Arsenic trioxide overcomes rapamycin-induced feedback activation of AKT and ERK signaling to enhance the anti-tumor effects in breast cancer
- PMID: 24392034
- PMCID: PMC3877392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085995
Arsenic trioxide overcomes rapamycin-induced feedback activation of AKT and ERK signaling to enhance the anti-tumor effects in breast cancer
Abstract
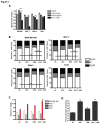
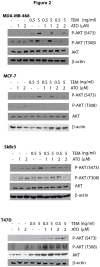
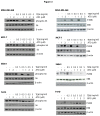
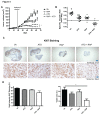
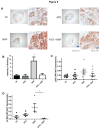
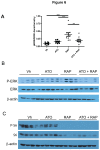
Inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTORi) have clinical activity; however, the benefits of mTOR inhibition by rapamycin and rapamycin-derivatives (rapalogs) may be limited by a feedback mechanism that results in AKT activation. Increased AKT activity resulting from mTOR inhibition can be a result of increased signaling via the mTOR complex, TORC2. Previously, we published that arsenic trioxide (ATO) inhibits AKT activity and in some cases, decreases AKT protein expression. Therefore, we propose that combining ATO and rapamycin may circumvent the AKT feedback loop and increase the anti-tumor effects. Using a panel of breast cancer cell lines, we find that ATO, at clinically-achievable doses, can enhance the inhibitory activity of the mTORi temsirolimus. In all cell lines, temsirolimus treatment resulted in AKT activation, which was decreased by concomitant ATO treatment only in those cell lines where ATO enhanced growth inhibition. Treatment with rapalog also results in activated ERK signaling, which is decreased with ATO co-treatment in all cell lines tested. We next tested the toxicity and efficacy of rapamycin plus ATO combination therapy in a MDA-MB-468 breast cancer xenograft model. The drug combination was well-tolerated, and rapamycin did not increase ATO-induced liver enzyme levels. In addition, combination of these drugs was significantly more effective at inhibiting tumor growth compared to individual drug treatments, which corresponded with diminished phospho-Akt and phospho-ERK levels when compared with rapamycin-treated tumors. Therefore, we propose that combining ATO and mTORi may overcome the feedback loop by decreasing activation of the MAPK and AKT signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased apoptotic efficacy of lonidamine plus arsenic trioxide combination in human leukemia cells. Reactive oxygen species generation and defensive protein kinase (MEK/ERK, Akt/mTOR) modulation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 1;82(11):1619-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.08.017. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21889928
-
Indomethacin-enhanced anticancer effect of arsenic trioxide in A549 cell line: involvement of apoptosis and phospho-ERK and p38 MAPK pathways.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:237543. doi: 10.1155/2013/237543. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24312908 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol enhances the anti-tumor activity of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin in multiple breast cancer cell lines mainly by suppressing rapamycin-induced AKT signaling.Cancer Lett. 2011 Feb 28;301(2):168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.11.012. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21168265
-
Enhancing mTOR-targeted cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 Oct;13(10):1193-203. doi: 10.1517/14728220903225008. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19694499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Advances of Nanomedicines Delivering Arsenic Trioxide for Enhanced Tumor Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 30;14(4):743. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040743. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Targeting of mTOR Activity with Torin2 Potentiates Anticancer Effects of Cisplatin in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Mol Med. 2015 May 26;21(1):466-78. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00238. Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26023849 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct inhibitory effects on mTOR signaling by ethanol and INK128 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Mar 1;13:15. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0091-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25849580 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Potential of Murraya koenigii (Curry Leaves) against Xenobiotics, Heavy Metals, and Hepatotoxic Agents: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025;22(3):e080724231704. doi: 10.2174/0115701638310869240628060001. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025. PMID: 38982918 Review.
-
6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase isoform 3 spatially mediates autophagy through the AMPK signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 8;8(46):80909-80922. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20757. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113354 Free PMC article.
-
Faster visual reaction times in elite athletes are not linked to better gaze stability.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 6;10(1):13216. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69975-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32764576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awada A, Cardoso F, Fontaine C, Dirix L, De Grève J et al. (2008) The oral mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) in combination with letrozole in patients with advanced breast cancer: results of a phase I study with pharmacokinetics. Eur J Cancer 44: 84-91. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.10.003. PubMed: 18039566. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yee KW, Zeng Z, Konopleva M, Verstovsek S, Ravandi F et al. (2006) Phase I/II study of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus (RAD001) in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 12: 5165-5173. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0764. PubMed: 16951235. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

