Identification of an L-phenylalanine binding site enhancing the cooperative responses of the calcium-sensing receptor to calcium
- PMID: 24394414
- PMCID: PMC3931085
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.537357
Identification of an L-phenylalanine binding site enhancing the cooperative responses of the calcium-sensing receptor to calcium
Abstract
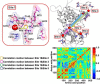
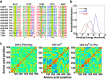
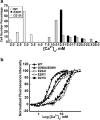
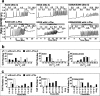
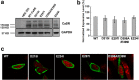
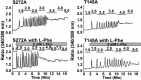
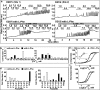
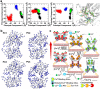
Functional positive cooperative activation of the extracellular calcium ([Ca(2+)]o)-sensing receptor (CaSR), a member of the family C G protein-coupled receptors, by [Ca(2+)]o or amino acids elicits intracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)]i) oscillations. Here, we report the central role of predicted Ca(2+)-binding site 1 within the hinge region of the extracellular domain (ECD) of CaSR and its interaction with other Ca(2+)-binding sites within the ECD in tuning functional positive homotropic cooperativity caused by changes in [Ca(2+)]o. Next, we identify an adjacent L-Phe-binding pocket that is responsible for positive heterotropic cooperativity between [Ca(2+)]o and L-Phe in eliciting CaSR-mediated [Ca(2+)]i oscillations. The heterocommunication between Ca(2+) and an amino acid globally enhances functional positive homotropic cooperative activation of CaSR in response to [Ca(2+)]o signaling by positively impacting multiple [Ca(2+)]o-binding sites within the ECD. Elucidation of the underlying mechanism provides important insights into the longstanding question of how the receptor transduces signals initiated by [Ca(2+)]o and amino acids into intracellular signaling events.
Keywords: Amino Acid; Calcium Imaging; Calcium Oscillation; Calcium Signaling; Calcium-sensing Receptor; Cooperativity; G Protein-coupled Receptors (GPCR).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Ca2+ and L-Phe in regulating functional cooperativity of disease-associated "toggle" calcium-sensing receptor mutations.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 24;9(11):e113622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113622. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25420019 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVIII. Calcium-Sensing Receptor Nomenclature, Pharmacology, and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Jul;72(3):558-604. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018531. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32467152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Ca(2+) oscillations generated via the extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor (CaSR) in response to extracellular Ca(2+) or L-phenylalanine: Impact of the highly conservative mutation Ser170Thr.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 6;467(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.144. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26431875 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Ca(2+)-binding sites in the extracellular domain of the Ca(2+)-sensing receptor corresponding to cooperative Ca(2+) response.Biochemistry. 2009 Jan 20;48(2):388-98. doi: 10.1021/bi8014604. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19102677 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of the Extracellular Ligands Mediated Signaling by the Calcium Sensing Receptor.Front Physiol. 2016 Sep 30;7:441. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00441. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27746744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for regulation of human calcium-sensing receptor by magnesium ions and an unexpected tryptophan derivative co-agonist.Sci Adv. 2016 May 27;2(5):e1600241. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600241. eCollection 2016 May. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 27386547 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ca2+ and L-Phe in regulating functional cooperativity of disease-associated "toggle" calcium-sensing receptor mutations.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 24;9(11):e113622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113622. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25420019 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-induced satiation and the calcium-sensing receptor.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018 Mar 9;11:45-51. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S156597. eCollection 2018. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018. PMID: 29563822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVIII. Calcium-Sensing Receptor Nomenclature, Pharmacology, and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Jul;72(3):558-604. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018531. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32467152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ophthalmate is a new regulator of motor functions via CaSR: implications for movement disorders.Brain. 2024 Oct 3;147(10):3379-3394. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae097. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38537648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown E. M., Gamba G., Riccardi D., Lombardi M., Butters R., Kifor O., Sun A., Hediger M. A., Lytton J., Hebert S. C. (1993) Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 366, 575–580 - PubMed
-
- Chang W., Shoback D. (2004) Extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptors. An overview. Cell Calcium 35, 183–196 - PubMed
-
- Breitwieser G. E. (2006) Calcium sensing receptors and calcium oscillations. Calcium as a first messenger. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 73, 85–114 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

