The effect of salsalate therapy on endothelial function in a broad range of subjects
- PMID: 24390146
- PMCID: PMC3959688
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000609
The effect of salsalate therapy on endothelial function in a broad range of subjects
Abstract
Background: Inflammation is fundamental to the development of atherosclerosis. We examined the effect of anti-inflammatory doses of salicylate on endothelium-dependent vasodilation, a biomarker of cardiovascular risk, in a broad range of subjects.
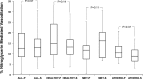
Methods and results: We performed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial evaluating the effects of 4 weeks of high-dose salsalate (disalicylate) therapy on endothelium-dependent flow-mediated and endothelium-independent vasodilation. Fifty-eight subjects, including 17 with metabolic syndrome, 13 with atherosclerosis, and 28 healthy controls, were studied. Among all subjects, endothelium-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation decreased after salsalate compared with placebo therapy (P=0.01), whereas nitroglycerin-mediated, endothelium-independent vasodilation was unchanged (P=0.97). Endothelium-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation after salsalate therapy was impaired compared with placebo therapy in subjects with therapeutic salicylate levels (n=31, P<0.02) but not in subjects with subtherapeutic levels (P>0.2).
Conclusions: Salsalate therapy, particularly when therapeutic salicylate levels are achieved, impairs endothelium-dependent vasodilation in a broad range of subjects. These data raise concern about the possible deleterious effects of anti-inflammatory doses of salsalate on cardiovascular risk.
Clinical trial registration url: www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique Identifiers: NCT00760019 and NCT00762827.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; endothelium; glucose; inflammation; vasodilation.
Figures


References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002; 105:1135-1143 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C‐reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:2195-2207 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM. Testing the inflammatory hypothesis of atherothrombosis: scientific rationale for the Cardiovascular Inflammation Reduction Trial (CIRT). J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7suppl 1:332-339 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Thuren T, Zalewski A, Libby P. Interleukin‐1beta inhibition and the prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events: rationale and design of the Canakinumab Anti‐inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Am Heart J. 2011; 162:597-605 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

