Kinetics of promoter Pol II on Hsp70 reveal stable pausing and key insights into its regulation
- PMID: 24395245
- PMCID: PMC3894409
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.231886.113
Kinetics of promoter Pol II on Hsp70 reveal stable pausing and key insights into its regulation
Abstract
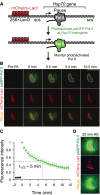
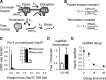
The kinetics with which promoter-proximal paused RNA polymerase II (Pol II) undergoes premature termination versus productive elongation is central to understanding underlying mechanisms of metazoan transcription regulation. To assess the fate of Pol II quantitatively, we tracked photoactivatable GFP-tagged Pol II at uninduced Hsp70 on polytene chromosomes and showed that Pol II is stably paused with a half-life of 5 min. Biochemical analysis of short nascent RNA from Hsp70 reveals that this half-life is determined by two comparable rates of productive elongation and premature termination of paused Pol II. Importantly, heat shock dramatically increases elongating Pol II without decreasing termination, indicating that regulation acts at the step of paused Pol II entry to productive elongation.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; escape to productive elongation; nascent RNA; photoactivation; promoter-proximal pausing; termination.
Figures


References
-
- Anindya R, Aygün O, Svejstrup JQ 2007. Damage-induced ubiquitylation of human RNA polymerase II by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, but not Cockayne syndrome proteins or BRCA1. Mol Cell 28: 386–397 - PubMed
-
- Ardehali MB, Lis JT 2009. Tracking rates of transcription and splicing in vivo. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16: 1123–1124 - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M 1986. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature 321: 702–706 - PubMed
-
- Chao SH, Price DH 2001. Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J Biol Chem 276: 31793–31799 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
