Role of regulator of G protein signaling proteins in bone
- PMID: 24389209
- PMCID: PMC3966557
- DOI: 10.2741/4232
Role of regulator of G protein signaling proteins in bone
Abstract
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins are a family with more than 30 proteins that all contain an RGS domain. In the past decade, increasing evidence has indicated that RGS proteins play crucial roles in the regulation of G protein coupling receptors (GPCR), G proteins, and calcium signaling during cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation in a variety of tissues. In bone, those proteins modulate bone development and remodeling by influencing various signaling pathways such as GPCR-G protein signaling, Wnt, calcium oscillations and PTH. This review summarizes the recent advances in the understanding of the regulation of RGS gene expression, as well as the functions and mechanisms of RGS proteins, especially in regulating GPCR-G protein signaling, Wnt signaling, calcium oscillations signaling and PTH signaling during bone development and remodeling. This review also highlights the regulation of different RGS proteins in osteoblasts, chondrocytes and osteoclasts. The knowledge from the recent advances of RGS study summarized in the review would provide the insights into new therapies for bone diseases.
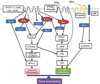
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Regulators of G Protein Signaling Proteins in Bone Physiology and Pathophysiology.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;133:47-75. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26123302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Regulator of G Protein Signaling Proteins on Bone.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 29;13:842421. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.842421. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35573989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and dexamethasone inversely regulate parathyroid hormone-induced regulator of G protein signaling-2 expression in osteoblast-like cells.Endocrinology. 2003 Jun;144(6):2496-504. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0160. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12746312
-
Regulators of G-protein-signaling proteins: negative modulators of G-protein-coupled receptor signaling.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;317:97-183. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26008785 Review.
-
Differential regulation of RGS-2 by constant and oscillating PTH concentrations.Calcif Tissue Int. 2009 Apr;84(4):305-12. doi: 10.1007/s00223-009-9222-1. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009. PMID: 19225708
Cited by
-
The role of GPCRs in bone diseases and dysfunctions.Bone Res. 2019 Jul 8;7:19. doi: 10.1038/s41413-019-0059-6. eCollection 2019. Bone Res. 2019. PMID: 31646011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression regulation and functional analysis of RGS2 and RGS4 in adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Biol Res. 2017 Dec 26;50(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40659-017-0148-1. Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 29279050 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G protein signaling 12 enhances osteoclastogenesis by suppressing Nrf2-dependent antioxidant proteins to promote the generation of reactive oxygen species.Elife. 2019 Sep 6;8:e42951. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42951. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31490121 Free PMC article.
-
Specific RNA m6A modification sites in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from the jawbone marrow of type 2 diabetes patients with dental implant failure.Int J Oral Sci. 2023 Jan 12;15(1):6. doi: 10.1038/s41368-022-00202-3. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 36631441 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Calcium-Induced Calcium Transient Regulating the Proliferation of Osteoblasts through Glycolysis Metabolism Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 5;24(5):4991. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054991. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyce BF, Rosenberg E, de Papp AE, Duong le T. The osteoclast, bone remodelling and treatment of metabolic bone disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2012;42(12):1332–1341. - PubMed
-
- Gensure RC, Gardella TJ, Juppner H. Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide, and their receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3):666–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

