Treadmill exercise preconditioning attenuates lung damage caused by systemic endotoxemia in type 1 diabetic rats
- PMID: 24392457
- PMCID: PMC3872431
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/527090
Treadmill exercise preconditioning attenuates lung damage caused by systemic endotoxemia in type 1 diabetic rats
Abstract
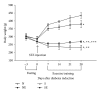
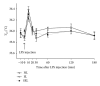
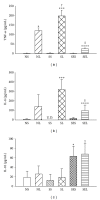
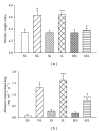
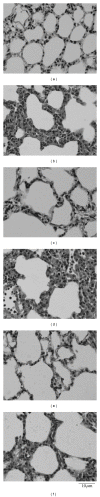
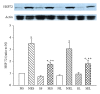
Endotoxemia induces a series of inflammatory responses that may result in lung injury. However, heat shock protein72 (HSP72) has the potential to protect the lungs from damage. The objective of this study was to determine whether prior exercise conditioning could increase the expression of HSP72 in the lungs and attenuate lung damage in diabetic rats receiving lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Streptozotocin was used to induce diabetes in adult male Wistar rats. Rats were randomly assigned to sedentary or exercise groups. Rats in the exercise condition ran on a treadmill 5 days/week, 30-60 min/day, with an intensity of 1.0 mile/hour over a 3-week period. Rats received an intravenous infusion of LPS after 24 hrs from the last training session. Elevated lavage tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF- α ) level in response to LPS was more marked in diabetic rats. HSP72 expression in lungs was significantly increased after exercise conditioning, but less pronounced in diabetic rats. After administration of LPS, exercised rats displayed higher survival rate as well as decreased lavage TNF- α level and lung edema in comparison to sedentary rats. Our findings suggest that exercise conditioning could attenuate the occurrence of inflammatory responses and lung damage, thereby reducing mortality rate in diabetic rats during endotoxemia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exercise pretraining attenuates endotoxin-induced hemodynamic alteration in type I diabetic rats.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2008 Oct;33(5):976-83. doi: 10.1139/H08-081. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2008. PMID: 18923573
-
Physical exercise induces excess hsp72 expression and delays the development of hyperalgesia and allodynia in painful diabetic neuropathy rats.Anesth Analg. 2013 Feb;116(2):482-90. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318274e4a0. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23302966
-
Exercise preconditioning and resveratrol reduce the susceptibility of rats with obstructive jaundice to endotoxin and alleviate lung injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1466615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466615. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39744639 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressed heat shock protein response in the kidney of exercise-trained diabetic rats.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 Jul;28(7):1808-1817. doi: 10.1111/sms.13079. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018. PMID: 29474750 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise pretraining protects against cerebral ischaemia induced by heat stroke in rats.Br J Sports Med. 2007 Sep;41(9):597-602. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.033829. Epub 2007 May 11. Br J Sports Med. 2007. PMID: 17496074 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress and decreased tissue HSP70 are involved in the genesis of sepsis: HSP70 as a therapeutic target.Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020 Oct-Dec;32(4):585-591. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20200084. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020. PMID: 33263705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise promotes motor functional recovery in rats with corticospinal tract injury: anti-apoptosis mechanism.Neural Regen Res. 2015 Apr;10(4):644-50. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.155441. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 26170828 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Models of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: a "Fishing Expedition".JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017 Dec;2(6):770-789. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Dec 25. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017. PMID: 29333506 Free PMC article.
-
Intramuscular Injection of Adenoassociated Virus Encoding Human Neurotrophic Factor 3 and Exercise Intervention Contribute to Reduce Spasms after Spinal Cord Injury.Neural Plast. 2019 Mar 11;2019:3017678. doi: 10.1155/2019/3017678. eCollection 2019. Neural Plast. 2019. PMID: 30984254 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Two Types of Exercise Preconditioning on the Expression of TrkB, TNF-α, and MMP2 Genes in Rats with Stroke.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 12;2021:5595368. doi: 10.1155/2021/5595368. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33954182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hillerdal G, Wibell L. Adult respiratory distress syndrome and diabetes. Acta Medica Scandinavica. 1982;211(3):221–223. - PubMed
-
- Carroll P, Matz R. Adult respiratory distress syndrome complicating severely uncontrolled diabetes mellitus: report of nine cases and a review of the literature. Diabetes Care. 1982;5(6):574–580. - PubMed
-
- Glass EJ, Stewart J, Matthews DM. Impairment of monocyte “lectin-like” receptor activity in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1987;30(4):228–231. - PubMed
-
- De Oliveira Martins J, Meyer-Pflug AR, Alba-Loureiro TC, et al. Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung inflammation: role of insulin. Shock. 2006;25(3):260–266. - PubMed
-
- Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AIM. Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology. 1999;26(3-4):259–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

