Pharmacokinetic delivery and metabolizing rate of nicardipine incorporated in hydrophilic and hydrophobic cyclodextrins using two-compartment mathematical model
- PMID: 24391458
- PMCID: PMC3866780
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/131358
Pharmacokinetic delivery and metabolizing rate of nicardipine incorporated in hydrophilic and hydrophobic cyclodextrins using two-compartment mathematical model
Abstract
The dispersion routes of cyclodextrin complexes with nicardipine (NC), such as hydrophilic hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (NC/HPβCD) and hydrophobic triacetyl-β-cyclodextrin (NC/TAβCD), through the body for controlled drug delivery and sustained release have been examined. The two-compartment pharmacokinetic model described the mechanisms of how the human body handles with ingestion of NC-cyclodextrin complexes in gastrointestinal tract (GI), distribution in plasma, and their metabolism in the liver. The model showed that drug bioavailability was significantly improved after oral administration of cyclodextrin complexes. The mathematical significance of this study to predict nicardipine delivery using pharmacokinetic two-compartment mathematical model with linear ordinary differential equations (ODE) approach represents a valuable tool to emphasize its effectiveness and metabolizing rate and diminish the side effects.
Figures

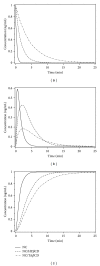


References
-
- Marques Fernandes C, Ramos P, Celta Falcão A, Baptista Veiga FJ. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic cyclodextrins in a new sustained release oral formulation of nicardipine: in vitro evaluation and bioavailability studies in rabbits. Journal of Controlled Release. 2003;88(1):127–134. - PubMed
-
- Watson CA, Vine KL, et al. The antiangiogenic properties of sulfated beta-cyclodextrins in anticancer formulations incorporating 5-fluorouracil. Anticancer Drugs. 2013;24(7):704–714. - PubMed
-
- Koester LS, Ortega GG, Mayorga P, Bassani VL. Mathematical evaluation of in vitro release profiles of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrix tablets containing carbamazepine associated to β-cyclodextrin. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2004;58(1):177–179. - PubMed
-
- McIntosh MP, Rajewski RA. Comparative canine pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of fospropofol disodium injection, propofol emulsion, and cyclodextrin-enabled propofol solution following bolus parenteral administration. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2012;101(9):3547–3552. - PubMed
-
- Langenbucher F. Linearization of dissolution rate curves by the Weibull distribution. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1972;24(12):979–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

