Dickkopf-1 is oncogenic and involved in invasive growth in non small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 24391982
- PMCID: PMC3877398
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084944
Dickkopf-1 is oncogenic and involved in invasive growth in non small cell lung cancer
Abstract
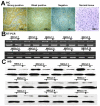
Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) is an inhibitor of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. However, the role of DKK1 in the progression of non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is not fully understood. In this study, RT-PCR and Western blot were used to examine the expression of DKK1 in a panel of ten human NSCLC cell lines and NSCLC tissues. DKK1 expression was highly transactivated in the great majority of these cancer lines. The expression of DKK1 was upregulated on both mRNA and protein levels in NSCLC tissues compared with the adjacent normal lung tissues. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluoresence revealed that DKK1 was mainly distributed in the cytoplasm in both carcinoma tissues and cell lines. DKK1 protein expression was also evaluated in paraffin sections from 102 patients with NSCLC by immunohistochemistry, and 65(63.73%)tumors were DKK1 positive. Relative analysis showed a significant relationship between DKK1 positive expression and lymph node metastasis(P<0.05). Patients with DKK1-positive tumors had poorer DFS than those with negative ESCC (5-year DFS; 15.4% versus 27%, P = 0.007). To further explore the biological effects of DKK1 in NSCLC cells, we over-expressed DKK1 in NSCLC 95C cell using eukaryotic expression vector pCMV-Tab-2b and performed a knockdown of DKK1 in LTEP-a-2 cell using a short hairpin RNA expression vector pSilencer 5.1. DKK1 did not have any effect on proliferation, but seemed to play a role in migration and invasion capability. Overexpression of DKK1 promotes migratory and invasive activity of 95C, while DKK1 knockdown resulted in the suppression of migration and invasion potentials of LTEP-a-2 cell. Taken together, these results indicate that DKK1 may be a crucial regulator in the progression of NSCLC. DKK1 might be a potential therapeutic target in NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dickkopf-1 is involved in invasive growth of esophageal cancer cells.J Mol Histol. 2011 Dec;42(6):491-8. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9347-1. Epub 2011 Sep 10. J Mol Histol. 2011. PMID: 21909757
-
Differential expression of Dickkopf-1 among non-small cell lung cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):1935-40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3654. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25901391
-
DKK1 promotes migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via β-catenin signaling pathway.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jul;39(7):1010428317703820. doi: 10.1177/1010428317703820. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28677426
-
The Dickkopf1-cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 axis creates a novel signalling pathway and may represent a molecular target for cancer therapy.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;174(24):4651-4665. doi: 10.1111/bph.13863. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28514532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of dickkopf-1 in patients with cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May 22;99(21):e20388. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020388. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32481337 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Mar 13;18(1):20230663. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0663. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 36941988 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics consensus portfolio to refine the classification of lung adenocarcinoma with prognostic stratification, tumor microenvironment, and unique sensitivity to first-line therapies.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Nov;11(11):2243-2260. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-775. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36519025 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic Acid Receptor α Knockdown Suppresses the Tumorigenicity of Esophageal Carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin Pathway.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Dec;63(12):3348-3358. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5254-6. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30155836
-
The assessment of Dickkopf-1 and Dickkopf-2 protein concentration in different subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer subtypes.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2024;28(1):9-14. doi: 10.5114/wo.2024.136981. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2024. PMID: 38800531 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Dickkopf-1 in Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jun 8;12:4253-4260. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S254596. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32606922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Subramanian J, Madadi AR, Dandona M, Williams K, Morgensztern D et al. (2010) Review of ongoing clinical trials in non-small cell lung cancer: a status report for 2009 from the ClinicalTrials.gov website. J Thorac Oncol 5: 1116-1119. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e76159. PubMed: 20592626. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

