The regulation of MDM2 oncogene and its impact on human cancers
- PMID: 24389645
- PMCID: PMC3932834
- DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gmt147
The regulation of MDM2 oncogene and its impact on human cancers
Abstract
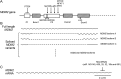
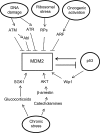
Tumor suppressor p53 plays a central role in preventing tumor formation. The levels and activity of p53 is under tight regulation to ensure its proper function. Murine double minute 2 (MDM2), a p53 target gene, is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. MDM2 is a key negative regulator of p53 protein, and forms an auto-regulatory feedback loop with p53. MDM2 is an oncogene with both p53-dependent and p53-independent oncogenic activities, and often has increased expression levels in a variety of human cancers. MDM2 is highly regulated; the levels and function of MDM2 are regulated at the transcriptional, translational and post-translational levels. This review provides an overview of the regulation of MDM2. Dysregulation of MDM2 impacts significantly upon the p53 functions, and in turn the tumorigenesis. Considering the key role that MDM2 plays in human cancers, a better understanding of the regulation of MDM2 will help us to develop novel and more effective cancer therapeutic strategies to target MDM2 and activate p53 in cells.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; MDM2; gene regulation; p53.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNA-1827 represses MDM2 to positively regulate tumor suppressor p53 and suppress tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):8783-96. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7088. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26840028 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of p53 gene by MDM2 inhibitors: A novel therapy for cancer treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.155. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551517 Review.
-
Regulation of the MDM2-p53 pathway by the ubiquitin ligase HERC2.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jan;14(1):69-86. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12592. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31665549 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2-p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;74(24):7161-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1446. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25477334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mdm2 ligase dead mutants did not act in a dominant negative manner to re-activate p53, but promoted tumor cell growth.Anticancer Res. 2003 Jul-Aug;23(4):3167-74. Anticancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12926050
Cited by
-
Murine Double-Minute 2 Homolog Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms 285 and 309 in Cervical Carcinogenesis.Mol Diagn Ther. 2015 Aug;19(4):235-44. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0153-4. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015. PMID: 26224627 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble peptidoglycan fragments produced by Limosilactobacillus fermentum with antiproliferative activity are suitable for potential therapeutic development: A preliminary report.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 15;10:1082526. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1082526. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36876040 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor p53 and metabolism.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr 1;11(4):284-292. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy070. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30500901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganoderic Acid A and Its Amide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Cancer Agents by Regulating the p53-MDM2 Pathway: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation.Molecules. 2023 Mar 4;28(5):2374. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052374. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903622 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Effects of Apatinib in Combination with Piperine on MDM-2 Gene Expression, Glutathione Peroxidase Activity and Nitric Oxide level as Mechanisms of Cytotoxicity in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 Mar;12(2):404-409. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.040. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35620326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, George DL. Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987;13:235–244. doi:10.1007/BF01535205. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roth J, Dobbelstein M, Freedman DA, Shenk T, Levine AJ. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the hdm2 oncoprotein regulates the levels of the p53 protein via a pathway used by the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. EMBO J. 1998;17:554–564. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.2.554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Lu H. Signaling to p53: ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:369–377. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.09.024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom MS, Jin A, Deisenroth C, White Wolf G, Zhang Y. Cancer-associated mutations in the MDM2 zinc finger domain disrupt ribosomal protein interaction and attenuate MDM2-induced p53 degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:1056–1068. doi:10.1128/MCB.01307-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

