Uncovering and testing the fuzzy clusters based on lumped Markov chain in complex network
- PMID: 24391729
- PMCID: PMC3877001
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082964
Uncovering and testing the fuzzy clusters based on lumped Markov chain in complex network
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94154
Abstract
Identifying clusters, namely groups of nodes with comparatively strong internal connectivity, is a fundamental task for deeply understanding the structure and function of a network. By means of a lumped Markov chain model of a random walker, we propose two novel ways of inferring the lumped markov transition matrix. Furthermore, some useful results are proposed based on the analysis of the properties of the lumped Markov process. To find the best partition of complex networks, a novel framework including two algorithms for network partition based on the optimal lumped Markovian dynamics is derived to solve this problem. The algorithms are constructed to minimize the objective function under this framework. It is demonstrated by the simulation experiments that our algorithms can efficiently determine the probabilities with which a node belongs to different clusters during the learning process and naturally supports the fuzzy partition. Moreover, they are successfully applied to real-world network, including the social interactions between members of a karate club.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
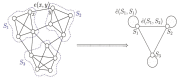
 on a network
on a network  , we define a lumped network
, we define a lumped network  by aggregating all nodes belonging to a subset
by aggregating all nodes belonging to a subset  into a meta-node. The new weights
into a meta-node. The new weights  are computed via weight averaging the transition probabilities between nodes
are computed via weight averaging the transition probabilities between nodes  and
and  –
– , and the lumped Markov chain with transition probabilities
, and the lumped Markov chain with transition probabilities  can also be obtained.
can also be obtained.
 and
and  respectively. In each figure, the lower peak corresponds to the nodes in this cluster, and the higher peak corresponds to the other nodes outside of this cluster.
respectively. In each figure, the lower peak corresponds to the nodes in this cluster, and the higher peak corresponds to the other nodes outside of this cluster.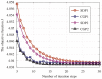

Similar articles
-
Finding and testing network communities by lumped Markov chains.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027028. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22073245 Free PMC article.
-
Analysing grouping of nucleotides in DNA sequences using lumped processes constructed from Markov chains.J Math Biol. 2006 Mar;52(3):343-72. doi: 10.1007/s00285-005-0358-y. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Math Biol. 2006. PMID: 16463190
-
Robust stability of stochastic delayed additive neural networks with Markovian switching.Neural Netw. 2007 Sep;20(7):799-809. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2007.07.003. Epub 2007 Jul 22. Neural Netw. 2007. PMID: 17714914
-
Fuzzy Stochastic Optimal Guaranteed Cost Control of Bio-Economic Singular Markovian Jump Systems.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2015 Nov;45(11):2512-21. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2375957. Epub 2015 Jan 15. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2015. PMID: 25608319
-
Fuzzy Markov random fields versus chains for multispectral image segmentation.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2006 Nov;28(11):1753-67. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.228. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2006. PMID: 17063681
References
-
- Albert R, Barabási AL (2002) Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of modern physics 74: 47.
-
- Newman M, Barabási AL, Watts DJ (2006) The structure and dynamics of networks. Princeton University Press.
-
- Börner K, Sanyal S, Vespignani A (2007) Network science. Annual review of information science and technology 41: 537–607.
-
- Shi J, Malik J (2000) Normalized cuts and image segmentation. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on 22: 888–905.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

