An approach for particle sinking velocity measurements in the 3-400 μm size range and considerations on the effect of temperature on sinking rates
- PMID: 24391276
- PMCID: PMC3873053
- DOI: 10.1007/s00227-012-1945-2
An approach for particle sinking velocity measurements in the 3-400 μm size range and considerations on the effect of temperature on sinking rates
Abstract
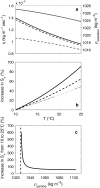
The flux of organic particles below the mixed layer is one major pathway of carbon from the surface into the deep ocean. The magnitude of this export flux depends on two major processes-remineralization rates and sinking velocities. Here, we present an efficient method to measure sinking velocities of particles in the size range from approximately 3-400 μm by means of video microscopy (FlowCAM®). The method allows rapid measurement and automated analysis of mixed samples and was tested with polystyrene beads, different phytoplankton species, and sediment trap material. Sinking velocities of polystyrene beads were close to theoretical values calculated from Stokes' Law. Sinking velocities of the investigated phytoplankton species were in reasonable agreement with published literature values and sinking velocities of material collected in sediment trap increased with particle size. Temperature had a strong effect on sinking velocities due to its influence on seawater viscosity and density. An increase in 9 °C led to a measured increase in sinking velocities of ~40 %. According to this temperature effect, an average temperature increase in 2 °C as projected for the sea surface by the end of this century could increase sinking velocities by about 6 % which might have feedbacks on carbon export into the deep ocean.
Figures



References
-
- Armstrong RA, Lee C, Hedges JI, Honjo S, Wakeham SG. A new, mechanistic model for organic carbon fluxes in the ocean based on the quantitative association of POC with ballast minerals. Deep-Sea Res Pt I. 2002;49:219–236.
-
- Bienfang PK. SETCOL: a technologically simple and reliable method for measuring phytoplankton sinking rates. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 1981;38:1289–1294. doi: 10.1139/f81-173. - DOI
-
- Bienfang PK, Harrison PJ, Quarmby LM. Sinking rate response to depletion of nitrate, phosphate and silicate in four marine diatoms. Mar Biol. 1982;67:295–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00397670. - DOI
-
- Brenner H. Effect of finite boundaries on the Stokes’ resistance of an arbitrary particle. J Fluid Mech. 1962;12:35–48. doi: 10.1017/S0022112062000026. - DOI
-
- Bruland KW, Silver MW. Sinking rates of fecal pellets from gelatinous zooplankton (salps, pteropods, doliolids) Mar Biol. 1981;63:295–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00395999. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
