Reduced fibulin-2 contributes to loss of basement membrane integrity and skin blistering in mice lacking integrin α3β1 in the epidermis
- PMID: 24390135
- PMCID: PMC4020984
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2014.10
Reduced fibulin-2 contributes to loss of basement membrane integrity and skin blistering in mice lacking integrin α3β1 in the epidermis
Abstract
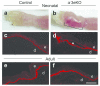
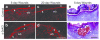
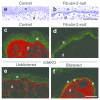
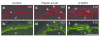
Deficient epidermal adhesion is a hallmark of blistering skin disorders and chronic wounds, implicating integrins as potential therapeutic targets. Integrin α3β1, a major receptor in the epidermis for adhesion to laminin-332 (LN-332), has critical roles in basement membrane (BM) organization during skin development. In the current study we identify a role for α3β1 in promoting stability of nascent epidermal BMs through induction of fibulin-2, a matrix-associated protein that binds LN-332. We demonstrate that mice lacking α3β1 in the epidermis display ruptured BM beneath neo-epidermis of wounds, characterized by extensive blistering. This junctional blistering phenocopies defects reported in newborn α3-null mice, as well as in human patients with α3 gene mutations, indicating that the developmental role of α3β1 in BM organization is recapitulated during wound healing. Mice lacking epidermal α3β1 also have reduced fibulin-2 expression, and fibulin-2-null mice display perinatal skin blisters similar to those in α3β1-deficient mice. Interestingly, α3-null wound epidermis or keratinocytes also show impaired processing of the LN-332 γ2 chain, although this defect was independent of reduced fibulin-2 and did not appear to cause blistering. Our findings indicate a role for integrin α3β1 in BM stability through fibulin-2 induction, both in neonatal skin and in adult wounds.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Opposing Roles of Epidermal Integrins α3β1 and α9β1 in Regulation of mTLD/BMP-1-Mediated Laminin-γ2 Processing during Wound Healing.J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Feb;138(2):444-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Invest Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28923241 Free PMC article.
-
alpha3beta1 Integrin is required for normal development of the epidermal basement membrane.J Cell Biol. 1997 May 5;137(3):729-42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.3.729. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9151677 Free PMC article.
-
alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrin receptors for laminin-5 are not essential for epidermal morphogenesis and homeostasis during skin development.J Cell Sci. 2000 Sep;113 ( Pt 17):3051-62. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.17.3051. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10934043
-
Integrin mutations in blistering skin diseases and related genetically engineered mouse models.Hum Immunol. 2024 Nov;85(6):111175. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2024.111175. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Hum Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39532028 Review.
-
The epidermal integrin-mediated secretome regulates the skin microenvironment during tumorigenesis and repair.Matrix Biol. 2024 Dec;134:175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.11.002. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Matrix Biol. 2024. PMID: 39491760 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin Regulation of Epidermal Functions in Wounds.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014 Mar 1;3(3):229-246. doi: 10.1089/wound.2013.0516. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014. PMID: 24669359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EMILIN proteins are novel extracellular constituents of the dentin-pulp complex.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 18;10(1):15320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72123-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32948785 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-mediated regulation of epidermal wound functions.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Sep;365(3):467-82. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2446-2. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27351421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matricellular Proteins in the Homeostasis, Regeneration, and Aging of Skin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 19;24(18):14274. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814274. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keratinocyte integrin α3β1 induces expression of the macrophage stimulating factor, CSF-1, through a YAP/TEAD-dependent mechanism.Matrix Biol. 2024 Mar;127:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.02.003. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Matrix Biol. 2024. PMID: 38340968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano S, Scott IC, Takahara K, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 1 is an extracellular processing enzyme of the laminin 5 gamma 2 chain. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22728–35. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter WG, et al. A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 2005;24:326–32. - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, El Khal A, Knoss N, et al. Laminin 5 processing and its integration into the ECM. Matrix Biol. 2003;22:49–54. - PubMed
-
- deHart GW, Healy KE, Jones JC. The role of alpha3beta1 integrin in determining the supramolecular organization of laminin-5 in the extracellular matrix of keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2003;283:67–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

