Scene perception and the visual control of travel direction in navigating wood ants
- PMID: 24395962
- PMCID: PMC3886323
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0035
Scene perception and the visual control of travel direction in navigating wood ants
Abstract
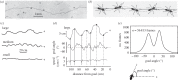
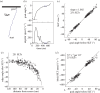
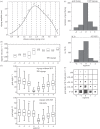
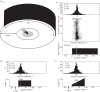
This review reflects a few of Mike Land's many and varied contributions to visual science. In it, we show for wood ants, as Mike has done for a variety of animals, including readers of this piece, what can be learnt from a detailed analysis of an animal's visually guided eye, head or body movements. In the case of wood ants, close examination of their body movements, as they follow visually guided routes, is starting to reveal how they perceive and respond to their visual world and negotiate a path within it. We describe first some of the mechanisms that underlie the visual control of their paths, emphasizing that vision is not the ant's only sense. In the second part, we discuss how remembered local shape-dependent and global shape-independent features of a visual scene may interact in guiding the ant's path.
Keywords: multi-modal directional control; phase-dependent visual control; saccades; visual learning; zigzag paths.
Figures



References
-
- Srinivasan MV. 2001. Honeybees as a model for the study of visually guided flight, navigation, and biologically inspired robotics. Physiol. Rev. 91, 389–411. - PubMed
-
- Taylor GK, Krapp HG. 2007. Sensory systems and flight stability: what do insects measure and why? Adv. Insect Physiol. 34, 231–316.
-
- Borst A. 1990. How do flies land? BioScience 40, 292–299. (10.2307/1311266) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

