Association between a genetic variant of type-1 cannabinoid receptor and inflammatory neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 24391723
- PMCID: PMC3877004
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082848
Association between a genetic variant of type-1 cannabinoid receptor and inflammatory neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
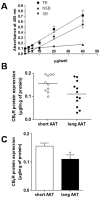
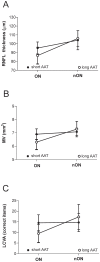
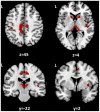
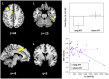
Genetic ablation of type-1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1Rs) exacerbates the neurodegenerative damage of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, the rodent model of multiple sclerosis (MS). To address the role on CB1Rs in the pathophysiology of human MS, we first investigated the impact of AAT trinucleotide short tandem repeat polymorphism of CNR1 gene on CB1R cell expression, and secondly on the inflammatory neurodegeneration process responsible for irreversible disability in MS patients. We found that MS patients with long AAT repeats within the CNR1 gene (≥12 in both alleles) had more pronounced neuronal degeneration in response to inflammatory white matter damage both in the optic nerve and in the cortex. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), in fact, showed more severe alterations of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness and of the macular volume (MV) after an episode of optic neuritis in MS patients carrying the long AAT genotype of CNR1. MS patients with long AAT repeats also had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence of increased gray matter damage in response to inflammatory lesions of the white matter, especially in areas with a major role in cognition. In parallel, visual abilities evaluated at the low contrast acuity test, and cognitive performances were negatively influenced by the long AAT CNR1 genotype in our sample of MS patients. Our results demonstrate the biological relevance of the (AAT)n CNR1 repeats in the inflammatory neurodegenerative damage of MS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Axonal damage in the optic radiation assessed by white matter tract integrity metrics is associated with retinal thinning in multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102293. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102293. Epub 2020 May 26. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32563921 Free PMC article.
-
Asymptomatic optic nerve lesions: An underestimated cause of silent retinal atrophy in MS.Neurology. 2020 Jun 9;94(23):e2468-e2478. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009504. Epub 2020 May 20. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32434868
-
Retinal imaging by laser polarimetry and optical coherence tomography evidence of axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis.Arch Neurol. 2008 Jul;65(7):924-8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.65.7.924. Arch Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18625859
-
Optical Coherence Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 15;17(11):1894. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111894. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27854301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical coherence tomography in optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis: a review.Eur J Neurol. 2007 Aug;14(8):841-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01736.x. Eur J Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17662003 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between interleukin-1β and type-1 cannabinoid receptor is involved in anxiety-like behavior in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Sep 2;13(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0682-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27589957 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Progressive Multiple Sclerosis by Cannabis-Based Cannabinoids.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;10(2):281-92. doi: 10.1007/s11481-014-9575-8. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25537576 Review.
-
CB1 receptor affects cortical plasticity and response to physiotherapy in multiple sclerosis.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2014 Dec 11;1(4):e48. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000048. eCollection 2014 Dec. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2014. PMID: 25520956 Free PMC article.
-
Short Tandem Repeat Variation in the CNR1 Gene Associated With Analgesic Requirements of Opioids in Postoperative Pain Management.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 3;13:815089. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.815089. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35360861 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations of the CNR1 Gene with Personality Traits in Women with Alcohol Use Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5174. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105174. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katona I (2009) Endocannabinoid receptors: CNS localization of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 1: 65–86. - PubMed
-
- Katona I, Freund TF (2008) Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat Med 14: 923–930. - PubMed
-
- Arévalo-Martín A, Molina-Holgado E, Guaza C (2012) A CB1/CB2 receptor agonist, WIN 55,212-2, exerts its therapeutic effect in a viral autoimmune model of multiple sclerosis by restoring self-tolerance to myelin. Neuropharmacology 63: 385–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

