Knocking-down Meloidogyne incognita proteases by plant-delivered dsRNA has negative pleiotropic effect on nematode vigor
- PMID: 24392004
- PMCID: PMC3877404
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085364
Knocking-down Meloidogyne incognita proteases by plant-delivered dsRNA has negative pleiotropic effect on nematode vigor
Abstract
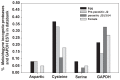
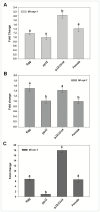
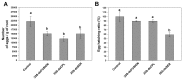
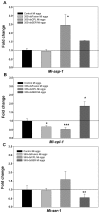
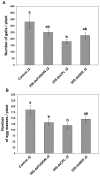
The root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita causes serious damage and yield losses in numerous important crops worldwide. Analysis of the M. incognita genome revealed a vast number of proteases belonging to five different catalytic classes. Several reports indicate that M. incognita proteases could play important roles in nematode parasitism, besides their function in ordinary digestion of giant cell contents for feeding. The precise roles of these proteins during parasitism however are still unknown, making them interesting targets for gene silencing to address protein function. In this study we have knocked-down an aspartic (Mi-asp-1), a serine (Mi-ser-1) and a cysteine protease (Mi-cpl-1) by RNAi interference to get an insight into the function of these enzymes during a host/nematode interaction. Tobacco lines expressing dsRNA for Mi-ser-1 (dsSER), Mi-cpl-1 (dsCPL) and for the three genes together (dsFusion) were generated. Histological analysis of galls did not show clear differences in giant cell morphology. Interestingly, nematodes that infected plants expressing dsRNA for proteases produced a reduced number of eggs. In addition, nematode progeny matured in dsSER plants had reduced success in egg hatching, while progeny resulting from dsCPL and dsFusion plants were less successful to infect wild-type host plants. Quantitative PCR analysis confirmed a reduction in transcripts for Mi-cpl-1 and Mi-ser-1 proteases. Our results indicate that these proteases are possibly involved in different processes throughout nematode development, like nutrition, reproduction and embryogenesis. A better understanding of nematode proteases and their possible role during a plant-nematode interaction might help to develop new tools for phytonematode control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Souza DS, de Souza JDA Jr., Grossi-de-Sá M, Rocha TL, Fragoso RR et al. (2011) Ectopic expression of a Meloidogyne incognita dorsal gland protein in tobacco accelerates the formation of the nematode feeding site. Plant Sci 180: 276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.09.003. PubMed: 21421371. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

