Efficacy and safety of artemether + lumefantrine, artesunate + sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine and artesunate + amodiaquine and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine + amodiaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Bangui, Central African Republic: a randomized trial
- PMID: 24393479
- PMCID: PMC3904925
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-9
Efficacy and safety of artemether + lumefantrine, artesunate + sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine and artesunate + amodiaquine and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine + amodiaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Bangui, Central African Republic: a randomized trial
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) has been established. The objective of the present study was to compare the efficacy and safety in the Central African Republic (CAR) of three commercially available artemisinin-based combinations, artemether + lumefantrine (AL), artesunate + sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine (AS-SMP) and artesunate + amodiaquine (AS-AQ), with those of sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine + amodiaquine (SP-AQ), which was the first-line reference treatment in the country from 2004, until it was replaced by ACT in 2006 in accordance with changes in international recommendations based on resistance identified in other regions.
Methods: Children aged six to 59 months with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria were recruited in Bangui, the capital of the CAR. The 251 patients selected were randomly assigned to receive AL (n = 60), AS-SMP (n = 58), AS-AQ (n = 68) or SP-AQ (n = 65) and were followed up for 28 days. Clinical outcome was classified according to the standard 2003 World Health Organization protocol.
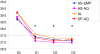
Results: At day 28, the cure rates in a per-protocol analysis were 92% (48/52) with AL, 93% (50/54) with AS-SMP, 93% (55/59) with AS-AQ and 100% (57/57) with SP-AQ, with no statistically significant difference between the four treatments. Defervescence was significantly faster with AS-AQ than with AL (p <0.035). Fatigue was reported significantly more frequently by patients receiving AQ than by those treated with AS-SMP or AL (p = 0.006). All the other adverse events reported were mild, and no significant difference was noted by treatment.
Conclusion: The three artemisinin-bsed combinations show similar, satisfactory results, comparable to that with SP-AQ. This evaluation is the first conducted in CAR since the official introduction of ACT. It should guide the National Malaria Control Programme in choosing the appropriate ACT for treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in the future.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of a fixed dose artesunate-sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine compared to artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria across Africa: a randomized multi-centre trial.Malar J. 2009 Apr 14;8:63. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-63. Malar J. 2009. PMID: 19366448 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of artemisinin-based antimalarial in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in children in southern Tanzania.Malar J. 2007 Nov 11;6:146. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-6-146. Malar J. 2007. PMID: 17996121 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and tolerability of combination antimalarial therapies for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Ugandan children.Malar J. 2008 Jun 11;7:106. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-7-106. Malar J. 2008. PMID: 18547415 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pyronaridine-artesunate for treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 8;1(1):CD006404. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006404.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6:CD006404. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006404.pub4. PMID: 30620055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A systematic review of the safety and efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine against uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria during pregnancy.Malar J. 2012 May 1;11:141. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-141. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 22548983 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of antimalarial treatment and chemoprevention on the drug sensitivity of malaria parasites isolated from ugandan children.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3018-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05141-14. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25753626 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological approaches for analysing data from therapeutic efficacy studies.Malar J. 2021 May 21;20(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03768-1. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 34020656 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic safety of repeated treatment with pyronaridine-artesunate versus artemether-lumefantrine in patients with uncomplicated malaria: a secondary analysis of the WANECAM 1 data from Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso.Malar J. 2021 Jan 29;20(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03593-6. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33514368 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of anti-malarial drugs efficacy in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in African children and adults using network meta-analysis.Malar J. 2017 Aug 3;16(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1963-0. Malar J. 2017. PMID: 28774303 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in northwest Benin.Malar J. 2016 Jan 22;15:37. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1091-2. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 26801767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Sagara I, Rulisa S, Mbacham W, Adam I, Sissoko K, Maiga H, Traore OB, Dara N, Dicko YT, Dicko A, Djimde A, Jansen FH, Doumbo OK. Efficacy and safety of a fixed dose artesunate-sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine compared to artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria across Africa: a randomized multi-centre trial. Malar J. 2009;8:63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gallup JL, Sachs JD. The economic burden of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:85–96. - PubMed
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2005. WHO/HTM/MAL/20051102 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

