenesis of this process remains largely unknown. Using whole-exome sequencing and copy-number analysis, we show here that the dominant clone of FL and transformed FL (tFL) arise by divergent evolution from a common mutated precursor through the acquisition of distinct genetic events. Mutations in epigenetic modifiers and antiapoptotic genes are introduced early in the common precursor, whereas tFL is specifically associated with alterations deregulating cell-cycle progression and DNA damage responses (CDKN2A/B, MYC, and TP53) as well as aberrant somatic hypermutation. The genomic profile of tFL shares similarities with that of germinal center B cell-type de novo DLBCL but also displays unique combinations of altered genes with diagnostic and therapeutic implications.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Akasaka T, Lossos IS, Levy R. BCL6 gene translocation in follicular lymphoma: a harbinger of eventual transformation to diffuse aggressive lymphoma. Blood. 2003;102:1443–1448. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Carlotti E, Wrench D, Matthews J, Iqbal S, Davies A, Norton A, Hart J, Lai R, Montoto S, Gribben JG, et al. Transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma may occur by divergent evolution from a common progenitor cell or by direct evolution from the follicular lymphoma clone. Blood. 2009;113:3553–3557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U54-AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA037295/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172492/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092625/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA171972/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01LM010140-01/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA164152/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010140/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA172492-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA37295/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA136537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

