Sapphire ball lensed fiber probe for common-path optical coherence tomography in ocular imaging and sensing
- PMID: 24392202
- PMCID: PMC3877324
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2005099
Sapphire ball lensed fiber probe for common-path optical coherence tomography in ocular imaging and sensing
Abstract
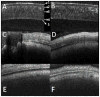
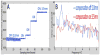
We describe a novel common-path optical coherence tomography (CP-OCT) fiber probe design using a sapphire ball lens for cross-sectional imaging and sensing in retina vitrectomy surgery. Single mode Gaussian beam (TEM00) simulation was used to optimize lateral resolution and working distance (WD) of the common-path probe. A theoretical sensitivity model for CP-OCT was prosed to assess its optimal performance based an unbalanced photodetector configuration. Two probe designs with working distances (WD) 415μm and 1221μm and lateral resolution 11μm and 18μm, respectively were implemented with sensitivity up to 88dB. The designs are also fully compatible with conventional Michelson interferometer based OCT configurations. The reference plane of the probe, located at the distal beam exit interface of the single mode fiber (SMF), was encased within a 25-gauge hypodermic needle by the sapphire ball lens facilitates its applications in bloody and harsh environments. The performances of the fiber probe with 11μm of lateral resolution and 19μm of axial resolution were demonstrated by cross-sectional imaging of a cow cornea and retina in vitro with a 1310nm swept source OCT system. This probe was also attached to a piezoelectric motor for active compensation of physiological tremor for handheld retinal surgical tools.
Keywords: fiber probe; optical coherence tomography; retina imaging.
Figures
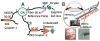

References
-
- Fercher AF, Hitzenberger CK, Kamp G, El-Zaiat SY. Measurement of intraocular distances by backscattering spectral interferometry. Opt Commun. 1995;17:6.
-
- Tearney GJ, Brezinski ME, Bouma BE, Boppart SA, Pitris C, Southern JF, Fujimoto JG. In Vivo Endoscopic Optical Biopsy with Optical Coherence Tomography. Science. 1997;276:3. - PubMed
-
- Yamanari M, Lim Y, Makita S, Yasuno Y. Visualization of phase retardation of deep posterior eye by polarization-sensitive swept-source optical coherence tomography with 1-μm probe. Opt Express. 2009;17:12. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
