Chlorpromazine versus placebo for schizophrenia
- PMID: 24395698
- PMCID: PMC10640712
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000284.pub3
Chlorpromazine versus placebo for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Chlorpromazine, formulated in the 1950s, remains a benchmark treatment for people with schizophrenia.
Objectives: To review the effects of chlorpromazine compared with placebo, for the treatment of schizophrenia.
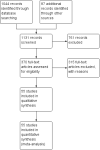
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Trials Register (15 May 2012). We also searched references of all identified studies for further trial citations. We contacted pharmaceutical companies and authors of trials for additional information.
Selection criteria: We included all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing chlorpromazine with placebo for people with schizophrenia and non-affective serious/chronic mental illness irrespective of mode of diagnosis. Primary outcomes of interest were death, violent behaviours, overall improvement, relapse and satisfaction with care.
Data collection and analysis: We independently inspected citations and abstracts, ordered papers, re-inspected and quality assessed these. We analysed dichotomous data using risk ratio (RR) and estimated the 95% confidence interval (CI) around this. We excluded continuous data if more than 50% of participants were lost to follow-up. Where continuous data were included, we analysed this data using mean difference (MD) with a 95% confidence interval. We used a fixed-effect model.
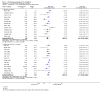
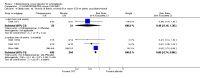
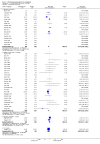
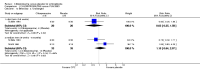
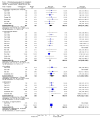
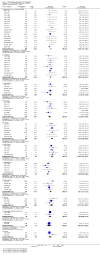
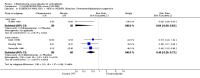
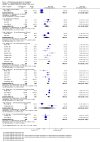
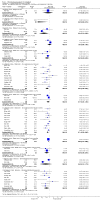
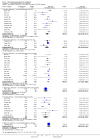
Main results: We inspected over 1100 electronic records. The review currently includes 315 excluded studies and 55 included studies. The quality of the evidence is very low. We found chlorpromazine reduced the number of participants experiencing a relapse compared with placebo during six months to two years follow-up (n = 512, 3 RCTs, RR 0.65 CI 0.47 to 0.90), but data were heterogeneous. No difference was found in relapse rates in the short, medium or long term over two years, although data were also heterogeneous. We found chlorpromazine provided a global improvement in a person's symptoms and functioning (n = 1164, 14 RCTs, RR 0.71 CI 0.58 to 0.86). Fewer people allocated to chlorpromazine left trials early ( n = 1831, 27 RCTs, RR 0.64 CI 0.53 to 0.78) compared with placebo. There are many adverse effects. Chlorpromazine is clearly sedating (n = 1627, 23 RCTs, RR 2.79 CI 2.25 to 3.45), it increases a person's chances of experiencing acute movement disorders (n = 942, 5 RCTs, RR 3.47 CI 1.50 to 8.03) and parkinsonism (n = 1468, 15 RCTs, RR 2.11 CI 1.59 to 2.80). Akathisia did not occur more often in the chlorpromazine group than placebo. Chlorpromazine clearly causes a lowering of blood pressure with accompanying dizziness (n = 1488, 18 RCTs, RR 2.38 CI 1.74 to 3.25) and considerable weight gain (n = 165, 5 RCTs, RR 4.92 CI 2.32 to 10.43).
Authors' conclusions: The results of this review confirm much that clinicians and recipients of care already know but aim to provide quantification to support clinical impression. Chlorpromazine's global position as a 'benchmark' treatment for psychoses is not threatened by the findings of this review. Chlorpromazine, in common use for half a century, is a well-established but imperfect treatment. Judicious use of this best available evidence should lead to improved evidence-based decision making by clinicians, carers and patients.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures



















Update of
-
Chlorpromazine versus placebo for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Apr 18;(2):CD000284. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000284.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 06;(1):CD000284. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000284.pub3. PMID: 17443500 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abrams 1958 {published data only}
-
- Abrams J. Chlorpromazine in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1958;19:20‐8. - PubMed
Baker 1959 {published data only}
-
- Baker JP. A controlled trial of ethylcrotonylurea. British Journal of Psychiatry 1959;105:852‐62. - PubMed
Ban 1975 {published data only}
-
- Ban TA, Lehmann HE, Sterlin C, Climan M. Comprehensive clinical studies with thiothixene. Diseases of the Nervous System 1975;36:473‐7. - PubMed
Bishop 1963 {published data only}
-
- Bishop M, Gallant DM. Behavioral toxicity associated with benzquinamide (Quantril) therapy in schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1963;120:180‐1.
Borison 1991 {published data only}
-
- Borison RL, Diamond BI, Dren AT. Does sigma receptor antagonism predict clinical antipsychotic efficacy?. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1991;27:103‐6. - PubMed
-
- Borison RL, Dren AT, Diamond BI. Sigma receptor antagonism and antipsychotic actions in schizophrenic patients. European Journal of Pharmacology 1990;183:23.
Chouinard 1990 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G. A placebo‐controlled clinical trial of remoxipride and chlorpromazine in newly admitted schizophrenic patients with acute exacerbation. Acta Psychiatria Scandinavica Supplementum 1990;358:111‐9. - PubMed
Clark 1961 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Ray T, Paredes A, Costiloe J, Chappell J, Hagans J, et al. Chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenic women. I. Experimental design and effects at maximum point of treatment. Psychopharmacologia 1961;2:107‐36. - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Ray TS, Ragland RE. Chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenic women: rate of onset and rate of dissipation of drug effects. Psychosomatic Medicine 1963;25:212‐7. - PubMed
-
- Ray TS, Ragland RE, Clark ML. Chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenic women: comparison of differential effects on various psychological modalities during and after treatment. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1964;138:348‐53. - PubMed
Clark 1967 {published data only}
-
- Clark M, Dubowski K, Colmore J. The effect of chlorpromazine on serum cholesterol in chronic schizophrenic patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1970;11:883‐9. - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Ray TS, Paredes A, Ragland RE, Costiloe JP, Smith CW, et al. Chlorpromazine in women with chronic schizophrenia: the effect on cholesterol levels and cholesterol‐behavior relationships. Psychosomatic Medicine 1967;29:634‐42. - PubMed
Clark 1968a {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Kyriakopoulos AA, Ray TS, Colmore JP, Ramsey HR. Evaluation of trifluperidol in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacologia 1968;12:193‐203. - PubMed
Clark 1968b {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Ray TS, Huber WK, Willis D, Ramsey HR. Evaluation of butaperazine in chronic schizophrenia. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1968;97:57‐64. - PubMed
Clark 1970a {published data only}
-
- Clark M, Dubowski K, Colmore J. The effect of chlorpromazine on serum cholesterol in chronic schizophrenic patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1970;11:883‐9. - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Sakata K, Fowles DC, Serafetinides EA. Molindone in chronic schizophrenia. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1970;11:680‐8. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Willis D, Clark ML. The EEG effects of chemically and clinically dissimilar antipsychotics: molindone vs. chlorpromazine. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1971;6:77‐82. - PubMed
Clark 1970b {published data only}
-
- Clark M, Dubowski K, Colmore J. The effect of chlorpromazine on serum cholesterol in chronic schizophrenic patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1970;11:883‐9. - PubMed
-
- Clark M, Ramsey H, Rahhal D, Serafetinides E, Wood F, Costiloe J. Chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. The effect of age and hospitalization on behavioral dose‐response relationships. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;27:479‐83. - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Ramsey HR, Ragland RE, Rahhal DK, Serafetinides EA, Costiloe JP. Chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia ‐ behavioral dose‐response relationships. Psychopharmacologia 1970;18:260‐70. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Willis D, Clark ML. EEG dose‐response relationships of chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia: the effects on the various rhythms and on alpha blocking. Biological Psychiatry 1972;4:251‐6. - PubMed
Clark 1971 {published data only}
-
- Clark. Phenothiazines in schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1969;6(3):37‐40.
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Charalampous KD, Serafetinides EA, Trousdale W, Colmore JP. Drug treatment in newly admitted schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1971;25:404‐9. - PubMed
Clark 1972 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Sullivan J, Wood F, Costiloe JP. Evaluation of loxapine succinate in chronic schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1972;33:783‐91. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Willis D, Clark ML. The EEG effects of dibenzoxazepines (loxapine succinate) as compared to CPZ: EEG changes as drug side effects. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1971;6:38‐44. - PubMed
Clark 1977 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Paredes A, Costiloe JP, Wood F. Evaluation of butaclamol in chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1977;17:529‐36. - PubMed
Cohen 1968 {published data only}
-
- Cohen M, Freedman N, Englehardt DM. Family interaction patterns, drug treatment, and change in social aggression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1968;19(1):50‐6. - PubMed
-
- Graupner OK, Kalman EV. Effects of various drugs on flicker fusion frequency. II. Phenothiazine derivatives (with reference to the dependence of the results on the chronological course of experiments [Die Flimmer‐Verschmelzung‐Frequenz unter dem Einfluss verschiedener Pharmaka. II. Phenothiazinderivate (mit einem Hinweis auf die Abhangigkeit der Ergebnisse vom zeitlichen Verlauf der Versuche)]. Psychopharmacologia 1972;27(4):343‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cole 1964 {published data only}
-
- Cole JO, Goldberg SC, Klerman GL National Institute of Mental Health Psychopharmacology Service Center Collaborative Study Group. Phenothiazine treatment in acute schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1964;10:246‐61. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg S, Klerman G, Cole J. Changes in schizophrenic psychopathology and ward behaviour as a function of phenothiazine treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1965;111:120‐33. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg SC, Mattsson NB. Schizophrenic subtypes defined by response to drugs and placebo. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29:153‐8. - PubMed
Cooper 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Welch CP. Zotepine in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. 10th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress. Vienna, Austria. Vienna, Austria, September 13‐17, 1997.
-
- Cooper SJ, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a comparison versus chlorpromazine and placebo. XXth Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Melbourne, Australia. Melbourne, Australia, 1996.
-
- Cooper SJ, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Butler A, Welch C. A placebo controlled comparison of zotepine versus chlorpromazine in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2000;101(3):218‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cooper SJ, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. A placebo‐controlled comparison of zotepine versus chlorpromazine in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Unpublished manuscript 1996. - PubMed
-
- Cooper SJ, Welch CP. A comparison of zotepine and chlorpromazine on BPRS subscores. 10th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress. Vienna, Austria. Vienna, Austria, September 13‐17, 1997.
Dean 1958 {published data only}
-
- Dean EF, Buker S. Schizophrenia treated with and without chlorpromazine. Rocky Mountain Medical Journal 1958;55:47‐50. - PubMed
Engelhardt 1960 {published data only}
-
- Engelhardt D, Freedman N, Rosen B, Mann D, Margolis R. Phenothiazines in prevention of psychiatric hospitalization. Archives of General Psychiatry 1964;11:162‐9. - PubMed
-
- Engelhardt DM, Freedman N, Glick BS, Hankoff LD, Mann D, Margolis R. Prevention of psychiatric hospitalization with use of psychopharmacological agents. JAMA 1960;173:147‐9. - PubMed
-
- Engelhardt DM, Margolis RA, Rudorfer L, Paley HM. Physician bias and the double‐blind. Archives of General Psychiatry 1969;20(3):315‐20. - PubMed
-
- Engelhardt DM, Rosen B, Freedman N, Mann D, Margolis R. Phenothiazines in prevention of psychiatric hospitalization. II. Duration of treatment exposure. JAMA 1963;186:981‐3. - PubMed
-
- Engelhardt DM, Rosen B, Freedman N, Margolis R. Phenothiazines in prevention of psychiatric hospitalization. IV. Delay or prevention of hospitalization ‐ a reevaluation. Archives of General Psychiatry 1967;16:98‐101. - PubMed
Fink 1963 {published data only}
-
- Belmont I, Pollack M, Willner A, Klein D, Fink M. The effects of imipramine and chlorpromazine on perceptual analytic ability, perceptual analytic responsivity and memory as revealed in rorschach responses. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1963;137(1):42‐50. - PubMed
-
- Fink M, Pollack M, Klein DF, Blumberg AG, Belmont I, Karp E, et al. Comparative studies of chlorpromazine and imipramine. I. Drug discriminating patterns. Neuropsychopharmacology 1963;3:370‐2.
-
- Klein DF. Importance of psychiatric diagnosis in prediction of clinical drug effects. Archives of General Psychiatry 1967;16:118‐26. - PubMed
-
- Klein DF. Psychiatric diagnosis and a typology of clinical drug effects. Psychopharmacologia 1968;13:359‐86. - PubMed
-
- Klein DF, Honigfeld G, Feldman S. Prediction of drug effect by diagnostic decision tree. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29:159‐87. - PubMed
Fleming 1959 {published data only}
-
- Fleming B, Spencer A, Whitelaw E. A controlled comparative investigation of the effects of promazine, chlorpromazine, and a placebo in chronic psychosis. British Journal of Psychiatry 1959;105:349‐58. - PubMed
Grygier 1958 {published data only}
-
- Grygier P, Waters MA. Chlorpromazine used with an intensive occupational therapy program. A.M.A. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1958;79:697‐705. - PubMed
Gwynne 1962 {published data only}
-
- Gwynne P, Hundziak M, Kavtschitsch J, Lefton M, Pasamanick B. Efficacy of trifluoperazine on withdrawal in chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1962;134:451‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hall 1955 {published data only}
-
- Hall RA, Dunlap DJ. A study of chlorpromazine: methodology and results with chronic semi‐disturbed schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1955;122:301‐14. - PubMed
-
- Hollister LE, Hall RA. Phenothiazine derivatives and morphologic changes in the liver. American Journal of Psychiatry 1966;123:211‐2. - PubMed
Hamill 1975 {published data only}
-
- Hamill WT, Fontana AF. The immediate effects of chlorpromazine in newly admitted schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1975;132:1023‐6. - PubMed
Hamilton 1960 {published data only}
-
- Hamilton M, Smith A, Lapidus HR, Cadogan EP. A controlled trial of Thiopropazate Dihydrochloride (Dartalan), Chlorpromazine and occupational therapy in chronic schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1960;106:40‐55. - PubMed
Hankoff 1962 {published data only}
-
- Hankoff LD, Rudorfer L, Paley HM. A reference study of ataraxics. A two‐week double blind outpatient evaluation. Journal of New Drugs 1962;2:173‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hine 1958 {published data only}
-
- Hine FR. Chlorpromazine in schizophrenic withdrawal and in the withdrawn schizophrenic. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1958;127:220‐7. - PubMed
Hogarty 1973 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg S, Schooler N, Hogarty G, Roper M. Prediction of relapse in schizophrenic outpatients treated by drug and sociotherapy. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34:171‐84. - PubMed
-
- Hogarty G, Goldberg S. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. One‐year relapse rates. Archives of General Psychiatry 1973;28:54‐64. - PubMed
-
- Hogarty G, Goldberg S, Schooler N. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. III. Adjustment of non relapsed patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:609‐18. - PubMed
-
- Hogarty G, Goldberg S, Schooler N, Ulrich R. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. II. Two‐year relapse rates. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:603‐8. - PubMed
-
- Hogarty G, Ulrich R. Temporal effects of drug and placebo in delaying relapse in schizophrenic outpatients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34:297‐301. - PubMed
Klein 1973 {published data only}
-
- Klein D, Rosen B. Premorbid asocial adjustment and response to phenothiazine treatment among schizophrenic inpatients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1973;29:480‐5. - PubMed
Kurland 1961 {published data only}
-
- Kurland AA, Hanlon TE, Tatom MH, Ota KY, Simopoulos AL. The comparative effectiveness of six phenothiazine compounds, phenobarbital and inert placebo in the treatment of acutely ill patients: global measures of severity of illness. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1961;133:1‐18. - PubMed
-
- Kurland AA, Hanlon TE, Tatom MH, Simopoulos AL. Comparative studies of the phenothiazine tranquilizers: methodological and logistical considerations. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1961;132:61‐74. - PubMed
-
- Kurland AA, Nilsson GL, Hanlon TE. Pre‐admission drug treatment of state psychiatric hospital patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1959;115:1028‐9. - PubMed
-
- Kurland AA, Sutherland GF. The phenothiazine tranquilizers ‐ their neurological complications and significance. Psychosomatics 1960;1:192‐4.
Letemendia 1967 {published data only}
-
- Letemendia F, Harris AD. Chlorpromazine and the untreated chronic schizophrenic: a long‐term trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 1967;113:950‐8. - PubMed
Nishikawa 1982 {published data only}
-
- Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effect of neuroleptics in symptom‐free schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology 1982;77:301‐4. - PubMed
Payne 1960 {published data only}
-
- Payne P. A comparison of trifluopromazine, chlorpromazine and a placebo in twenty‐one chronic schizophrenic patients. Manitoba Medical Review 1960:196‐8.
Peet 1981 {published data only}
-
- Peet M, Bethell M, Coates A, Khamnee A, Hall P, Cooper S, et al. Propranolol in schizophrenia. I. Comparison of propranolol, chlorpromazine and placebo. British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;139:105‐11. - PubMed
Prien 1968 {published data only}
-
- Crane GE. Tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenic patients treated with psychotropic drugs. Agressologie 1968;2:209‐18. - PubMed
-
- Long SL. Incidence and significance of chlorpromazine‐induced eye changes. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29:19‐22. - PubMed
-
- Gardos G, Cole JO, LaBrie RA. A 12‐year follow‐up study of chronic schizophrenics. Hospital and Community Psychiatry 1982;33:983‐4. - PubMed
-
- Mandel A, Gross M. Agranulocyctosis and phenothiazines. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29:32‐6. - PubMed
-
- Prien R, Cole JO. High dose chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Report of National Institute of Mental Health ‐ psychopharmacology research branch collaborative study group. Archives of General Psychiatry 1968;18:482‐95. - PubMed
Ramu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ramu MG, Chaturvedi DD, Venkataram BS, Shankara MR, Leelavathy S, Janakiramiah N, et al. A double blind controlled study on the role of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in navonmada (acute schizophrenia). Ayurvedic Management of Unmada (Schizophrenia). New Delhi: Central Council for Research in Ayurveda & Siddha, 1999:59‐76.
Ramu 1999a {published data only}
-
- Ramu MG, Chaturvedi DD, Venkataram BS, Shankara MR, Leelavathy S, Janakiramiah N, et al. A DOUBLE BLIND controlled study on the role of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in jirnomada (chronic schizophrenia). Ayurvedic Management of Unmada (Schizophrenia). New Delhi: Central Council for Research in Ayurveda & Siddha, 1999:77‐88.
Rappaport 1978 {published data only}
-
- Rappaport M, Hopkins HK, Hall K, Belleza T, Silverman J. Are there schizophrenics for whom drugs may be unnecessary or contraindicated?. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1978;13:100‐11. - PubMed
Reardon 1966 {published data only}
-
- Reardon JD, Abrams S. Acute paranoid schizophrenia (treatment with chlorpromazine, trifluoperazine and placebo). Diseases of the Nervous System 1966;27:265‐70. - PubMed
Reschke 1974 {published data only}
-
- Reschke RW. Parenteral haloperidol for rapid control of severe, disruptive symptoms of acute schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1974;35:112‐5. - PubMed
Saretsky 1966 {published data only}
-
- Saretsky T. Effects of chlorpromazine on primary‐process thought manifestations. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1966;71:247‐52. - PubMed
Schiele 1961 {published data only}
-
- Schiele BC, Vestre ND, Stein KE. A comparison of thioridazine, chlorpromazine, and placebo: a double‐blind controlled study on the treatment of chronic, hospitalized, schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical and Experiemental Psychopathology 1961;22:151‐62. - PubMed
Serafetinides 1972 {published data only}
-
- Serafetinides EA, Clark ML. Psychological effects of single dose antipsychotic medication. Biological Psychiatry 1973;7:263‐7. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Collins S, Clark ML. Haloperidol, clopenthixol, and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Chemically unrelated antipsychotics as therapeutic alternatives. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1972;154:31‐42. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Willis D. A method of quantifying EEG for psychopharmacological research. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1973;8:245‐7. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Willis D, Clark ML. Haloperidol, clopenthixol, and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. II. The electroencephalographic effects of chemically unrelated antipsychotics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1972;155:366‐9. - PubMed
Shepherd 1956 {published data only}
Simon 1958 {published data only}
-
- Simon W, Wirt AL, Wirt RD, Halloran AV. Long‐term follow‐up study of schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1965;12:510‐5. - PubMed
-
- Simon W, Wirt R, Wirt A, Halloran A, Hinckley R, Lund J, et al. A controlled study of the short‐term differential treatment of schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;114:1077‐86. - PubMed
Smith 1961 {published data only}
-
- Smith ME. A clinical study of chlorpromazine and chlordiazepoxide. Connecticut State Medical Journal 1961;25:153‐7.
Somerville 1960 {published data only}
-
- Somerville DM, Cohen PH, Graves GD. Phenothiazine side‐effects. Comparison of two major tranquillizers. British Journal of Psychiatry 1960;106:1417‐24.
Spohn 1977 {published data only}
-
- Spohn H, Lacoursiere R, Thompson K, Coyne L. Phenothiazine effects on psychological and psychophysiological dysfunction in chronic schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34(6):633‐44. - PubMed
Tetreault 1969 {published data only}
-
- Tetreault L. Comparative study of two drugs and a placebo in chronic schizophrenia [Etude comparative de deux medicaments et d'un placebo chez le schizophrene chronique]. Actualites Pharmacologiques 1969;22:221‐8. - PubMed
-
- Tetreault L, Bordeleau JM, Gauthier R, Vulpe M, Lapointe L. Comparative study of TPS‐23, chlorpromazine and placebo in chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1969;30(2):74‐84. - PubMed
Vaughan 1955 {published data only}
-
- Vaughan GF, Leiberman DM, Cook LC. Chlorpromazine in psychiatry. Lancet 1955;1:1083‐7. - PubMed
Walsh 1959 {published data only}
-
- Walsh GP, Walton D, Black DA. The relative efficacy of "Vespral" and chlorpromazine in the treatment of a group of chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1959;105:199‐209. - PubMed
Weckowicz 1960 {published data only}
-
- Weckowicz TE, Ward T. Clinical trial of RO 5‐0690 and chlorpromazine on disturbed chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1960;21:527‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xiong 1994 {published data only}
-
- Xiong, Hu. A double‐blind comparative study of pheytoin and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenics. Medical Journal of Chinese Civil Administration 1994;6(4):160‐1.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abse 1960 {published data only}
-
- Abse WD, Dahlstrom WG, Tolley AG. Evaluation of tranquilizing drugs in the management of acute mental disturbance. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960;117:973‐80. - PubMed
Acker 1965 {published data only}
-
- Acker CW. An exploration of the autonomic effects of phenothiazines. Psychopharmacologia 1965;7:150‐8. - PubMed
Affleck 1966 {published data only}
-
- Affleck DC, Eaton MT, Mansfield E. The action of a medication and the physician's expectations. Nebraska State Medical Journal 1966;51:331‐4. - PubMed
Agarwal 1985 {published data only}
Akimoto 1966 {published data only}
-
- Akimoto H, Shimazaki T, Shibata N, Sato Y, Takahashi R. Current status of pharmacotherapy in schizophrenia. Folia Psychiatrica et Neurologica Japonica 1966;20(1):1‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Alpert 1966 {published data only}
-
- Alpert M, Hekimian LJ, Frosch WA. Evaluation of treatment with recorded interviews. American Journal of Psychiatry 1966;122:1258‐64. - PubMed
Alpert 1978 {published data only}
-
- Alpert M, Friedhoff A, Marcos L, Diamond F. Paradoxical reaction to L‐dopa in schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1978;135:1329‐32. - PubMed
Alson 1964 {published data only}
-
- Alson E, Hastings K. The use of adjective check lists with psychotic patients: the problem of pseudo‐responses. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1964;20(4):462‐3. - PubMed
Aman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Aman MG, Singh NN. Dyskinetic symptoms in profoundly retarded residents following neuroleptic withdrawal and during methylphenidate treatment. Journal of Mental Deficiency Research 1985;29(2):187‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Amin 1977 {published data only}
-
- Amin MM, Ban TA, Lehmann HE. A standard‐controlled clinical study with benzquinamide in the treatment of chronic schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13:20‐1. - PubMed
Ananth 1972 {published data only}
-
- Ananth JV, Vacaflor L, Kekhwa G, Sterlin C, Ban TA. Nicotinic acid in the treatment of newly admitted schizophrenic patients: a placebo‐controlled study. Internationale Zeitschrift Fur Klinische Pharmakologie Therapie und Toxikologie 1972;5(4):406‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Andrews 1976 {published data only}
-
- Andrews P, Hall JN, Snaith RP. A controlled trial of phenothiazine withdrawal in chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;128:451‐5. - PubMed
Ashcroft 1961 {published data only}
-
- Ashcroft GW, MacDougall EJ, Barker PA. A comparison of tetrabenazine and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Mental Science (British Journal of Psychiatry from 1963) 1961;107:287‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ayers 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ayers T, Liberman RP, Wallace CJ. Subjective response to antipsychotic drugs: failure to replicate predictions of outcome. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1984;4:89‐93. - PubMed
Azima 1954 {published data only}
Bagadia 1981 {published data only}
Ban 1977 {published data only}
Beech 1990 {published data only}
-
- Beech A, Powell TJ, McWilliam J, Claridge GS. The effect of a small dose of chlorpromazine on a measure of 'cognitive inhibition'. Personality and Individual Differences 1990;11:1141‐5.
Benaim 1960 {published data only}
-
- Benaim S. The effect of chlorpromazine on the incidence of epileptic phenomena during insulin coma therapy: A statistical investigation. Journal of Mental Science 1960;106:317‐21. - PubMed
Bennett 1956 {published data only}
-
- Bennett A, Ford F, Turk RE. Clinical investigation of chlorpromazine and reserpine in private psychiatric practice. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;112:782‐7. - PubMed
Blumberg 1964 {published data only}
-
- Blumberg AG, Klein DF, Pollack M. Effects of chlorpromazine and imipramine on systolic blood pressure in psychiatric patients: Relationships to age, diagnosis and initial blood pressure. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1964;2(1):51‐60. - PubMed
Blumberg 1969 {published data only}
-
- Blumberg AG, Klein DF. Chlorpromazine‐procyclidine and imipramine: effects on thyroid function in psychiatric patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1969;10:350‐4. - PubMed
Boullin 1975 {published data only}
Bowes 1956 {published data only}
-
- Bowes, HA. The ataractic drugs: the present position of chlorpromazine, frenquel, pacatal, and reserpine in the psychiatric hospital. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;113:530‐9. - PubMed
Bressler 1971 {published data only}
-
- Bressler B, Friedel RO. A comparison between chlorpromazine and thiothixene in a Veterans Administration Hospital population. Psychosomatics 1971;12:275‐7. - PubMed
Brizer 1985 {published data only}
-
- Brizer DA, Hartman N, Sweeney J, Millman RB. Effect of methadone plus neuroleptics on treatment‐resistant chronic paranoid schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1985;142(9):1106‐7. - PubMed
Burnett 1975 {published data only}
-
- Burnett GB, Little SR, Graham N, Forrest AD. The assessment of thiothixene in chronic schizophrenia. A double‐blind controlled trial. Diseases of the Nervous System 1975;36:625‐9. - PubMed
Cabrera Gomez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Cabrera Gomez JA, Cordero Gutierrez JR, Fernandez Lopez O, Reyes Gutierrez B, Romero Garcia K, Simon Consuegra J, et al. Treatment of schizophrenic disorder, paranoid type, with intramuscular recombinant alpha‐2b interferon. Biotherapy 1994;7(1):27‐37. - PubMed
Caffey 1963 {published data only}
-
- Caffey E, Forrest I, Frank T, Klett CJ. Phenothiazine excretion in chronic schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 1963;120:578‐82. - PubMed
-
- Caffey EM, Diamond LS, Frank TV, Grasberger JC, Herman L, Klett CJ, et al. Discontinuation or reduction of chemotherapy in chronic schizophrenics. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1964;17(4):347‐58. - PubMed
Caffey 1975 {published data only}
-
- Caffey EMJ, Prien RF. Practical considerations on treatment with antipsychotic preparations [Prakticheskie soobrazheniia o lechenii antipsikhoticheskimi preparatami]. Zhurnal Nevropatologii i Psikhiatrii 1975;75:1399‐401. - PubMed
Campbell 1972 {published data only}
-
- Campbell M, Fish B, Shapiro T, Floyd A. Acute responses of schizophrenic children to a sedative and a 'stimulating' neuroleptic: a pharmacologic yardstick. Current Therapeutic Research 1972;14:759‐66. - PubMed
-
- Campbell M, Fish B, Shapiro T, Floyd A. Thiothixene in young disturbed children. A pilot study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1970;23:70‐2. - PubMed
Cardone 1969 {published data only}
-
- Cardone S, Olson R. Chlorpromazine and body image. Effects on chronic schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry 1969;20:576‐82. - PubMed
Carrillo 1971 {published data only}
-
- Carrillo C. Pharmacologlal treatment of the emotionally unstable character disorder. Vth World Congress of Psychiatry. Ciudad de Mexico. 1971.
Casey 1960 {published data only}
-
- Casey JF, Bennet IF, Lindley CJ, Hollister LE, Gordon MH, Springer NN. Drug therapy in schizophrenia. A controlled study of the relative effectiveness of chlorpromazine, promazine, phenobarbital, and placebo. Archives of General Psychiatry 1960;2:210‐20. - PubMed
Casey 1961 {published data only}
-
- Casey JF, Hollister LE, Klett CJ, Lasky JJ, Caffey EM. Combined drug therapy of chronic schizophrenics. Controlled evaluation of placebo, dextro‐amphetamine, imipramine, isocarboxazid and trifluoperazine added to maintenance doses of chlorpromazine. American Journal of Psychiatry 1961;117:997‐1003. - PubMed
Chacon 1972 {published data only}
-
- Chacon C, Harper P. Clinical and work performance variables in phenothiazine therapy of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1973;49:65‐76. - PubMed
-
- Chacon Carlos, Harper P, Harvey GF. Work study in the assessment of the effects of phenothiazines in schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1972;13(6):549‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Childers 1961 {published data only}
-
- Childers RT, Therrien R. A comparison of the effectiveness of triluoperazine and chlorpromazine in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1961;118:552‐4. - PubMed
Chouinard 1977 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G, Annable L, Kolivakis TN. Penfluridol in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenic patients newly discharged from a brief therapy unit. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1977;17(2‐3):162‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chouinard‐G 1983 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard‐G, Annable‐L. Fluspirilene in the treatment of newly admitted schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin. 1983;19(1):136‐8. - PubMed
Claghorn 1983 {published data only}
-
- Claghorn J, Abuzzahab F, Wang R, Larson C, Gelenberg A, Klerman G, et al. The current status of clozapine. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1983;19:138‐40.
Clark 1970c {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Serafetinides EA, Wise JB, Colmore JP. Ocular pigment deposits: drug‐induced false‐positives. JAMA 1970;214:2339. - PubMed
Clark 1970d {published data only}
-
- Clark M, Dubowski K, Colmore J. The effect of chlorpromazine on serum cholesterol in chronic schizophrenic patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1970;11:883‐9. - PubMed
Clark 1975 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Kaul PN. A preliminary report on clinical response and blood levels of chlorpromazine and its sulfoxide during chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenic patients. In: Gottschalk LA, Merlis S editor(s). Pharmacokinetics of Psychoactive Drugs. New York: Spectrum Publications, 1976:191‐7.
-
- Clark ML, Kaul PN. A preliminary report on clinical response and blood levels of chlorpromazine and its sulfoxide during chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1975;11:28‐30. - PubMed
-
- Clark ML, Kaul PN, Whitfield LR. Chlorpromazine kinetics and clinical response. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1978;14:43‐5. - PubMed
Cobb 1956 {published data only}
-
- Cobb W. Changes in the electroencephalogram, the electrodermogram, and the electromyogram provoked by chlorpromazine in man. Abstracts of World Medicine 1956;20:177.
Cole 1967 {published data only}
-
- Cole JO, Schooler NR. Differences in clinical effects of three phenothiazines in "acute" schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1967;28:369‐83. - PubMed
Coons 1962 {published data only}
-
- Coons WH, Boyd BA, White JG. Chlorpromazine, trifluoperazine and placebo with long term mental hospital patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1962;7:159‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cowden 1956 {published data only}
-
- Cowden RC, Zax M, Hague JR, Finney RC. Chlorpromazine: alone and as an adjunct to group psychotherapy in the treatment of psychiatric patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;4:898‐902. - PubMed
Crane 1970 {published data only}
-
- Crane GE. High doses of trifluperazine and tardive dyskinesia. Archives of Neurology 1970;22(2):176‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Crane 1971 {published data only}
-
- Crane GE. Persistence of neurological symptoms due to neuroleptic drugs. American Journal of Psychiatry 1971;127:1407‐10. - PubMed
Crow 1986 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. The Northwick Park study of first episodes of schizophrenia. II. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:120‐7. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Johnson AL, MacMillan JF. The Northwick Park study of first episodes of schizophrenia. I. Presentation of the illness and problems relating to admission. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:115‐20. - PubMed
-
- MacMillan JF, Crow TJ, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. The Northwick Park study of first episodes of schizophrenia. III. Short‐term outcome in trial entrants and trial eligible patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:128‐33. - PubMed
Curry 1972 {published data only}
-
- Curry SH, Adamson L. Double‐blind trial of fluphenazine decanoate. Lancet 1972;2:543‐4. - PubMed
Cutler 1957 {published data only}
-
- Cutler RP, Monroe JJ, Anderson TE. Effects of "tranquilizers" upon pathological activity in psychotic patients: II. Reserpine. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1957;78:61‐8. - PubMed
Dally 1966 {published data only}
Danion 1992 {published data only}
-
- Danion JM, Peretti S, Grange D, Bilik M, Imbs JL, Singer L. Effects of chlorpromazine and lorazepam on explicit memory, repetition priming and cognitive skill learning in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 1992;108(3):345‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Daston 1958 {published data only}
-
- Daston PG. Stylus maze performance of chronic schizophrenics taking chlorpromazine. Journal of Consulting Psychology 1958;22(5):384. - PubMed
Daston 1959 {published data only}
-
- Daston PG. Effects of two phenothiazine drugs on concentrative attention span of chronic schizophrenics. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1959;15:106‐9. - PubMed
Davies 1973 {published data only}
-
- Davies AL, O'Leary J. The use of chlorpromazine in schizophrenia. Nursing Times 1973;69:1694‐5. - PubMed
Dean 1967 {published data only}
-
- Dean G. Mefenamic acid and chlorpromazine in porphyria variegata. South African Medical Journal 1967;41:925‐7. - PubMed
Denber 1955 {published data only}
-
- Denber HCB, Merlis S. Studies on Mescaline. VI. Therapeutic Aspects of the Mescaline‐Chlorpromazine Combination. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1955;122:463. - PubMed
Denber 1956 {published data only}
-
- Denber H, Bird EG. Chlorpromazine in the treatment of mental illness. III. The problem of depression. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;112:1021. - PubMed
Denber 1957 {published data only}
-
- Denber HCB. Chlorpromazine‐diethazine in the treatment of depression. Diseases of the Nervous System 1957;18:76‐9. - PubMed
Den Boer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Boer JA, Vahlne JO, Post P, Heck AH, Daubenton F, Olbrich R. Ritanserin as add on medication to neuroleptic therapy for patients with chronic or subchronic schizophrenia. Human Psychopharmacology 2000;15(3):179‐89. - PubMed
Desager 1988 {published data only}
-
- Desager JP, Hulhoven R, Harvengt C, Hermann P, Guillet P, Thiercelin JF. Possible interactions between zolpidem, a new sleep inducer and chlorpromazine, a phenothiazine neuroleptic. Psychopharmacology Berlin 1988;96:63‐6. - PubMed
Douglas 1969 {published data only}
-
- Douglas KW, Hindley JP. A comparison of mesoridazine and chlorpromazine in chronic psychiatric patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and The Journal of New Drugs 1969;9:176‐82. - PubMed
Downing 1963 {published data only}
-
- Downing RW, Ebert JN, Shubrooks SJ. Effect of phenothiazines on the thinking of acute schizophrenics. Perceptual and Motor Skills 1963;17(2):511‐20. - PubMed
Dube 1981 {published data only}
Eitan 1991 {published data only}
-
- Eitan N, Levin Y, Ben‐Artzi E, Levy A, Neumann M. Effects of antipsychotic drugs on memory functions of schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1992;85:74‐6. - PubMed
Ekdawi 1966 {published data only}
-
- Ekdawi MY, Fowke R. A controlled trial of anti‐parkinson drugs in drug‐induced parkinsonism. British Journal of Psychiatry 1966;112(487):633‐6. - PubMed
Elkes 1954 {published data only}
Feldman 1956 {published data only}
-
- Feldman PE, Lacy BS, Walker AE, Garrez NJ. A controlled, blind study of effects of thorazine on psychotic behavior. Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic 1956;20:25‐47. - PubMed
Fink 1958 {published data only}
-
- Fink M, Shaw R, Gross GE, Coleman FS. Comparative study of chlorpromazine and insulin coma in therapy of psychosis. Journal of the American Medical Association 1958;166(15):1846‐50. - PubMed
Fink 1965 {published data only}
-
- Fink M, Klein DF, Kramer JC. Clinical efficacy of chlorpromazine‐procyclidine combination, imipramine and placebo in depressive disorders. Psychopharmacologia 1965;7:27‐36. - PubMed
Fleischhacker 1995 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker W. Broadening treatment perspectives of schizophrenia: a clinical update on seroquel. 8th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 1995 Sep 30 ‐ Oct 4; Venice, Italy. 1995.
Fleming 1958 {published data only}
-
- Fleming B, Currie J. Investigation of a new compound, B.W.203, and of Chlorpromazine in the treatment of psychosis. British Journal of Psychiatry 1958;104:749‐57. - PubMed
Foote 1958 {published data only}
-
- Foote E. Combined Chlorpromazine and Reserpine in the treatment of chronic psychotics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1958;104:201‐5. - PubMed
Forrest 1967 {published data only}
-
- Forrest GL, Bortner TW, Bakker CB. The role of personality variables in response to chlorpromazine, dextroamphetamine and placebo. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1967;5:281‐8. - PubMed
Freed 1956 {published data only}
-
- Freed H, Peifer CA. Treatment of hyperkinetic emotionally disturbed children with prolonged administration of chlorpromazine. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;113:22. - PubMed
Freedman 1965 {published data only}
-
- Freedman N, Engelhardt D, Mann D, Margolis R, London S. Communication of body complaints and paranoid symptom change under conditions of phenothiazine treatment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1965;1(4):310‐8. - PubMed
Freeman 1956 {published data only}
-
- Freeman H, Arnold AL, Cline HS. Effects of chlorpromazine and reserpine in chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1956;17:213‐9. - PubMed
-
- Freeman H, Cline HS. Effects of chlorpromazine on chronic lobotomized schizophrenic patients. A.M.A. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1956;76:500‐7. - PubMed
Freeman 1973 {published data only}
-
- Freeman H. A double blind comparison of mesoridazine and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenics. Diseases of the Nervous System 1973;34(6):289‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Friedhoff 1960 {published data only}
-
- Friedhoff A, Alpert M. The effect of chlorpromazine on the variability of motor task performance in schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1960;131:110‐6. - PubMed
Fromm 1956 {published data only}
-
- Fromm GH, Forsberg IA. Controlled study on the value of chlorpromazine in allaying anxiety. Diseases of the Nervous System 1956;17:16‐9. - PubMed
Gaitz 1955 {published data only}
-
- Gaitz CM, Roy H, Thompson W, Kimbell I, Mullen AJ, Pokorny AD. Evaluation of Chlorpromazine in Comparison with other Methods of treatments of hospitalized psychiatric patients, using the lorr multidimensional scale for rating psychiatric patients. Psychiatric Research Reports 1955;1:1984.
Galbrecht 1968 {published data only}
-
- Galbrecht CR, Klett CJ. Predicting response to phenothiazines: the right drug for the right patient. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1968;147:173‐83. - PubMed
Galdi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Galdi J, Bonato RR. Relationship of adverse drug reactions to length of hospital‐stay in genetically subgrouped schizophrenics. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1988;33:816‐8. - PubMed
Gallant 1963 {published data only}
-
- Gallant D, Bishop M, Steele C, Noblin CD. The relationship between serotonin antagonism and tranquilizing activity. American Journal of Psychiatry 1963;119:882. - PubMed
Gallant 1967 {published data only}
-
- Gallant DM, Bishop MP, O'Meallie L. BL‐KR140: a controlled evaluation in chronic schizophrenic patients previously stabilized on chlorpromazine. Current Therapeutic Research 1967;9:447‐50. - PubMed
Gardner 1955 {published data only}
-
- Gardner MJ, Hawkins HM, Judah LN, Murphree OD. Objective measurement of psychiatric changes produced by chlorpromazine and reserpine in chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatric Research Reports 1955;1:77‐83.
Gardos 1968 {published data only}
-
- Gardos G, Rapkin RM, DiMascio A. Trifluoperazine and chlorpromazine in combination and individually. Current Therapeutic Research Clinical and Experimental 1968;10(12):609‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gardos 1976 {published data only}
-
- Gardos G, Cole J O. Maintenance antipsychotic therapy: is the cure worse than the disease?. American Journal of Psychiatry 1976;133:32‐6. - PubMed
Garfield 1962 {published data only}
-
- Garfield SL, Helper MM, Wilcott RC, Muffly R. Effects of chlorpromazine on behaviour in emotionally disturbed children. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1962;135:147‐54. - PubMed
Garmezy 1969 {published data only}
-
- Garmezy N. Effects of censure and chlorpromazine on visual discrimination behavior of schizophrenic and alcoholic patients. Proceedings of the Annual Convention of the American Psychological Association 1969;4(2):491‐2.
Gauthier 1967 {published data only}
-
- Gauthier R, Hillel J, Bordeleau JM, Tetreault L. Comparative study of trifluperidol and trifluoperazine in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Union Medicale du Canada 1967;96:936‐43. - PubMed
Gendron 1973 {published data only}
-
- Gendron JL, Zimmermann RL, Schiele BC. A double blind comparison of AL 1021 and chlorpromazine in hospitalized schizophrenics. Current Therapeutic Research 1973;15(6):333‐6. - PubMed
Gibbs 1956 {published data only}
-
- Gibbs JJ, Wilkens B, Lauterbach CG. A controlled clinical psychiatric study of chlorpromazine. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Psychopathology 1957;18:269‐83. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs JJ, Wilkens B, Lauterbach CG. A controlled clinical psychiatric study of the drug chlorpromazine. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;113:254‐5. - PubMed
Gilgash 1957 {published data only}
-
- Gilgash CA. Effects of Thorazine on Wechsler scores of adult catatonic schizophrenics. Psychological Reports 1957;3:561‐4.
Goldberg 1968 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg SC, Mattsson NB. Schizophrenic subtypes defined by response to drugs and placebo. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29(5):S153‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goldberg 1970 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg GJ, Brooke G, Townsend HR, Brahma RK, Hill GB. A comparison of oxypertine and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1970;46(2):126‐35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goldberg 1972 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg S, Frosch W, Drossman A, Schooler N, Johnson G. Prediction of response to phenothiazines in schizophrenia. A crossvalidation study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;26:367‐73. - PubMed
Goldman 1955 {published data only}
-
- Goldman D. Treatment of psychotic states with chlorpromazine. Journal of the American Medical Association 1955;157:1274‐8. - PubMed
Good 1958 {published data only}
-
- Good WW, Sterling M, Holtzman WH. Termination of chlorpromazine with schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:443‐8. - PubMed
-
- Mefferd RB, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1958;127:167‐79. - PubMed
Goodwin‐Austin 1971 {published data only}
Goyne 1958 {published data only}
-
- Goyne J B, Groebner E, Pueblita M. Clinical Research ‐ Vesperin‐Chlorpromazine Therapy. Scientific Papers of the 114th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. 1958:104‐5.
Graupner 1972 {published data only}
-
- Graupner OK, Kalman EV. Effects of various drugs on flicker fusion frequency. II. Phenothiazine derivatives (with reference to the dependence of the results on the chronological course of experiments [Die Flimmer‐Verschmelzung‐Frequenz unter dem Einfluss verschiedener Pharmaka. II. Phenothiazinderivate (mit einem Hinweis auf die Abhangigkeit der Ergebnisse vom zeitlichen Verlauf der Versuche)]. Psychopharmacologia 1972;27(4):343‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Green 1996 {published data only}
-
- Green JF, McElholm A, King DJ. A comparison of the sedative and amnestic effects of chlorpromazine and lorazepam. Psychopharmacology 1996;128(1):67‐73. - PubMed
Green 1998 {published data only}
-
- Green JF, King DJ. Antisaccade and no‐saccade distractibilty with chlorpromazine and lorazepam. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1,2):117.
Greenberg 1966 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg LM, Roth S. Differential effects of abrupt versus gradual withdrawal of chlorpromazine in hospitalized chronic schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1966;123:221‐6. - PubMed
Griffiths 1979 {published data only}
-
- Griffiths RR, Bigelow G, Liebson I. Human drug self‐administration: double‐blind comparison of pentobarbital, diazepam, chlorpromazine and placebo. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1979;210:301‐10. - PubMed
Guy 1978 {published data only}
-
- Guy W, Petrie W, Cleary P. The incidence of treatment emergent symptoms under chlorpromazine and placebo conditions. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1978;14:22‐4. - PubMed
Hammond 1978 {published data only}
-
- Hammond NV, Gruzelier JH. Laterality, attention and rate effects in the auditory temporal discrimination of chronic schizophrenics ‐ the effect of treatment with chlorpromazine. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 1978;30:91‐103. - PubMed
Hamner 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hamner MB, Arvanitis LA, Miller BG, Link CGG, Hong WW. Plasma prolactin in schizophrenia subjects treated with seroquel (TM) (ICI 204,636). Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32(1):107‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hankoff 1960 {published data only}
-
- Hankoff L, Engelhardt D, Freedman N, Mann D, Margolis R. Denial of illness in schizophrenic outpatients: effects of psychopharmacological treatment. Archives of General Psychiatry 1960;3:657‐64. - PubMed
Hanlon 1958 {published data only}
-
- Hanlon TE, Kurland AA, Esquibel AJ, Ota KY. A comparative study of chlorpromazine and triflupromazine in the management of the chronic hospitalized psychotic patient. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1958;127:17‐20. - PubMed
Hanlon 1960 {published data only}
-
- Hanlon TE, Wiener G, Kurland AA. The psychiatric physician and the phenothiazine tranquilizers. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1960;130:67‐71. - PubMed
Harper 1976 {published data only}
Hartley 1978 {published data only}
-
- Hartley L, Henry T, Couper‐Smartt J. Chlorpromazine and serial reaction performance. British Journal of Psychology 1978;69:271‐6. - PubMed
Hartley 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hartley LR, Coxon L, Spencer J. Pharmacological effects on lateralized behavior. Current Psychology Research and Reviews 1987;6:301‐12.
Hartley 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hartley LR, Strother N, Arnold PK, Mulligan B. Lateralization of emotional expression under a neuroleptic drug. Physiology and Behavior 1989;45:917‐21. - PubMed
Hartley 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hartley LR, Ireland LK, Arnold PK, Spencer J. Chlorpromazine and the lateralisation of the perception of emotion. Physiology and Behavior 1991;50:881‐5. - PubMed
Hartmann 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hartmann E, Cravens J. The effects of long term administration of psychotrophic drugs on human sleep. IV. The effects of chlorpromazine. Psychopharmacologia 1973;33:203‐18. - PubMed
Haskell 1974 {published data only}
-
- Haskell DS, McNair DM, Fisher S, Kahn RJ. A controlled outpatient trial of perphenazine‐amitriptyline and chlorpromazine. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1974;14:536‐42. - PubMed
Heilizer 1959 {published data only}
-
- Heilizer F. The effects of chlorpromazine upon psychomotor and psychiatric behavior of chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1959;128:358‐64. - PubMed
-
- Planansky K, Heilizer F. Weight changes in relation to the characteristics of patients on chlorpromazine. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Psychopathology 1959;20:53‐7. - PubMed
Hekimian 1967 {published data only}
-
- Hekimian LJ, Friedhoff AJ. A controlled study of placebo, chlordiazepoxide and chlorpromazine with thirty male schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1967;28:675‐8. - PubMed
Herrera 1988 {published data only}
-
- Herrera JN, Sramek JJ, Costa JF, Roy S. High potency neuroleptics and violence in schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1988;176(9):558‐61. - PubMed
Herrmann 1991a {published data only}
-
- Herrmann WM, Scharer E, Delini‐Stula A. Predictive value of pharmaco electroencephalography in early human pharmacological evaluations of psychoactive drugs ‐ first example ‐ Savoxepine. Pharmacopsychiatry 1991;24:196‐205. - PubMed
Herrmann 1991b {published data only}
-
- Herrmann WM, Scharer E, Wendt G, Delini‐Stula A. Pharmaco EEG profile of maroxepine ‐ third example to discuss the predictive value of pharmaco electroencephalography in early human pharmacological evaluations of psychoactive drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 1991;24:214‐24. - PubMed
Herz 1991 {published data only}
-
- Herz M, Glazer W, Mostert M, Sheard M, Szymanski H, Hafez H, et al. Intermittent versus maintenance medication in schizophrenia. Two‐year results. Archives of General Psychiatry 1991;48:333‐9. - PubMed
Hoffer 1975 {published data only}
-
- Hoffer J. Megavitamin treatment of schizophrenia. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1975;20:492‐5. - PubMed
Hogarty 1976 {published data only}
-
- Hogarty GE, Ulrich RF, Mussare F, Aristigueta N. Drug discontinuation among long term, successfully maintained schizophrenic outpatients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1976;37:494‐500. - PubMed
Hollis 1968 {published data only}
-
- Hollis JH. Chlorpromazine: direct measurement of differential behavioral effect. Science 1968;159:1487‐9. - PubMed
Hollister 1955 {published data only}
-
- Hollister LE, Traub L, Beckman WG. Psychiatric use of reserpine and chlorpromazine: results of double‐blind studies. In: Kline NS editor(s). Psychopharmacology. Washington DC: AAAS, 1956:65‐74. [Publication Number 42]
Holt 1984 {published data only}
-
- Holt RJ. Neuroleptic drug‐induced changes in platelet levels. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1984;4:130‐2. - PubMed
Hong 1996a {published data only}
-
- Hong W, Arvanitis L. Reduction of the positive symptoms of schizophrenia by '(ICI 204,636): results from phase II and III clinical trials. 9th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 1996 Sep 21‐25; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 1996. [MEDLINE: ]
Hong 1996b {published data only}
-
- Hong WW, Arvanitis LA. The atypical profile of '(ICI 204,636) is supported by the lack of sustained elevation of plasma prolactin in schizophrenic patients. 9th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 1996 Sep 21‐25; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 1996. [MEDLINE: ]
Hopkin 1954 {published data only}
-
- Hopkin DA. Action of chlorpromazine and promethazine. British Medical Journal 1954;1:1036.
Hrushka 1966 {published data only}
-
- Hrushka M, Bruck M, Hsu JJ. Therapeutic effects of different modes of chlorpromazine administration. Diseases of the Nervous System 1966;27:522‐7. - PubMed
Huang 1967 {published data only}
-
- Huang CL, Hirano K. The effect of antipyretic analgesics on the metabolism of chlorpromazine in man. Biochemical Pharmacology 1967;16:2023‐6. - PubMed
Hughes 1967 {published data only}
-
- Hughes JS, Little JC. An appraisal of the continuing practice of prescribing tranquillizing drugs for long‐stay psychiatric patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1967;113:867‐73. - PubMed
Hurst 1960 {published data only}
-
- Hurst L. Chlorpromazine and Pecazine in chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Mental Science (British Journal of Psychiatry from 1963) 1960;106:726‐31. - PubMed
Hurst 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hurst BC, Link C. A comparison of the tolerance profile of seroquel with typical neuroleptics and placebo. Xth World Congress of Psychiatry. Madrid, Spain. Madrid, Spain, August 23‐28, 1996.
Hussar 1969 {published data only}
-
- Hussar AE, Bragg DG. The effect of chlorpromazine on the swallowing function in chronic schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1969;126:570‐3. - PubMed
IRCT138811022935N3 2010 {published data only}
-
- IRCT138811022935N3. The effect of omega‐3 on negative and positive symptoms in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A DOUBLE BLIND and PLACEBO controlled trial. http://www.irct.ir/ 2010.
Itil 1968 {published data only}
-
- Itil T, Shapiro D, Fink M. Differentiation of psychotropic drugs by quantitative EEG analysis. Agressologie 1968;9:267‐80. - PubMed
Itil 1971 {published data only}
-
- Itil TM, Ulett GA, Fukuda T. Quantitative pharmaco‐electroencephalography in early evaluation of psychotropic drugs. Folia Psychiatrica et Neurologica Japonica 1971;25:195‐202. - PubMed
Jia 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jia H, Tang Y, Jiang Z. Clinical observation of the treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia by the TCM therapy of enforcing spleen and nourishing kidney. Journal of Beijing University of TCM 2004;27(5):80‐3.
Johnstone 1978 {published data only}
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Frith CD, Carney MW, Price JS. Mechanism of the antipsychotic effect in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Lancet 1978;1(8069):848‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jones 1969 {published data only}
-
- Jones IH. Drugs and motor activity in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1969;115:851‐6. - PubMed
Jones 1971 {published data only}
-
- Jones IH, Pikler N. Effects of chlorpromazine and trifluoperazine on the activity of chronic schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1971;119:545‐6. - PubMed
Joseph 1979 {published data only}
-
- Joseph MH, Baker HF, Johnstone EC, Crow TJ. 3‐Methoxy‐4‐hydroxyphenylglycol excretion in acutely schizophrenic patients during a controlled clinical trial of the isomers of flupenthixol. Psychopharmacology 1979;64(1):35‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Joshi 1980 {published data only}
-
- Joshi VG, Nagesh R, Eswaran S, Nagesh R, Pai M, Mathews G, et al. Vitamins B1, B6, and B12 in the adjunctive treatment of schizophrenia ‐ further studies to examine the effect of reduction of chlorpromazine dosage. Journal of Orthomolecular Psychiatry 1980;11:45‐9.
Kabes 1982 {published data only}
-
- Kabes J, Sikora J, Pisvejc J. Effect of piracetam on extrapyramidal side effects induced by neuroleptic drugs. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1982;17(3):185‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kammerer 1968 {published data only}
-
- Kammerer M, Wartel R, Gurfein L, Weil J, Wysoki V, Gelb F. Clinical experimentation with desipramine with statistical control [Experimentation clinique de la desipramine avec controle statistique]. Annales Medico‐psychologiques 1968;1:109‐13. - PubMed
Kaplan 1974 {published data only}
-
- Kaplan J, Dawson S, Vaughan T, Green R, Wyatt RJ. Effect of prolonged chlorpromazine administration on the sleep of chronic schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:62‐6. - PubMed
Keskiner 1970 {published data only}
-
- Keskiner A, Itil TM, Todt N. A comparative study of butaperazine, chlorpromazine and placebo in chronic schizophrenics. Psychosomatics 1970;11:120‐6. - PubMed
Kim 1960 {published data only}
-
- Kim K. Responses to treatment‐refractory chronic schizophrenics to chlorpromazine with concurrent adrenocortical steroid. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960;116:1023‐4. - PubMed
Kimbell 1971 {published data only}
-
- Kimbell I Jr, Winkelman GW, Hughes WM. Comparison of thioridazine and chlorpromazine in doctor's choice research design. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1971;12:825‐32. - PubMed
King 1959 {published data only}
-
- King PD, Weinberger W. Comparison of proclorperazine and chlorpromazine in hospitalized chronic schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 1959;115:1026‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
King 1994 {published data only}
-
- King DJ. Psychomotor impairment and cognitive disturbances induced by neuroleptics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1994;89(380):53‐8. - PubMed
Klein 1974 {published data only}
-
- Klein RH, Lynn EJ, Axelrod H, Dluhy J. Self‐administration of medication by psychiatric inpatients. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1974;158:450‐5. - PubMed
Kopell 1968 {published data only}
-
- Kopell BS, Wittner WK. The effects of chlorpromazine and methamphetamine on visual signal‐from‐noise detection. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1968;147:418‐24. - PubMed
Kordas 1968 {published data only}
-
- Kordas S, Kazamias N, Georgas J, Papadokostakis J. Clopenthixol: a controlled trial in chronic hospitalised schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1968;114:833‐6. - PubMed
Kornetsky 1957 {published data only}
-
- Kornetsky C, Humphries O. Relationship between effects of a number of centrally acting drugs and personality. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1957;77:325‐7. - PubMed
-
- Kornetsky C, Humphries O, Evarts EV. Comparison of psychological effects of certain centrally acting drugs in man. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1957;77:318‐24. - PubMed
-
- Primac DW, Mirsky AF, Rosvold HE. Effects of centrally acting drugs on two tests of brain damage. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1957;77:328‐32. - PubMed
Kornetsky 1958 {published data only}
Kornetsky 1959 {published data only}
-
- Kornetsky C, Pettit M, Wynne R, Evarts EV. A comparison of the psychological effects of acute and chronic administration of chlorpromazine and secobarbital (quinalbarbitone) in schizophrenic patients. Journal of Mental Science 1959;105:190‐8. - PubMed
Korol 1965 {published data only}
-
- Korol B, Lang WJ, Brown ML, Gershon S. Effects of chronic chlorpromazine administration on systemic arterial pressure in schizophrenic patients: relationship of body position to blood pressure. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1965;6:587‐91. - PubMed
Kovitz 1955 {published data only}
-
- Kovitz B, Carter JT, Addison WP. A comparison of chlorpromazine and reserpine in chronic psychosis. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1955;74:467‐71. - PubMed
Kramer 1975 {published data only}
-
- Kramer M, Roth T, Goldstein S, Ryan MS, Blackwell B. A double‐blind evaluation of metiapine in hospitalized acute schizophrenics. Current Therapeutic Research 1975;18:839‐48. - PubMed
Kugler 1980 {published data only}
-
- Kugler BT, Gruzelier JH. The influence of chlorpromazine and amylobarbitone on the recovery limb of the electrodermal response. Psychiatry Research 1980;2:75‐84. - PubMed
Kupfer 1971 {published data only}
-
- Kupfer DJ, Wyatt RJ, Synder F, Davis JM. Chlorpromazine and sleep in psychiatric patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1971;24:185‐9. - PubMed
Kurland 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kurland AA, Nagaraju A. Viloxazine and the depressed schizophrenic ‐ methodological issues. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1981;21(1):37‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lampe 1969 {published data only}
-
- Lampe WT. A double blind study of clomacran. Current Therapeutic Research 1969;11:300‐6. - PubMed
Latz 1965 {published data only}
-
- Latz A, Kornetsky C. The effects of chlorpromazine and secobarbital under two conditions of reinforcement on the performance of chronic schizophrenic subjects. Psychopharmacologia 1965;7:77‐88. - PubMed
Laurian 1981 {published data only}
-
- Laurian S, Le PK, Baumann P, Perey M, Gaillard JM. Relationship between plasma‐levels of chlorpromazine and effects on EEG and evoked potentials in healthy volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatria 1981;14:199‐204. - PubMed
Leff 1971 {published data only}
Leszek 1991 {published data only}
-
- Leszek J, Inglot AD, Cantell K, Wasik A. Natural human leukocyte interferon in the treatment of schizophrenia. European Journal of Psychiatry 1991;5(1):55‐63.
Levin 1959 {published data only}
-
- Levin ML. A comparison of the effects of phenobarbital, promethazine, chlorpromazine, and placebo upon mental hospital patients. Journal of Consulting Psychology 1959;23:167‐70. - PubMed
Levine 1997 {published data only}
-
- Levine J, Caspi N, Laufer N. Immediate effects of chlorpromazine and perphenazine following neuroleptic washout on word association of schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Research 1997;26(1):55‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levita 1961 {published data only}
-
- Levita E. Effects of chlorpromazine and promazine on perseveration. Journal of General Psychology 1961;65:181‐7. - PubMed
Lewis 1973 {published data only}
-
- Lewis PJ, James NM. Haloperidol and chlorpromazine ‐ a double‐blind cross‐over trial and clinical study in children and adolescents. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1973;7:59‐65. - PubMed
Li 2006 {published data only}
-
- Li H‐F, Xie S‐P, Li M, Zhang M‐L, Li J, Su B‐H, et al. Ziprasidone in treatment of schizophrenia: a double blind, randomized, controlled, parallel group, and multicenter study [齐拉西酮治疗精神分裂症的随机、双盲、双模拟、多中心研究]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies [中国新药与临床杂志] 2006;25(10):747‐52.
Liberman 1973 {published data only}
-
- Liberman RP, Davis J, Moon W, Moore J. Research design for analyzing drug‐environment‐behavior interactions. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1973;156:432‐9. - PubMed
Little 1958 {published data only}
-
- Little JC. A double‐blind controlled comparison of the effects of Chlorpromazine, Barbiturate and a placebo in 142 chronic psychotic in‐patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1958;4:334‐49. - PubMed
Loranger 1968 {published data only}
-
- Loranger AW. Treatment of acute mental disorders with an adrenal steroid. British Journal of Psychiatry 1968;114:843‐4. - PubMed
Lorr 1961 {published data only}
-
- Lorr M, McNair DM, Weinstein GJ, Michaux WW, Raskin A. Meprobamate and chlorpromazine in psychotherapy. Some effects on anxiety and hostility of outpatients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1961;4:381‐9. - PubMed
Lyberi 1956 {published data only}
-
- Lyberi G, Last SL. The use of chlorpromazine as an activating agent. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 1956;8:71‐2.
Maculans 1964 {published data only}
-
- Maculans GA. Comparison of diazepam, chlorprothixine and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1964;25:164‐8. - PubMed
Mahal 1976 {published data only}
-
- Mahal AS, Ramu NG, Chaturvedi DD. Double blind controlled study of brahmyadiyoga and tagara in the management of various types of unmada (schizophrenia). Indian Journal of Psychiatry 1976;18(4):283‐92.
Majewski 1968 {published data only}
-
- Majewski J, Stempurska K. Results of treatment of schizophrenic psychoses with neuroleptics combined with subcomatic insulin [Wyniki leczenia psychoz schizofrenicznych neuroleptykami skojarzonymi z insulina podspiaczkowa]. Psychiatria Polska 1968;2(1):37‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marjerrison 1969 {published data only}
-
- Marjerrison G, Keogh RP. Integrated EEG variability ‐ drug effects in acute schizophrenics. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1969;14:403‐5. - PubMed
Marrazzi 1972 {published data only}
-
- Marrazzi AS, Woodruff S, Kennedy D. Perceptual challenge to measure illness and therapy. American Journal of Psychiatry 1972;128:886‐90. - PubMed
Mason‐Browne 1957 {published data only}
Mathur 1981 {published data only}
-
- Mathur S, Hall JN. Phenothiazine withdrawal in schizophrenics in a hostel (letter). British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:271‐2. - PubMed
Mattila 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mattila MJ, Vanakoski J, Mattila Evenden ME, Karonen SL. Suriclone enhances the actions of chlorpromazine on human psychomotor performance but not on memory or plasma prolactin in healthy subjects. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1994;46:215‐20. - PubMed
McClelland 1990 {published data only}
Melnyk 1966 {published data only}
-
- Melnyk WT, Worthington AG, Laverty SG. Abrupt withdrawal of chlorpromazine and thioridazine from schizophrenic in‐patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1966;11(5):410‐3.
Merry 1957 {published data only}
-
- Merry J, Pargiter MB, Munro H. Chlorpromazine and chronic neurotic tension. American Journal of Psychiatry 1957;113:988‐90. - PubMed
Michaux 1966 {published data only}
-
- Kurland AA, Bethon GD, Michaux MH, Agallianos DD. Chlorpromazine‐chlordiazepoxide and chlorpromazine‐imipramine treatment: side effects and clinical laboratory findings. Journal of New Drugs 1966;6:80‐95. - PubMed
-
- Michaux MH, Kurland AA, Agallianos DD. Chlorpromazine‐chlordiazepoxide and chlorpromazine‐imipramine treatment of newly hospitalized, acutely ill psychiatric patients. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1966;8(supplement):117‐52. - PubMed
Millar 1963 {published data only}
-
- Millar J. A trial of fluphenazine in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1963;109:428‐32. [MEDLINE: ]
Milne 1960 {published data only}
-
- Milne H, Fowler DB. A clinical trial of Largactil (chlorpromazine), Stemeticl (prochlorperazine) and Veractil (methotrimeprazine). British Journal of Psychiatry 1960;106:1105‐10. - PubMed
Milstein 1994 {published data only}
-
- Milstein V, Small JG, Brecher M, Kellams JJ, Small IF. Pharmaco‐eeg studies of single doses of an atypical neuroleptic iloperidone, compared with chlorpromazine and PLACEBO in schizophrenic‐patients. Biological Psychiatry 1994;35(9):671‐.
Milton 1978 {published data only}
-
- Milton F, Patwa VK, Hafner RJ. Confrontation versus belief modification in persistently deluded patients. British Journal of Medical Psychology 1978;51:127‐30. - PubMed
Mitchell 1956 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell P. Chlorpromazine in the treatment of the chronic disturbed schizophrenic patient. British Journal of Psychiatry 1956;102:151‐4. - PubMed
Mitchell 1960 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell LE, Zax M. Psychological response to chlorpromazine in a group of psychiatric patients. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1960;16:440‐2. - PubMed
Monteleone 1999 {published data only}
-
- Monteleone P, Tortorella A, Borriello R, Cassandro P, Maj M. Prolactin hyperresponsiveness to D fenfluramine in drug free schizophrenic patients: a placebo controlled study. Biological Psychiatry 1999;45(12):1606‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morgenstern 1960 {published data only}
-
- Morgenstern FV, Funk IC, Holt WL. Comparative short‐term evaluation of triflupromazine hydrochloride, chlorpromazine hyrochloride, and placebo in acutely disturbed patients. New York State Journal of Medicine 1960;60:254‐8. - PubMed
Morton 1968 {published data only}
-
- Morton MR. A study of the withdrawal of chlorpromazine or trifluoperazine in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1968;124:1585‐8. - PubMed
Moss 1958 {published data only}
-
- Moss CS, Jensen RE, Morrow W, Freund HG. Specific behavioural changes produced by chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:449‐51. - PubMed
Neal 1969 {published data only}
-
- Neal CD, Collis MP, Imlah NW. A comparative trial of oxypertine and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Current Therapeutic Research ‐ Clinical and Experimental 1969;11:367‐78. - PubMed
Newbold 1956 {published data only}
-
- Newbold HL, Steed WD. The use of chlorpromazine in psychotherapy. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1956;123(3):270‐4. - PubMed
Okuma 1979 {published data only}
-
- Okuma T, Inanaga K, Otsuki S, Sarai K, Takahashi R, Hazama H, et al. A preliminary double‐blind study on the efficacy of carbamazepine in prophylaxis of manic‐depressive illness. Psychopharmacology Berlin 1981;73:95‐6. - PubMed
Orzack 1969 {published data only}
-
- Orzack MH, Taylor CL, Kornetsky C. A comparison of the behavioral effects of periodic administration of chlorpromazine and a "sustained‐release" form of chlorpromazine. Clinical Pharamacology and Therapeutics 1969;10(2):258‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Osmakova 1972 {published data only}
-
- Osmakova EI. Use of psychological methods for studying the particular psychotropic action of various psychopharmacologic drugs [Primenenie psikhologicheskikh metodik dlia issledovaniia sobstvenno psikhotropnogo deistviia nekotorykh psikhofarmakologic heskikh sredtsv]. Zhurnal Nevropatologii i Psikhiatrii 1972;72:1705‐8. - PubMed
-
- Rojo‐Sierra M, Alonso J, Díez E, Giner J, Lloret E. [Aportación sobre el espectro psicofarmacoterápico del R P. 19 366 y R P. 19 552]. 5th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1971 Nov 28 ‐ Dec 4; Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico. 1971. [MEDLINE: ]
Pai 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pai Y‐M, Yu S‐C, Lin C‐C. Risperidone in reducing tardive dyskinesia: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA. Marathon Multimedia, 2001. [MEDLINE: ]
Paredes 1966 {published data only}
-
- Paredes A, Baumgold J, Pugh LA, Ragland R. Clinical judgment in the assessment of psychopharmacological effects. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1966;142(2):153‐60. - PubMed
Park 1981 {published data only}
-
- Park S, Hardesty AS, Garcia E. Effects of triiodothyronine and chlorpromazine combination treatment in schizophrenia. Current Therapeutic Research ‐ Clinical and Experimental 1981;29:929‐35.
Pasamanick 1967 {published data only}
-
- Pasamanick B, Scarpitti FR, Dinitz S. Schizophrenics in the Community: an Experimental Study in the Prevention of Hospitalization. New York: Appleton‐Century‐Crofts, 1967.
Patterson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Patterson T, Venables PH. Bilateral skin conductance and the pupillary light dark reflex ‐ manipulation by chlorpromazine, haloperidol, scopolamine, and placebo. Psychopharmacology 1981;73:63‐9. - PubMed
Peet 1980 {published data only}
-
- Peet M, Middlemiss DN, Yates RA. Pharmacokinetic interaction between propranolol and chlorpromazine in schizophrenic patients [letter]. Lancet 1980;2:978. - PubMed
Pennington 1957 {published data only}
-
- Pennington V. A two‐year comparative study of ataraxics in neuropsychiatric patients. Journal of the American Geriatric Association 1957;5:42‐9. - PubMed
Pietzcker 1978 {published data only}
Pigache 1973 {published data only}
-
- Pigache RM. The clinical relevance of an auditory attention task (PAT) in a longitudinal study of chronic schizophrenia, with placebo substitution for chlorpromazine. Schizophrenia Research 1993;10:39‐50. - PubMed
-
- Pigache RM, Norris HN. Measurement of drug action in schizophrenia. Clinical Science 1973;44:28. - PubMed
Pigache 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pigache RM. Effects of placebo, orphenadrine, and rising doses of chlorpromazine, on PAT performance in chronic schizophrenia. A two‐year longitudinal study. Schizophrenia Research 1993;10:51‐9. - PubMed
Platz 1967 {published data only}
-
- Platz AR, Klett CJ, Caffey EMJ. Selective drug action related to chronic schizophrenic subtype. (A comparative study of carphenazine, chlorpromazine, and trifluoperazine). Diseases of the Nervous System 1967;28:601‐5. - PubMed
Pleasure 1956 {published data only}
-
- Pleasure H. Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) for mental illness in the presence of pulmonary tuberculosis. Psychiatry Quarterly 1956;30:23‐30. - PubMed
Pollack 1956 {published data only}
-
- Pollack, B. The effect of chlorpromazine on the return rate of 250 patients released from the Rochester State Hospital. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;112:937. - PubMed
Pollard 1959 {published data only}
-
- Pollard JC. Combined effects of chlorpromazine and meprobamate in chronically disturbed psychotic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1959;20:427‐9.
Quigley 1996 {published data only}
-
- Quigley N, Morgan D, Idzikowski C, King DJ. The effect of chlorpromazine and benzhexol on memory and psychomotor function in healthy volunteers. Journal of Psychopharmacology 1996;10:146‐52. - PubMed
Quinn 1960 {published data only}
-
- Quinn PJG, Johnston J, Latner G, Kiloh LG. A comparative controlled trial of methotrimeprazine ('veractil') in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1960;106:161‐70. - PubMed
Raaska 2000 {published data only}
-
- Raaska K, Neuvonen PJ. Ciprofloxacin increases serum clozapine and N‐desmethylclozapine: a study in patients with schizophrenia. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2000;56(8):585‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ragland 1968 {published data only}
-
- Ragland R, Clark ML, Ray TS, Paredes A, Costiloe JP, Segal B, et al. The evaluation of chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenic women. A replicated experiment. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1968;21:445‐60. - PubMed
Raja 2000 {published data only}
-
- Raja M, Azzoni A. Second generation antipsychotics in the emergency care setting. A prospective naturalistic study. General Hospital Psychiatry 2000;22(2):107‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rappaport 1967 {published data only}
-
- Rappaport M. Competing voice messages. Effects of message load and drugs on the ability of acute schizophrenics to attend. Archives of General Psychiatry 1967;17:97‐103. - PubMed
Rappaport 1968 {published data only}
-
- Rappaport M. Attention to competing voice messages by nonacute schizophrenic patients. Effects of message load, drugs, dosage levels and patient background. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1968;146:404‐11. - PubMed
Rathod 1958 {published data only}
-
- Rathod N, Rees L. A controlled study of the prognostic significance of autonomic responses in the chlorpromazine treatment of disturbed psychotic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1958;104:705‐12. - PubMed
Raymond 1957 {published data only}
Remr 1970 {published data only}
-
- Remr J. The effects of chlorpromazine on fine psychomotor performance with a simultaneous secondary task in schizophrenics. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1971;13:179. - PubMed
-
- Remr J. The effects of chlorpromazine on some components of psychomotor performance in schizophrenics. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1970;12:253‐4. - PubMed
Rifkin 1978 {published data only}
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Kane J, Struve F, Klein DF. Are prophylactic antiparkinson drugs necessary? A controlled study of procyclidine withdrawal. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35(4):483‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rinaldi 1956 {published data only}
-
- Rinaldi F, Rudy L, Himwich HE. Clinical evaluation of azacyclonol, chlorpromazine, and reserpine on a group of chronic psychotic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;112:678‐83. - PubMed
Rivera‐Calimlim 1973 {published data only}
-
- Rivera Calimlim L, Castaneda L, Lasagna L. Effects of mode of management on plasma chlorpromazine in psychiatric patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1973;14:978‐86. - PubMed
Rojo‐Sierra 1971 {published data only}
-
- Rojo‐Sierra M, Alonso J, Díez E, Giner J, Lloret E. [Aportación sobre el espectro psicofarmacoterápico del R P. 19 366 y R P. 19 552]. 5th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1971 Nov 28 ‐ Dec 4; Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico. 1971:495‐6. [MEDLINE: ]
Rosen 1972 {published data only}
-
- Rosen B, Engelhardt DM, Freedman N, Margolis R, Rudorfer L, Paley HM. Prediction of psychiatric hospitalization. II. The Hospitalization Proneness Scale: a cross‐validation. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1972;80:271‐4. - PubMed
Rosenheck 2000 {published data only}
-
- Rosenheck R, Cramer J, Jurgis G, Perlick D, Xu W, Thomas J, et al. Clinical and psychopharmacologic factors influencing family burden in refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2000;61(9):671‐6. - PubMed
Rosner 1955 {published data only}
-
- Rosner H, Levine S, Hess H, Kaye H. A comparative study of the effect on anxiety of chlorpromazine, reserpine, phenobarbital, and a placebo. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1955;122:505‐12. - PubMed
Rudy 1957 {published data only}
-
- Rudy L, Himwich H, Tasher DC. Clinical evaluation of two phenothiazine compounds Promazine and Mepazine. American Journal of Psychiatry 1957;113:979‐83. - PubMed
Rudy 1958 {published data only}
-
- Rudy L, Rinaldi E, Himwich H, Tuteur W, Glotzer J. Trifluoperazine in the treatment of psychotic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:364‐5. - PubMed
Sainz 1955 {published data only}
-
- Sainz A. Chlorpromazine in psychiatric disorders. Prescriber 1955;2(2):14. [MEDLINE: ]
Saletu 1972 {published data only}
-
- Saletu B, Saletu M, Itil T. Effect of minor and major tranquilizers on somatosensory evoked potentials. Psychopharmacologia 1972;24:347‐58. - PubMed
Salisbury 1957 {published data only}
-
- Salisbury BJ, Hare EH. Ritalin and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia: a controlled clinical trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 1957;103:830‐4. - PubMed
Schiele 1959 {published data only}
-
- Schiele BC, Mendelsohn RM, Penman AS, Schofield W. Comparison of low and high dosage procedures in chlorpromazine therapy. Psychiatric Quarterly 1959;33:252‐9. - PubMed
Schmidt 1957 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt KE. Combined treatment with chlorpromazine and reserpine: an attempt at quantitative assessments in chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1957;103:200‐8. - PubMed
Schooler 1976 {published data only}
-
- Sakalis G, Chan TL, Sathananthan G, Schooler N, Goldberg S, Gershon S. Relationships among clinical response, extrapyramidal syndrome and plasma chlorpromazine and metabolite ratios. Communucations in Psychopharmacology 1977;1:157‐66. - PubMed
-
- Schooler NR, Sakalis G, Chan TL. Chlorpromazine metabolism and clinical response in acute schizophrenia ‐ a preliminary report. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1975;11:30‐3. - PubMed
-
- Schooler NR, Sakalis G, Chan TL, Gershon S, Goldberg SC, Collins P. Chlorpromazine metabolism and clinical response in acute schizophrenia ‐ a preliminary report. Pharmacokinetics of Psychoactive Drugs. Unknown, 1976:199‐219.
Seager 1955 {published data only}
Serafetinides 1973 {published data only}
-
- Serafetinides EA. Consistency and similarity of drug EEG responses in chronic schizophrenic patients. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1973;8:214‐6. - PubMed
Shaskan 1975 {published data only}
-
- Becker RE, Shaskan EG. Platelet monoamine oxidase activity in schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1977;134:512‐7. - PubMed
-
- Shaskan EG, Becker RE. Blood platelet monoamine oxidase activity in anergic schizophrenics. National Institute of Drug Abuse Research Monograph Services 1975;3:29‐35. - PubMed
-
- Shaskan EG, Becker RE. Platelet monoamine oxidase in schizophrenics. Nature 1975;253:659‐60. - PubMed
Shawver 1959 {published data only}
-
- Shawver JR, Gorham DR, Leskin LW, Good WW, Kabnick DE. Comparison of chlorpromazine and reserpine in maintenance drug therapy. Diseases of the Nervous System 1959;20:452‐7. - PubMed
Shopsin 1978 {published data only}
-
- Shopsin B, Klein H, Aronson M. Clozapine: double‐blind control trial in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1978;14:12‐4. - PubMed
Shopsin 1979 {published data only}
-
- Honigfeld G, Patin J, Singer J. Clozapine: antipsychotic activity in treatment‐resistant schizophrenics. Advances in Therapy 1984;1:77‐97.
-
- Shopsin B, Klein H, Aaronson M, Collora M. Clozapine, chlorpromazine, and placebo in newly hospitalized, acutely schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1979;36:657‐64. - PubMed
Silver 2000 {published data only}
-
- Silver H, Barash I, Aharon N, Kaplan A, Poyurovsky M. Fluvoxamine augmentation of antipsychotics improves negative symptoms in psychotic chronic schizophrenic patients: a placebo‐controlled study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2000;15(5):257‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simopoulos 1971 {published data only}
-
- Simopoulos AM, Pinto A, Uhlenhuth EH, Mcgee J. Old wine in new bottles: decreased hostility in chronic psychotic inpatients treated with diphenylhydantoin (Dilantin). 5th World Congress of Psychiatry. Ciudad de Mexico. Ciudad de Mexico, 1971:abstract 1077.
Simpson 1974 {published data only}
-
- Simpson GM, Varga E, Reiss M, Cooper TB, Bergner PE, Lee JH. Bioequivalency of generic and brand‐named chlorpromazine. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1974;15:631‐41. - PubMed
Simpson 1980 {published data only}
-
- Simpson GM, Cooper TB, Bark N, Sud I, Lee JH. Effect of antiparkinsonian medication on plasma levels of chlorpromazine. Archives of General Psychiatry 1980;37:205‐8. - PubMed
Singh 1974 {published data only}
-
- Singh MM. Dysphoric response to neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia and its prognostic significance. Diseases of the Nervous System 1976;37:191‐6. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM. Dysphoric response to neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia and its prognostic significance. Journal of the Bronx State Hospital 1974;2:173‐83. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM, Kay SR. A comparative study of haloperidol and chlorpromazine in terms of clinical effects and therapeutic reversal with benzotropine in schizophrenia. Theoretical implications for potency differences among neuroleptics. Psychopharmacologia 1975;43:103‐13. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM, Kay SR. Therapeutic reversal with benztropine in schizophrenics: practical and theoretical significance. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1975;160:258‐66. - PubMed
Singh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Singh H, Hunt JI, Vitiello B, Simpson GM. Neuroleptic withdrawal in patients meeting criteria for supersensitivity psychosis. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1990;51:319‐21. - PubMed
Small 1987 {published data only}
-
- Small J, Milstein V, Small IF, Miller MJ, Kellams JJ, Corsaro CJ. Computerized EEG profiles of haloperidol, chlorpromazine, clozapine and placebo in treatment resistant schizophrenia. Clinical Electroencephalography 1987;18:124‐35. - PubMed
Smith 1958 {published data only}
-
- Smith JA, Christian D, Rutherford A, Mansfield E. A comparison of triflupromazine (Vesprin), chlorpromazine and placebo in 85 chronic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:253‐4. - PubMed
Smith 1960 {published data only}
-
- Smith ME. A comparative controlled study with chlordiazepoxide. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960;117:362‐3.
Smith 1967 {published data only}
-
- Smith K, Surphlis WRP, Gynther MD, Shimkunas AM. ECT‐chlorpromazine and chlorpromazine compared in the treatment of schizophrenia. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1967;144:284‐90.
Sommerness 1957 {published data only}
-
- Sommerness MD, Lucero RJ, Hamlon JS, Mahowald AM. Chlorpromazine: a controlled study with highly disturbed patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1957;18:16‐20. - PubMed
South‐East 1961 {published data only}
-
- South‐East Region (Scotland) Therapeutic Trials Committee. Controlled trial of Prochlorperazine (Stemetil) in schizophrenia. Journal of Mental Science (British Journal of Psychiatry from 1963) 1961;107:514‐22. [MEDLINE: ]
Soyka 1968 {published data only}
-
- Soyka D. The effect of psychopharmacological drugs and other central nervous system effecting drugs on experimental nystagmus [Die Wirkung von Psychopharmaka und anderen zentral wirksamen substanzen auf den experimentellen Nystagmus]. Fortschritte Der Neurologie, Psychiatrie Und Ihrer Grenzgebiete 1968;36:526‐39. - PubMed
Spiegel 1967 {published data only}
-
- Spiegel DE, Keith‐Spiegel P. The effects of carphenazine, trifluoperazine and chlorpromazine on ward behavior, physiological functioning and psychological test scores in chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1967;144:111‐6. - PubMed
Spohn 1974 {published data only}
-
- Spohn HE, Lacoursiere RB, Williams RO. The effect of chlorpromazine on visual information processing in normal subjects. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1974;159:198‐204. - PubMed
Sugerman 1964 {published data only}
-
- Pfeiffer CC, Goldstein L, Murphree HB, Sugerman AA. Time‐series frequency analysis, and electrogenesis of the EEGs of normals and psychotics before and after drugs. American Journal of Psychiatry 1965;122:1147‐55. - PubMed
-
- Sugerman AA, Goldstein L, Murphree HB, Pfieffer CC, Jenney EH. EEG and behavioural changes in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1964;10:340‐4. - PubMed
Sun 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sun Q‐X, You H‐F, Wang X‐L. Venlafaxine combined with chlorpromazine in treating negative symptoms of schizophrenia [文拉法辛合并氯丙嗪治疗精神分裂症阴性症状的临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry 2006;39(2):90‐3.
Syvalahti 1997 {published data only}
-
- Syvalahti EK, Taiminen T, Saarijarvi S, Lehto H, Niemi H, Ahola V, et al. Citalopram causes no significant alterations in plasma neuroleptic levels in schizophrenic patients. Journal of International Medical Research 1997;25(1):24‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Talbot 1964 {published data only}
-
- Talbot DR. Are tranquilizer combinations more effective than a single tranquilizer?. American Journal of Psychiatry 1964;121:597‐600. - PubMed
Tang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tang Y, Hongxiao J, Zhou F, Cao X, Yuan H, Zhang J. Improving the memory impairment of schizophrenia patients by strengthening the spleen and invigorating the kidney [健脾补肾法治疗精神分裂症记忆损害的临床观察]. Chinese Journal of the Practical Chinese with Modern Medicine [中华实用中西医杂志] 2005;18(12):1750‐1.
Tang 2005a {published data only}
-
- Tang YY, Jia HX, Jiang ZK, Cao XD, Yuan HN, Zhang JZ. Clinical observation of Jian‐Pi‐Bu‐Shen (TCM) treating memory deterioration in patients with schizophrenia. Proceedings of the 8th Conference of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine for Mental Health Problems. 2005:32‐4.
Tang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tang Y‐Y, Jia H‐X, Zhou F, Cao X‐D, Yuan H‐N, Zhang J‐Z. Attention impairment in patients with schizophrenia after the treatment of strengthening the spleen and invigorating the kidney [健脾补肾法治疗精神分裂症患者注意损害的效果评估]. Modern Rehabilitation [现代康复] 2006;10(39):10‐2.
Tassis 1959 {published data only}
-
- Tassis JA. Full coma Insulin therapy, chlorpromazine and electoconvulsive treatment. A control study of 600 schizophrenic patients. Medical journal of Malaya 1959;14:135‐43. - PubMed
Teja 1975 {published data only}
-
- Teja JS, Grey WH, Clum JM, Warren C. Tranquilizers or anti‐depressants for chronic schizophrenics: a long‐term study. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1975;9:241‐7. - PubMed
Tenenblatt 1956 {published data only}
-
- Tenenblatt SS, Spagno A. A controlled study of chlorpromazine therapy in chronic psychotic patients. Journal of Clinical & Experimental Psychopathology 1956;17:81‐92. - PubMed
Terminska 1989 {published data only}
-
- Terminska K, Mrowiec W. No English title available [Badanie porownawcze wplywu perazyny, flufenazyny, trifluoroperazyny, chloropromazny i haloperydolu na objawy pierwotne i deficytowe pierwszego zachorowania na schizofrenie paranoidalna]. Psychiatria Polska 1989;23:24‐30. - PubMed
Tetreault 1969a {published data only}
-
- Tetreault L, Bordeleau JM, Albert JM, Rajotte P. Comparative study of fluphenazine ethanate, fluphenazine bichlorhydrate and placebos in chronic schizophrenics [Etude comparative de l'enanthate de fluphenazine, du bichlorhydrate de fluphenazine et du placebo chez le schizophrene chronique]. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1969;14(2):191‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thorpe 1956 {published data only}
-
- Thorpe J, Baker A. A research method to assess a new tranquillizing drug. British Journal of Psychiatry 1956;102:790‐5. - PubMed
Tourlentes 1958 {published data only}
-
- Tourlentes TL, Hunsicker AL, Hurd DE. Chlorpromazine and communication processes. A.M.A. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 1958;79:468‐73. - PubMed
Troshinsky 1962 {published data only}
-
- Troshinsky CH, Aaronson HG, Stone RK. Maintenance phenothiazines in aftercare of schizophrenic patients. Pennsylvania Psychiatric Bulletin 1962;2:11‐5.
Turner 1956 {published data only}
-
- Turner M, Berard, E, Turner N, Franco N. Changes in the electroencephalogram, the electrodermogram, and the electromyogram provoked by chlorpromazine in man. Abstracts of World Medicine 1956;20:177.
Turner 1966 {published data only}
-
- Turner P. A comparison of fluphenazine and chlorpromazine on critical flicker fusion frequency. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 1966;18:836. - PubMed
Urquhart 1959 {published data only}
-
- Urquhart R, Forrest AD. Clinical trial of promazine hydrochloride and acetylpromazine in chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1959;105:260‐4. - PubMed
van Praag 1975 {published data only}
-
- Praag HM, Dols LC, Schut T. Biochemical versus psychopathological action profile of neuroleptics. A comparative study of chlorpromazine and oxypertine in acute psychotic disorders. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1975;16:255‐63. - PubMed
-
- Praag HM, Korf J. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Some direct observations. In: Praag HM editor(s). On the Origin of Schizophrenic Psychoses. Amsterdam: De Erven Bohn BV, 1975:81‐98.
Vestre 1961 {published data only}
-
- Vestre ND. An experimental study of the effects of chlorpromazine on association learning in schizophrenic patients. Dissertation Abstracts 1961:2374.
Vinar 1973 {published data only}
-
- Vinar O. Whom do neuroleptic drugs help?. Psychopharmacology, Sexual Disorders and Drug Abuse. Amsterdam, Netherlands: North‐Holland, 1973:247‐56.
Vinar 1976 {published data only}
-
- Vinar O, Taussigova D. Schizophrenic syndromes improving without neuroleptic drug treatment [Schizofrenni syndromy zlepsujici se bez neurolepticke lecby]. Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 1976;72(3):176‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Volavka 1983 {published data only}
-
- Volavka J, Hui KS, Anderson B, Nemes Z, O'Donnell J, Lajtha A. Short‐lived effect of (des‐tyr)‐gamma‐endorphin in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research 1983;10:243‐52. - PubMed
Warner 1996 {published data only}
-
- Warner JP, Barnes TR, Henry JA. Electrocardiographic changes in patients receiving neuroleptic medication. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1996;93:311‐3. - PubMed
Weir 1968 {published data only}
-
- Weir TW, Kernohan GA, MacKay DN. The use of pericyazine and chlorpromazine with disturbed mentally subnormal patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1968;114:111‐2. - PubMed
Welbel 1980 {published data only}
-
- Welbel L. No English title available [Roznice w dziallaniu klinicznym niektorych neuroleptykow]. Psychiatria Polska 1980;14:113‐8. - PubMed
Whitehead 1958 {published data only}
-
- Whitehead WA, Thune LE. The effects of chlorpromazine on learning in chronic psychotics. Journal of Consulting Psychology 1958;22:379‐83. - PubMed
Wilcott 1962 {published data only}
-
- Wilcott RC, Helper MM, Garfield SL. Some psychophysiological effects of chlorpromazine on emotionally disturbed children. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1962;135:233‐8. - PubMed
Wilson 1961 {published data only}
-
- Wilson IC, McKay J, Sandifer MG. A double‐blind trial to investigate the effects of thorazine (largactil, chlorpromazine), compazine (stemetil, prochlorperazine) and stelazine (trifluoperazine) in paranoid schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1961;107:90‐9. - PubMed
Winkelman 1957 {published data only}
-
- Winkelman NW. An appraisal of chlorpromazine. General principles for administration of chlorpromazine, based on experience with 1,090 patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1957;113(11):961‐71. - PubMed
Winter 1956 {published data only}
-
- Winter WD, Frederickson WK. The short‐term effects of chlorpromazine on psychiatric patients. Journal of Consulting Psychology 1956;20:431‐4. - PubMed
Wode‐Helgodt 1977 {published data only}
-
- Wode‐Helgodt B, Eneroth P, Fyro B, Gullberg B, Sedvall G. Effect of chlorpromazine treatment on prolactin levels in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of psychotic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1977;56:280‐93. - PubMed
Wold 1959 {published data only}
-
- Wold PN. A long term evaluation of chlorpromazine in six chronic schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1959;116:461‐2. - PubMed
Wolpert 1969 {published data only}
-
- Wolpert A, Yaryura TJA, White L, Merlis S. Triiodothyronine and phenothiazines in schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1969;30(7):487‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wyatt 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wyatt RJ, Green MF, Tuma AH. Long‐term morbidity associated with delayed treatment of first admission schizophrenic patients: a re‐analysis of the Camarillo State Hospital data. Psychological Medicine 1997;27:261‐8. - PubMed
Wykes 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wykes T, Reeder C, Landau S, Everitt B, Knapp M, Patel A. Cognitive remediation therapy: predictive factors & side effects. Unknown source. 1994.
Yan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yan M, Zhou Y, Wang A. Preventive effect of ferrous sulfate on extrapyramidal side effects of neuroleptics. Shandong Archives of Psychiatry [山东精神医学] 2004;17(1):16‐8.
Yang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yang R‐l, Lv H‐X, Lou F. The rehabilitation effect of group psychotherapy on chronic schizophrenic patient [小组心理治疗对慢性精神分裂症患者的康复作用]. Occupation and Health [职业与健康] 2005;21(6):936.
Yorkston 1977 {published data only}
-
- Yorkston NJ, Zaki SA, Pitcher DR, Gruzelier JH, Hollander D, Sergeant HG. Propranolol as an adjunct to the treatment of schizophrenia. Lancet 1977;2:575‐8. - PubMed
Yuan‐guang 1994 {published data only}
-
- Yuan‐Guang C, Guang‐Rong X, Jing Ping Z. A study on the relationship between the chlorprmazine plasma levels and clinical response to chlorpromazine administrations in the schizophrenics. Chinese Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 1994;27(3):153‐5.
Zeller 1956 {published data only}
-
- Zeller WW, Graffagnino PN, Cullen CF, Rietman HJ. Use of chlorpromazine and reserpine in the treatment of emotional disorders. Journal of the American Medical Association 1956;160:179‐84. - PubMed
王强, 1995 {published data only}
-
- 王强, 袁风来, 艾莉, 尹定富, 肖迎光. [only Chinese Title available] [氯丙嗪合并碳酸锂治疗难治性精神分裂症随机双盲交叉试验]. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine [临床精神医学杂志] 1995;5(3):185.
金建烽, 2008 {published data only}
-
- 金建烽, 巢亚琴, 徐乐平, 宋梓样, 邵亚琴. [Title only available in Chinese characters] [合并小剂量阿立哌唑改善氯丙嗪所致高催乳素血症的临床研究]. Shandong Archives of Psychiatry [山东精神医学] 2008;21(6):455‐6.
Additional references
Ahmed 1998
-
- Ahmed I, Soares K, Seifas R, Adams CE. Randomised controlled trials in Archives of General Psychiatry (1959‐1995): a prevalence study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1998;55(8):754‐5. - PubMed
Altman 1996
APA 1992
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Tardive dyskinesia: a task force report of the American Psychiatric Association. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1992.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
Awad 1993
-
- Awad AG. Subjective response to neuroleptics in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1993;19:609‐18. - PubMed
Birchwood 1997
-
- Birchwood M, McGorry P, Jackson H. Early interventions in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;170:2‐5. - PubMed
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. - PubMed
Bollini 1994
-
- Bollini P, Pampallona S, Orza MJ, Adams ME, Chalmers TC. Antipsychotic drugs: is more worse? A meta‐analysis of the published randomized control trials. Psychological Medicine 1994;24:307‐16. - PubMed
Caldwell 1992
-
- Caldwell CB, Gottesman II. Schizophrenia ‐ a high‐risk factor for suicide: clues to risk reduction. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior 1992;22:479‐93. - PubMed
Chong 2004
-
- Chong MY, Tan CH, Fujii S, Yang S, Ungvari GS, Si T, et al. Antipsychotic drug prescription for schizophrenia in East Asia: rationale for change. Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2004;58:61‐7. - PubMed
Davis 1978
-
- Davis JM, Garver DL. Neuroleptics: clinical use in psychiatry. In: Iverson A, Iverson B, Snyder C editor(s). Handbook of Psychopharmacology. New York and London: Plenum, 1978.
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Abstracts of 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28th; Cape Town, South Africa. 2000.
Delay 1952
-
- Delay J, Deniker P. [Le traitement des Psychoses par une Methode neuroleptique derivee de l'Hibernotherapie]. CR Congres des Medicins alienistes et neurologistes de France. Luxembourg. 1952:479.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtina F, Worthingtond HV, Vaile A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(7):7‐10. - PubMed
Grozier 1973
-
- Grozier L. The third revolution in psychiatry: fluphenazine decanoate. In: Ayd FJ editor(s). The Future of Pharmacotherapy: Drug Delivery Systems. Baltimore: International Drug Therapy Newsletter, 1973:97.
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. Early Clinical Drug Evaluation (ECDEU) Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Washington DC: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976. [Publication No.76‐338]
Hambrecht 1992
-
- Hambrecht T, Maurer K, Hafner H, Sartorius N. Transnational stability of gender differences in schizophrenia? An analysis based on the WHO study on determinants of outcome of severe mental disorders. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 1992;242:6‐12. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. The Cochrane Library. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005, issue Issue 3.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org..
Hill 1992
-
- Hill C, Keks NA, Jackson H, Kulkarni J, Hannah D, Copolov D, et al. Symptomatic response to antipsychotics differs between recent onset and recurrent chronic schizophrenic patients. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1992;26:417‐22. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Jenicek 1990
-
- Jenicek M, Berthelette D, Breton J, Croteau N, Leduc N, Pineault R. Content and methods of studies on the prevention and treatment of mental disorders in selected psychiatric journals. Revue d'Epidemiologie et de Sante Publique 1990;38:357‐64. - PubMed
Jusic 1994
-
- Jusic N, Lader M. Post‐mortem antipsychotic drug concentrations and unexplained deaths. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994;165:787‐91. - PubMed
Kane 1985
-
- Kane JM, Rifkin A, Woerner M, Reardon G, Kreisman D, Blumenthal R, et al. High‐dose versus low‐dose strategies in the treatment of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacological Bulletin 1985;21:533‐7. - PubMed
Kaplan 1990
-
- Kaplan MJ, Lazoff M, Kelly K, Lukin R, Garver DL. Enlargement of cerebral third ventricle in psychotic patients with delayed response to neuroleptics. Biological Psychiatry 1990;27:205‐14. - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kendler 1995
-
- Kendler KS, Walsh D. Gender and schizophrenia. Results of an epidemiologically‐based family study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1995;167:184‐92. - PubMed
Laborit 1951
-
- Laborit H, Huguenard P. no English title available [L'Hibernation artificielle par Moyens pharmacodynamiques et physiques]. Presse Medicale 1951;59:1329. - PubMed
Leucht 2005
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79(2‐3):231‐8. [PUBMED: 15982856] - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale Scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. - PubMed
Leucht 2007
Lucero 1951
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
Odejide 1982
-
- Odejide AO, Ban TA. Psychotropic drug prescription pattern in a developing country (Nigeria). The need for an essential psychotherapeutic drug list. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1982;17:163‐9. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
PPA, 2003
-
- Prescription Pricing Authority: NHS 2003. http://www.ppa.org.uk/index.htm.
Rosen 1990
-
- Rosen J, Bohon S, Gershon S. Antipsychotics in the elderly. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplement 1990;358:170‐5. - PubMed
Rosenthal 1963
-
- Rosenthal D. Ratings of disturbance in various categories of behavior during hospitalization. In: Rosenthal D editor(s). The Gerain Quadruplets: a Study of Heredity and Environment in Schizophrenia. New York: Basic Books, 1963.
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Schünemann 2008
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008:359‐83.
Sedvall 1995
-
- Sedvall G, Farde L. Chemical brain anatomy in schizophrenia. Lancet 1995;346:743‐9. - PubMed
Szymanski 1995
-
- Szymanski S, Lieberman JA, Alvir JM, Mayerhoff D, Loebel A, Geisler S, et al. Gender differences in onset of illness, treatment response, course, and biologic indexes in first‐episode schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1995;152:698‐703. - PubMed
Szymanski 1996
-
- Szymanski SR, Cannon TD, Gallacher F, Erwin RJ, Gur RE. Course of treatment response in first‐episode and chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1996;153:519‐25. - PubMed
Thornley 1998
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organistation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- WHO: Global Health Statistics Online, 1998. WHO: Global Health Statistics Online, 1998. WWHO: Global Health Statistics Online, 1998. http://w3.whosea.org/en/section1174/section1199/section1567_6744.htm.
WHO 2003
-
- WHO: Essential Medicines 13th edition, WHO Model List 2003. http://www.who.int/hac/techguidance/pht/essentialmed/en/.
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
References to other published versions of this review
Adams 2007
Thornley 1998a
-
- Thornley B, Adams CE, Awad G. Chlorpromazine versus placebo for those with schizophrenia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1998, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

