An absolute index (Ab-index) to measure a researcher's useful contributions and productivity
- PMID: 24391941
- PMCID: PMC3877305
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084334
An absolute index (Ab-index) to measure a researcher's useful contributions and productivity
Abstract
Bibliographic analysis has been a very powerful tool in evaluating the effective contributions of a researcher and determining his/her future research potential. The lack of an absolute quantification of the author's scientific contributions by the existing measurement system hampers the decision-making process. In this paper, a new metric system, Absolute index (Ab-index), has been proposed that allows a more objective comparison of the contributions of a researcher. The Ab-index takes into account the impact of research findings while keeping in mind the physical and intellectual contributions of the author(s) in accomplishing the task. The Ab-index and h-index were calculated for 10 highly cited geneticists and molecular biologist and 10 young researchers of biological sciences and compared for their relationship to the researchers input as a primary author. This is the first report of a measuring method clarifying the contributions of the first author, corresponding author, and other co-authors and the sharing of credit in a logical ratio. A java application has been developed for the easy calculation of the Ab-index. It can be used as a yardstick for comparing the credibility of different scientists competing for the same resources while the Productivity index (Pr-index), which is the rate of change in the Ab-index per year, can be used for comparing scientists of different age groups. The Ab-index has clear advantage over other popular metric systems in comparing scientific credibility of young scientists. The sum of the Ab-indices earned by individual researchers of an institute per year can be referred to as Pr-index of the institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

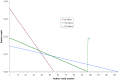
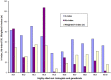


References
-
- Daniel H-D (2005) Publications as a measure of scientific advancement and of scientists’ productivity. Learn Publ 18: 143–148. Available: http://www.ingentaselect.com/rpsv/cgi-bin/cgi?ini=xref&body=linker&reqdo.... Accessed 24 November 2013.
-
- Dance A (2012) Authorship: Who’s on first? Nature 489: 591–593. Available: http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nj7417-591a. Accessed 10 July 2013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martinson B, Anderson M, Crain A, De Vries R (2006) Scientists’ perceptions of organizational justice and self-reported misbehaviors. J Empir Res Hum Res ethics 1: 51–66. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1483900/. Accessed 6 June 2012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bornmann L (2010) Mimicry in science? Scientometrics 86: 173–177. Available: http://www.springerlink.com/index/10.1007/s11192-010-0222-8. Accessed 11 March 2012. - DOI
-
- Qiu J (2010) Publish or perish in China. Nature 463: 142–143 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20075887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

