N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 24394384
- PMCID: PMC4640932
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2902
N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
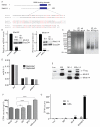
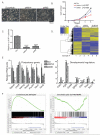
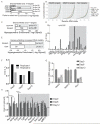
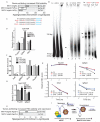
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) has been identified as the most abundant internal modification of messenger RNA in eukaryotes. m(6)A modification is involved in cell fate determination in yeast and embryo development in plants. Its mammalian function remains unknown but thousands of mammalian mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) show m(6)A modification and m(6)A demethylases are required for mammalian energy homeostasis and fertility. We identify two proteins, the putative m(6)A MTase, methyltransferase-like 3 (Mettl3; ref. ), and a related but uncharacterized protein Mettl14, that function synergistically to control m(6)A formation in mammalian cells. Knockdown of Mettl3 and Mettl14 in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) led to similar phenotypes, characterized by lack of m(6)A RNA methylation and lost self-renewal capability. A large number of transcripts, including many encoding developmental regulators, exhibit m(6)A methylation inversely correlated with mRNA stability and gene expression. The human antigen R (HuR) and microRNA pathways were linked to these effects. This gene regulatory mechanism operating in mESCs through m(6)A methylation is required to keep mESCs at their ground state and may be relevant to thousands of mRNAs and lncRNAs in various cell types.
Figures

Comment in
-
RNA decay: stabilizing stemness through m⁶A.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;15(2):76-7. doi: 10.1038/nrm3745. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24452463 No abstract available.
-
Methyltransferases modulate RNA stability in embryonic stem cells.Nat Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;16(2):129-31. doi: 10.1038/ncb2914. Nat Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24481042
References
-
- Dominissini D, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. doi:10.1038/nature11112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

