Nesfatin-1 stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in STZ-induced type 2 diabetic mice
- PMID: 24391760
- PMCID: PMC3877039
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083397
Nesfatin-1 stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in STZ-induced type 2 diabetic mice
Abstract
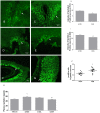
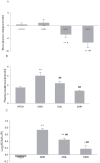
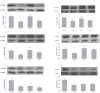
Nesfatin-1 is an anorexigenic peptide involved in energy homeostasis. Recently, nesfatin-1 was reported to decrease blood glucose level and improve insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-fed rats. However, little information is known about the influence of nesfatin-1 on lipid metabolism either in physiological or diabetic condition. This study undertook whether nesfatin-1 was involved in the pathophysiology in Streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice (T2DM), which was induced by a combination of high-calorie diet and two low-doses Streptozotocin. We observed that plasma nesfatin-1 was significantly increased while expression of nesfatin-1 neurons were decreased in hypothalamus in diabetes group compared to only high-calorie diet control group; intravenous injection of nesfatin-1 decreased 0-1h, 0-2h, 0-3h cumulative food intake in T2DM, but 0-24h total food intake had no difference between groups. Body weight and plasma FFA were normalized after nesfatin-1(10 µg/Kg) administration for 6 days. These results suggested that nesfatin-1 improved lipid disorder in T2DM. It was found that blood glucose and insulin resistance coefficient decreased with treatment of nesfatin-1 (both in 1 µg/Kg and 10 µg/Kg doses) in diabetes mice. For further understanding the role of nesfatin-1 on lipid metabolism, we detected p-AMPK and p-ACC of skeletal muscle in T2DM using western blotting. The expression of p-AMPK and p-ACC increased when nesfatin-1 was given with doses 1 µg/Kg but not in doses 10 µg/Kg. Taken together, nesfatin-1 participated in the development of T2DM and stimulated free fatty acid utilization via AMPK-ACC pathway in skeletal muscle in T2DM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Oh I, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi S, et al.. (2006) Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus, Nature. 443, : 709–712. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez R, Perry RL, Gao X, Gaidhu MP, Tsushima RG, et al.. (2011) Nutrient responsive nesfatin-1 regulates energy balance and induces glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rats 1, Endocrinology. 152, 3628–3637. - PubMed
-
- Pan W, Hsuchou H, Kastin AJ (2007) Nesfatin-1 crosses the blood-brain barrier without saturation, Peptides. 28, : 2223–2228. - PubMed
-
- Price TO, Samson WK, Niehoff ML, Banks WA (2007) Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to a novel satiety molecule nesfatin-1, Peptides. 28, : 2372–81. - PubMed
-
- Gantulga D, Maejima Y, Nakata M, Yada T (2012) Glucose and insulin induce Ca2+ signaling in nesfatin-1 neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 420, : 811–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

